Brassica napus L. grain weight major QTLs molecular marker and application thereof
A Brassica napus and molecular marker technology, applied in the direction of recombinant DNA technology, microbial measurement/inspection, DNA/RNA fragments, etc., can solve the problems of few reports on gene cloning and analysis related to grain weight, limited number of SSR markers, no Problems such as main effect QTLs, to achieve the effect of shortening the breeding period, speeding up the process, and reducing the breeding workload
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
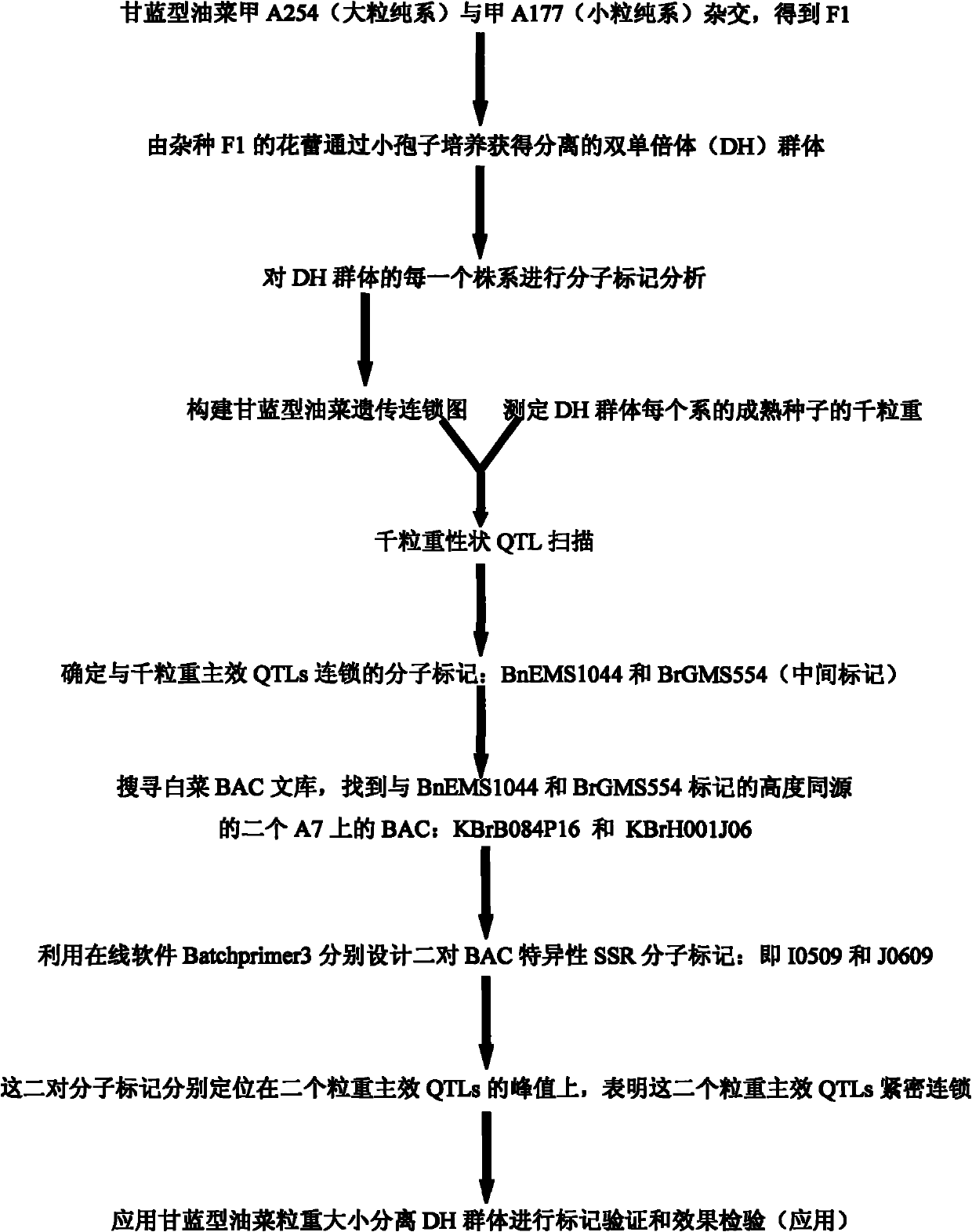
[0032] Example 1: Acquisition of site-specific molecular markers for major QTLs for grain weight in Brassica napus
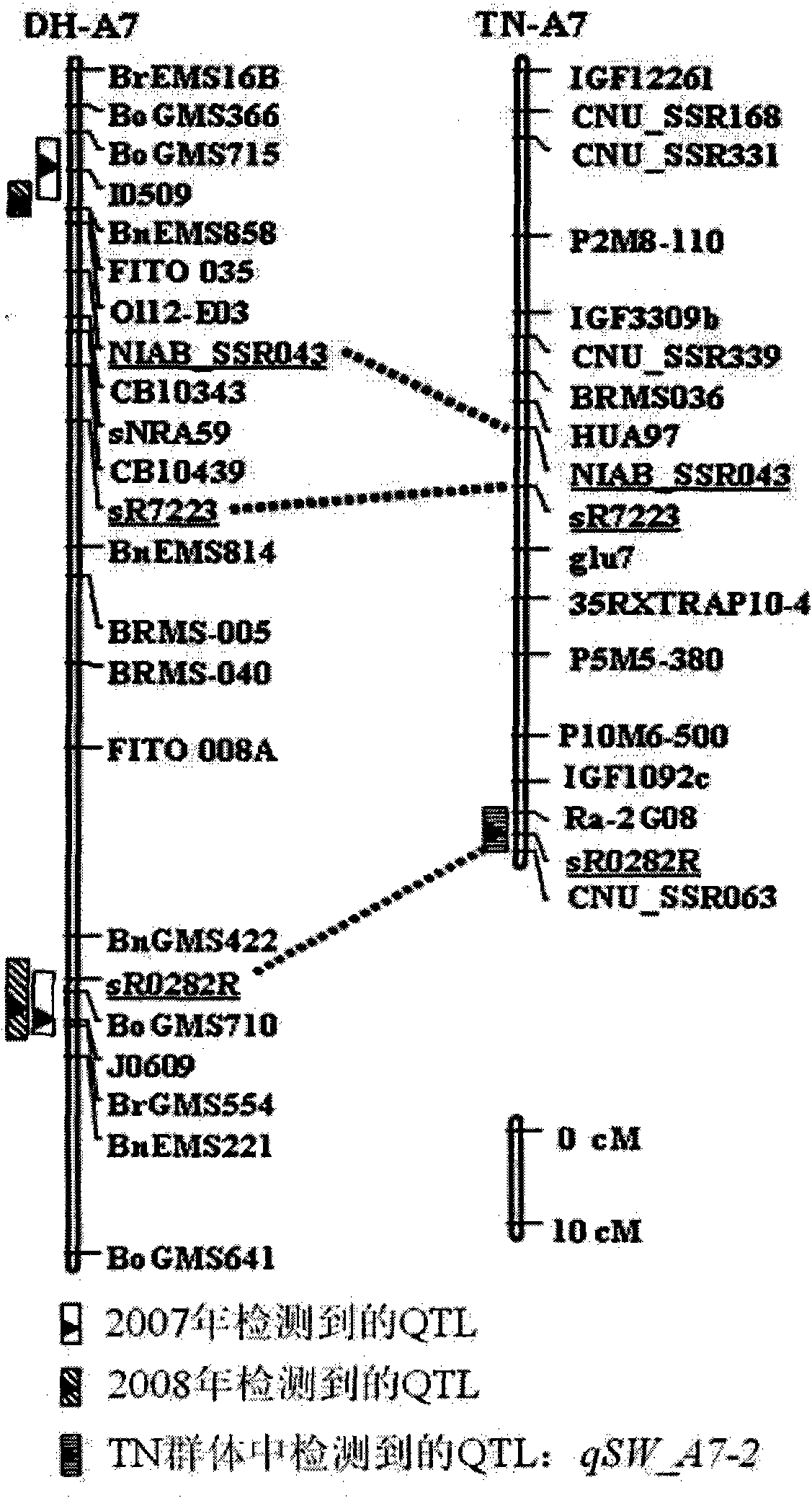
[0033] (1) Construction of DH population of Brassica napus A254 / A177 grain relocation population, field experiment and 1000-grain weight analysis. line) as the male parent to obtain F1, plant F1, take flower buds from the F1 plant and carry out microspore culture to obtain double haploid (DH) segregation population, a total of 238 lines of DH lines were obtained, and 190 lines were randomly selected for use. Construction of genome-wide genetic linkage map and mapping of grain weight QTL.
[0034] The DH line obtained above and its parents A254 / A177 and F1 were planted in the field in 2007-2008 and 2008-2009. The field experiment adopted a completely randomized block design, repeated three times, and each line planted two rows. There are 11-12 individual plants in each row, the average distance between plants is about 24cm, and the distance between rows is 30cm....
Embodiment 2
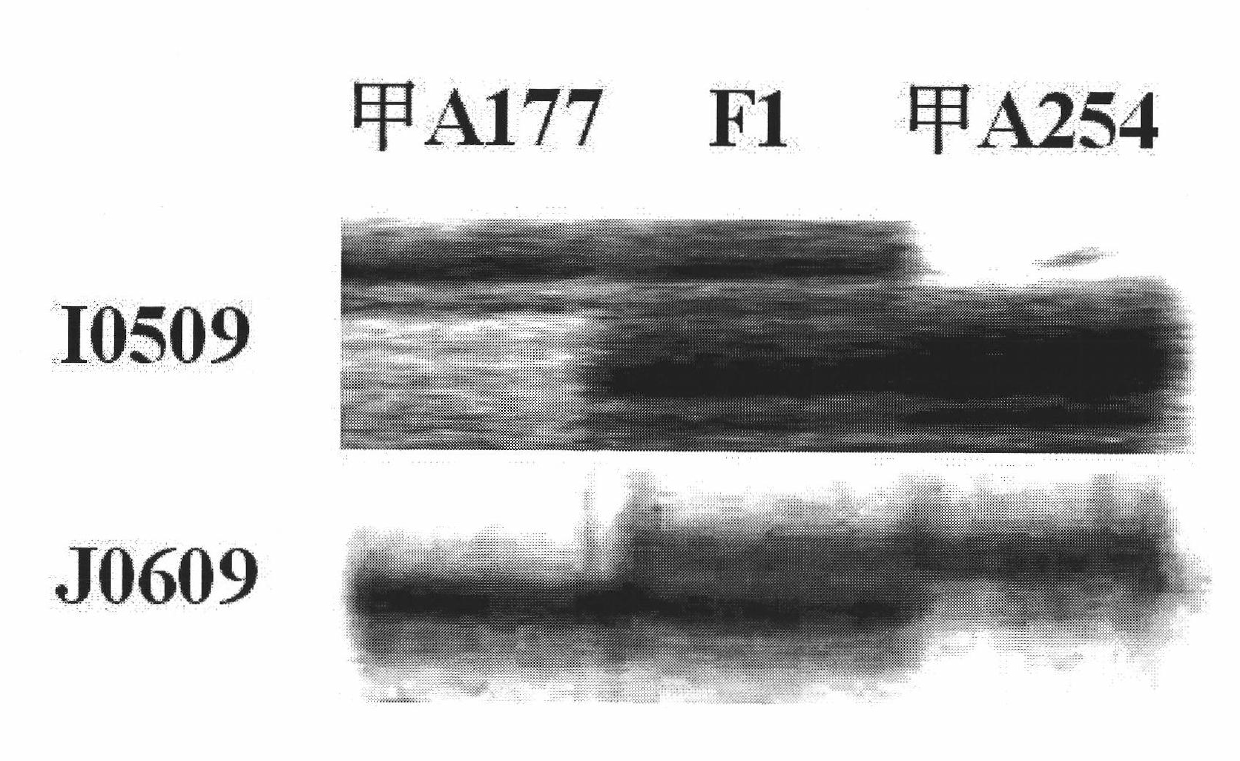
[0045] Example 2: Verification of the validity of the locus-specific markers of the main QTLs for grain weight in Brassica napus
[0046] (1) Validation of locus-specific markers for major QTLs for grain weight in Brassica napus
[0047] In order to detect the main effect of the two markers I0509 and J0609 on phenotypic variation, in the DH population, each line was grouped by the genotypes of these two loci, and the average value of thousand-grain weight was calculated. For the I0509 locus, in the AA genotype (allele locus from A254) group, the number of alleles containing positive additive effects from A254 in two years was significantly higher than that from A177 is higher. There is the same trend for J0609 (Table 3). It can be seen from the results in the table that the two sites located at A7 in Brassica napus are the main factors determining the grain weight.
[0048] (2) Verification of the combined effects of QTLs for grain weight in Brassica napus
[0049] The com...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com