Method for strengthening side wall of debris flow drainage groove with stone masonry structure
A drainage channel and debris flow technology, applied in water conservancy projects, artificial waterways, embankments, etc., can solve the problems of difficulty in large-scale promotion and application, insufficient construction convenience, and insufficient utilization, so as to ensure normal performance and improve resistance to debris flow impact. The effect of performance and engineering cost saving
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
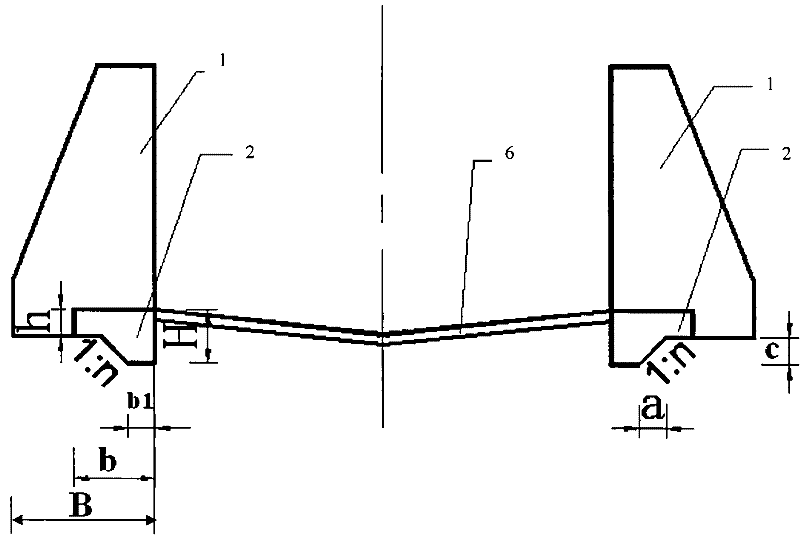
[0034] like figure 1 , figure 2 , image 3 shown. For a watershed area of 1.2km 2 , The slope of the accumulation fan is 15%. On the debris flow accumulation fan, build a 150m-long fully-lined debris flow drainage channel, including the fully lined bottom plate 6 and the side walls 1 of the drainage channel on both sides, and use the L-shaped beam foundation 2 to guide the debris flow of the masonry structure The groove side wall 1 is reinforced. The L-shaped beam foundation 2 is firstly constructed, and then the side wall 1 of the drainage channel of the mortar masonry structure is constructed, and then the fully lined bottom plate 6 is constructed.
[0035]Both sides are provided with an L-shaped beam foundation 2 to reinforce the foundation of the side wall 1 of the guide groove, and the L-shaped beam foundation 2 is connected with the side wall 1 of the guide groove to form a whole. The L-shaped beam foundation 2 includes a toe 3 and a thin plate 4, the toe 3 is l...
Embodiment 2
[0038] like figure 1 , Figure 4 , Figure 5 shown. The same as the first embodiment will not be repeated, the difference is: the basin area is 26.0km 2 , The slope of the accumulation fan is 5%. On the debris flow accumulation fan, build a 600m-long soft foundation energy-dissipating debris flow drainage channel, including the side walls 1 of the drainage channel on both sides and the anti-scour tooth sill 7 placed in between, and adopt the L-shaped beam foundation with 2 pairs of slurry The side wall 1 of the debris flow drainage channel of the masonry structure is reinforced.
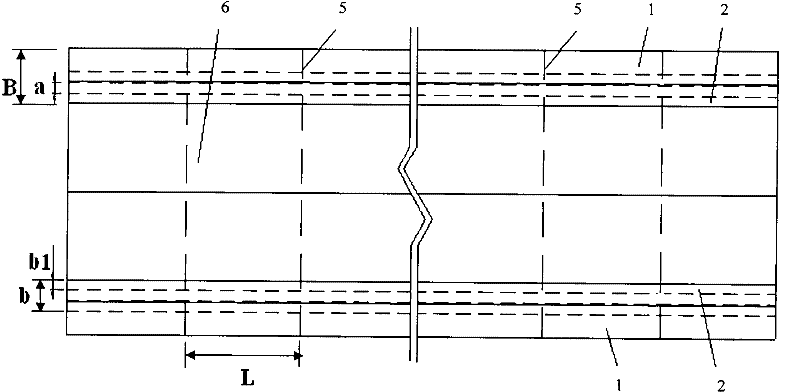
[0039] There are 19 settlement joints 5, and the distance L between the settlement joints 5 is 30.0m. The thickness H of the toe foot 3 plus the thin plate 4 is 3.0m, the thickness h of the thin plate 4 is 1.0m, the foundation width b of the L-shaped beam foundation 2 is 4.0m, the width b1 of the toe foot 3 is 1.0m, and the side wall of the drainage channel 1 The foundation width B is 4.5m. Th...
Embodiment 3
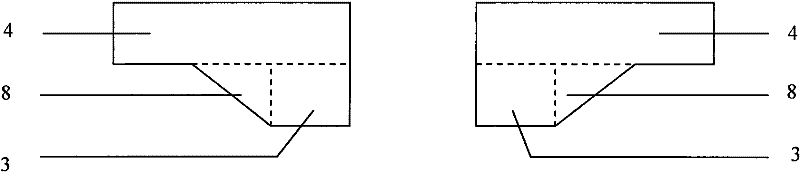
[0042] like figure 1 , Image 6 shown. The same as the first embodiment will not be repeated, the difference is: the full-lined debris flow drainage channel is a slanted wall structure, the right side of the toe foot 3 and the right side of the thin plate 4 and the left side wall of the drainage channel 1 The fold line on the inner side of the toe pin 3 and the left side of the thin plate 4 are continuously connected to the inner side of the side wall 1 of the right row of guide grooves. The foundation width b of the L-shaped beam foundation 2 is equal to the foundation width B of the side wall 1 of the row channel, both of which are 1.5m. The top surface of the thin plate 4 is on the same surface as the bottom surface of the side wall 1 of the guide groove.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com