Wound dressing
A wound and wound contact layer technology, applied in dressings, viscous dressings, wound drainage devices, etc., can solve problems such as time-consuming, rupture, and cross-infection of users, and achieve the effect of reducing the risk of infection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
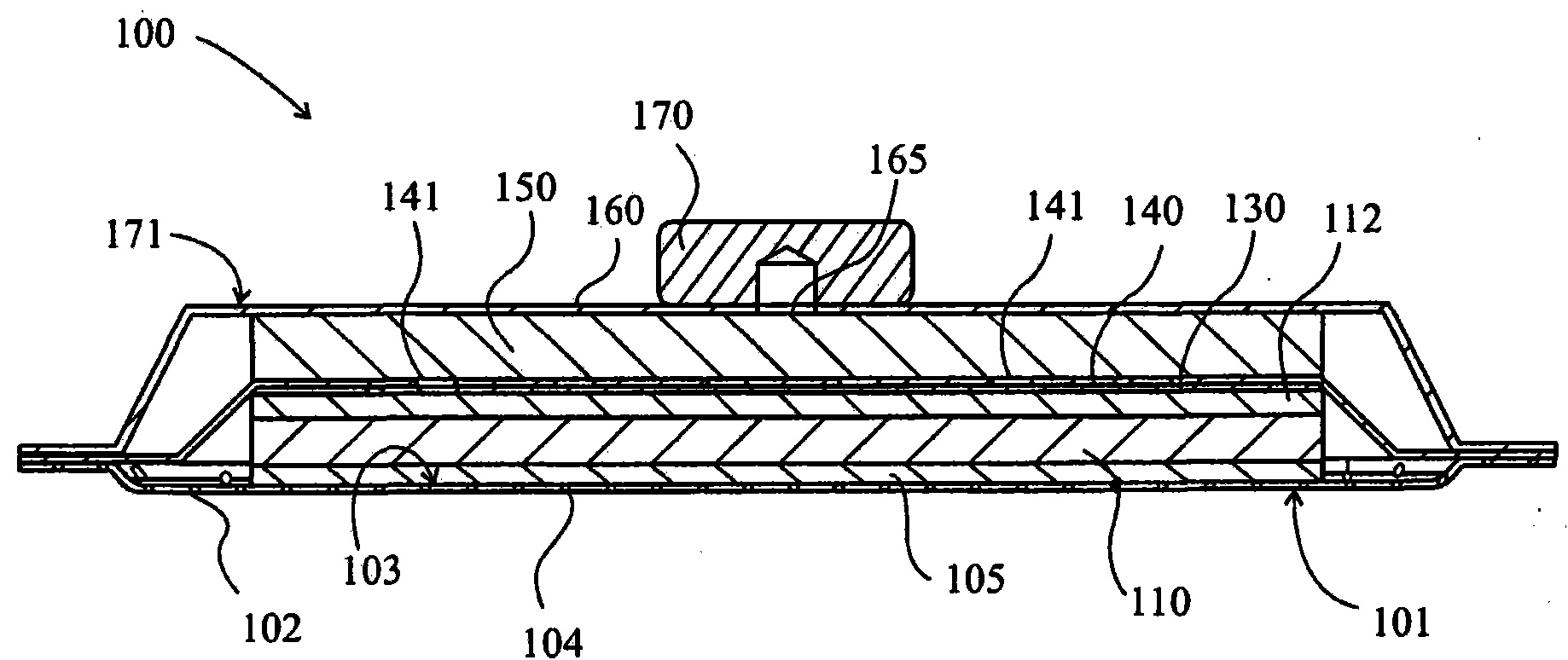
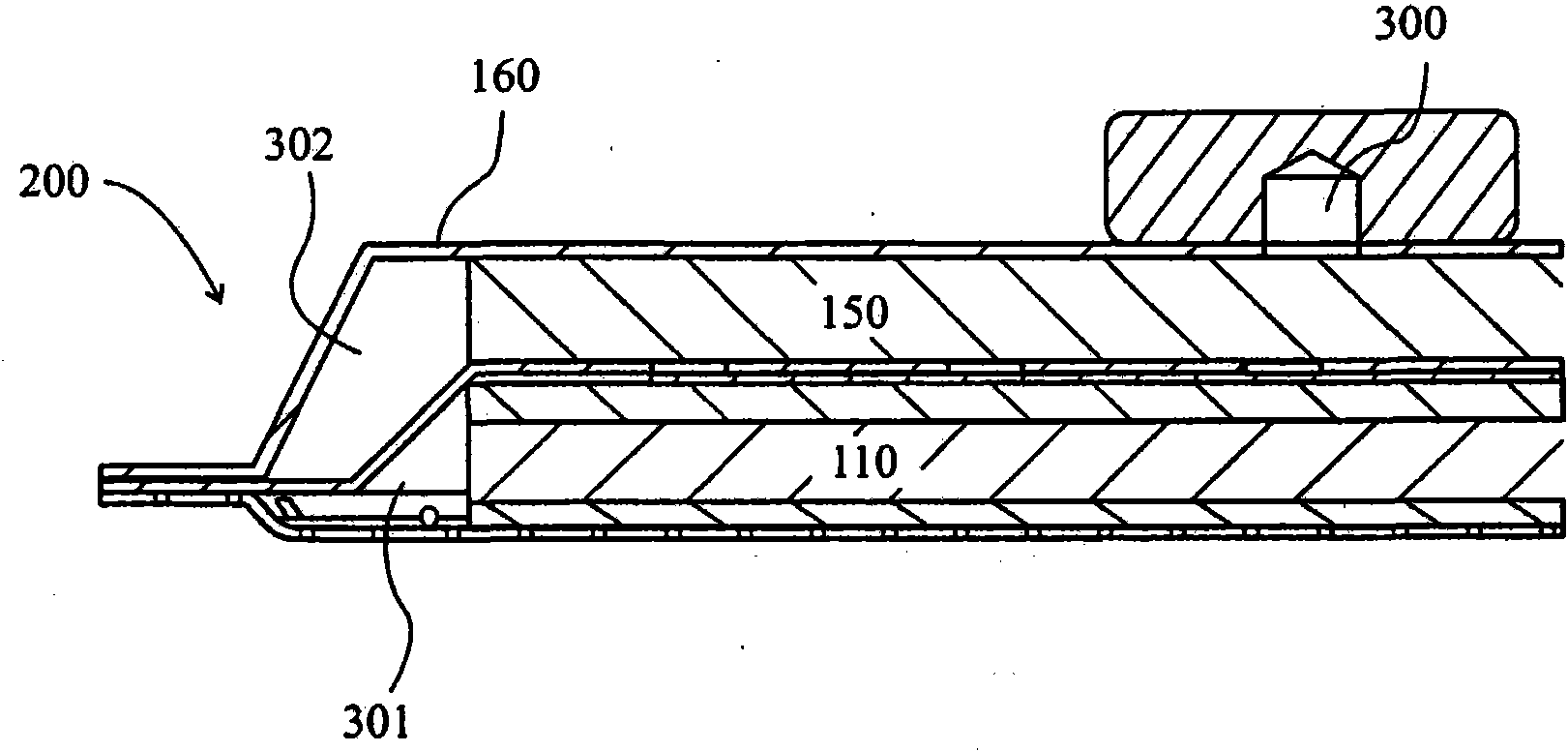
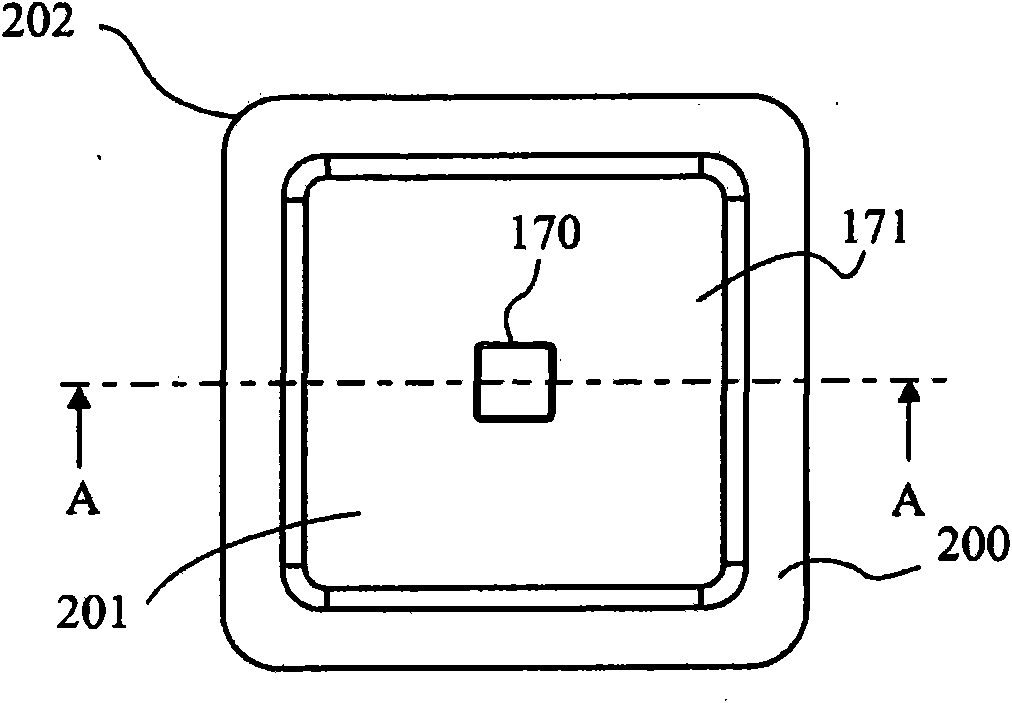
[0035] figure 1 A cross-sectional view through a wound dressing 100 according to an embodiment of the invention is illustrated. A top view of wound dressing 100 is illustrated at figure 2 , where line A-A indicates the figure 1 The location of the section shown in . It should be understood that figure 1 A generalized schematic diagram of device 100 is illustrated. It should be understood that embodiments of the present invention are generally applicable to body partial negative pressure (TNP) systems. In short, negative pressure wound therapy aids in the closure of many forms of "hard-to-heal" wounds by reducing tissue edema, promoting blood flow and particulate tissue formation, removing excess exudate, and reducing bacterial growth (and risk of infection). heal. In addition, the treatment results in less wound disturbance, resulting in faster healing.
[0036] Wound dressing 100 may be positioned over a wound site to be treated. The dressing 100 forms a sealed cavit...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com