A comprehensive water-saving control method for urban water supply plants
A technology for urban water supply and control methods, applied in water supply devices, water supply devices, computer control and other directions, can solve the problems of lack of systematization and correlation, lack of key technologies for water saving, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0034] Specific implementation mode one: a control method for comprehensive water saving in urban water supply plants, this implementation mode is realized by the following steps:
[0035] Step 1: Determine the water consumption rate of the process unit, evaluate the water consumption status of the water purification process and recycling treatment system, and determine whether the urban water supply plant has the ability to save water and tap the potential;
[0036] Step 2: Under the condition that the urban water supply plant has water-saving potential, determine the key links and key points of the recovery and treatment system to optimize water conservation, and implement the control technology to improve the water-saving capacity for the key links and key points; re-determine the urban water supply plant Water consumption rate, to achieve comprehensive water saving.
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0037] Specific embodiment two: This embodiment is a further description of the control method for comprehensive water conservation in a city water supply plant described in specific embodiment one. The calculation method of the water consumption rate described in step one is expressed by formula one:
[0038] Formula one:
[0039] The net production volume mentioned in the formula is based on the net production volume in the actual operation of the treatment system of the urban water supply plant; the self-use water volume refers to the self-use water volume obtained by subtracting the supernatant water volume from the sum of the sludge discharge water volume and backwash water volume.
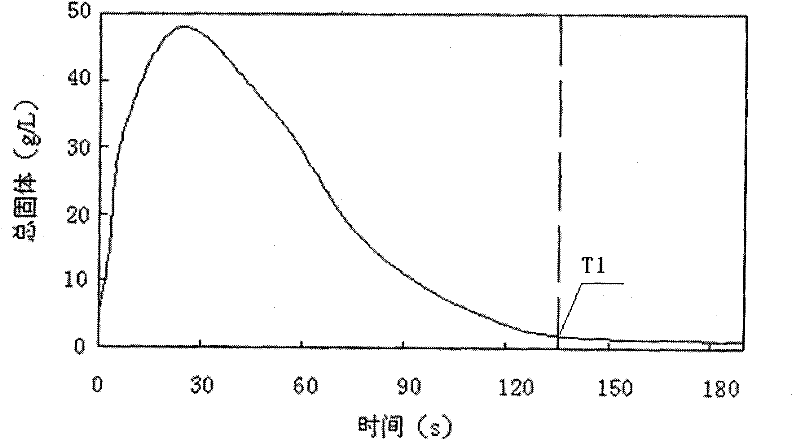
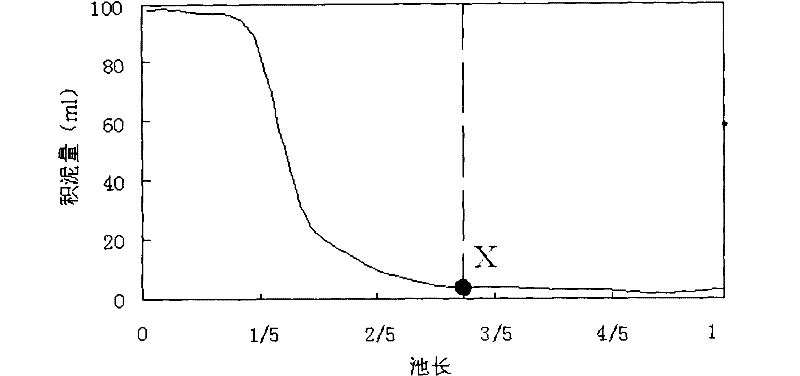
[0040] The amount of sludge discharge in the personal water consumption mentioned in this embodiment refers to: during the operation of the sedimentation unit and the coagulation unit, mud will be accumulated at the bottom of the tank. In order not to affect the effluent water quality or hyd...
specific Embodiment approach 3
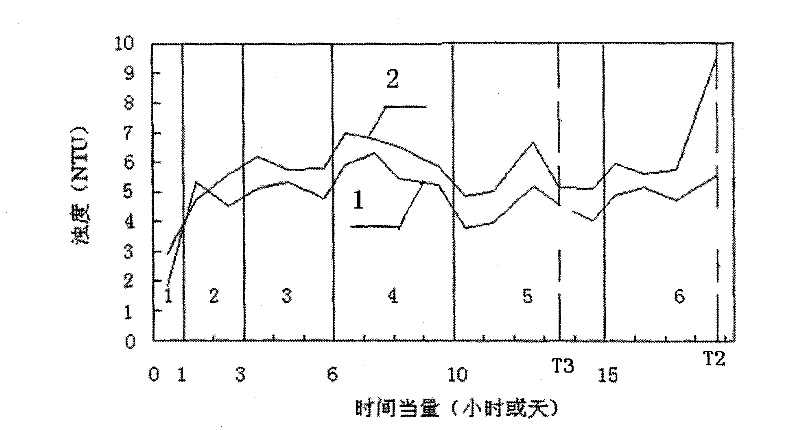
[0059] Specific embodiment three: This embodiment is a further description of the comprehensive water-saving control method of a city water supply plant described in the specific embodiment one, and the evaluation of the water consumption status of the water purification process and the recovery treatment system described in step one Specifically, it refers to the comparison between the actual water consumption rate of the urban water supply plant and the water consumption rate within the determined empirical water-saving range, to determine the current status of the urban water supply plant’s self-use water, and to evaluate the self-use water consumption and water conservation of the urban water supply plant’s treatment system. potential to be evaluated.
[0060] The evaluation standard for determining the empirical water-saving water consumption rate described in this embodiment is: 3% of the water consumption rate of the urban water supply plant treatment system is defined a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com