Modularized artificial hip joint femoral shaft
A technology for hip joints and femoral stems, which is applied in the direction of hip joints, femoral heads, joint implants, etc., and can solve problems such as easy detachment, failure to meet public needs, and difficult placement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0034] In order to further explain the technical means and effects of the present invention to achieve the intended purpose of the invention, below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and preferred embodiments, the specific implementation, structure, Features and their effects are detailed below.
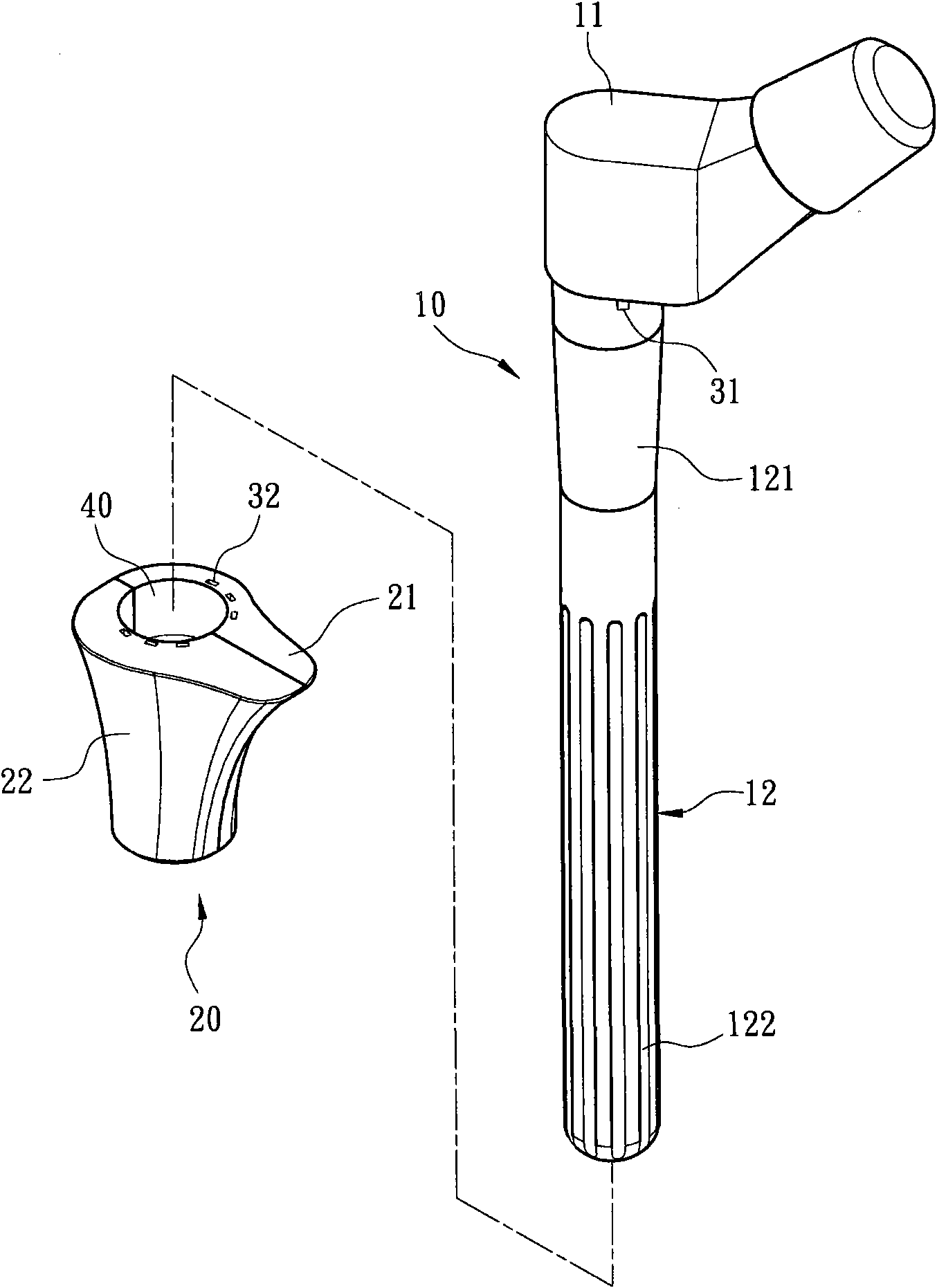
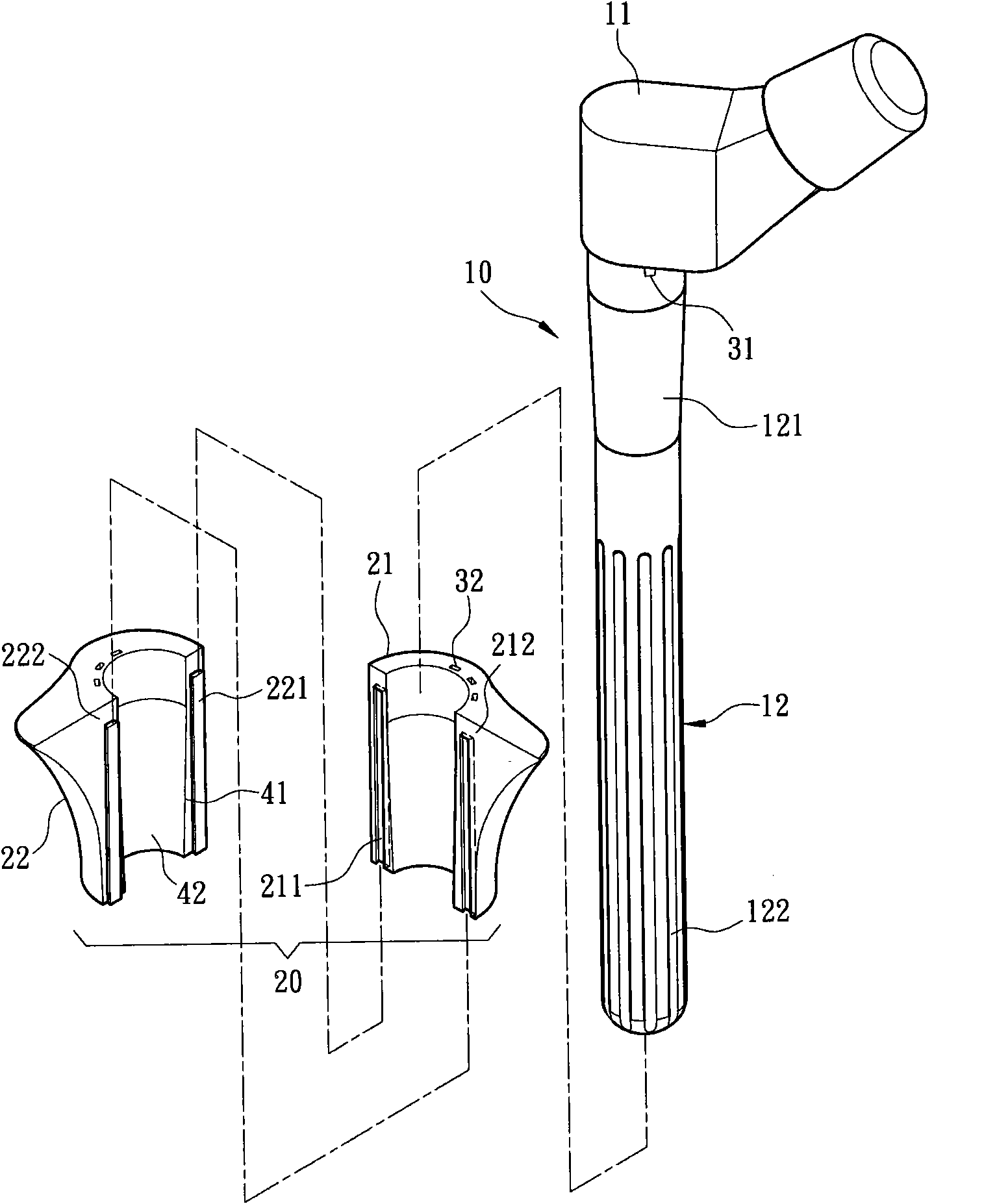
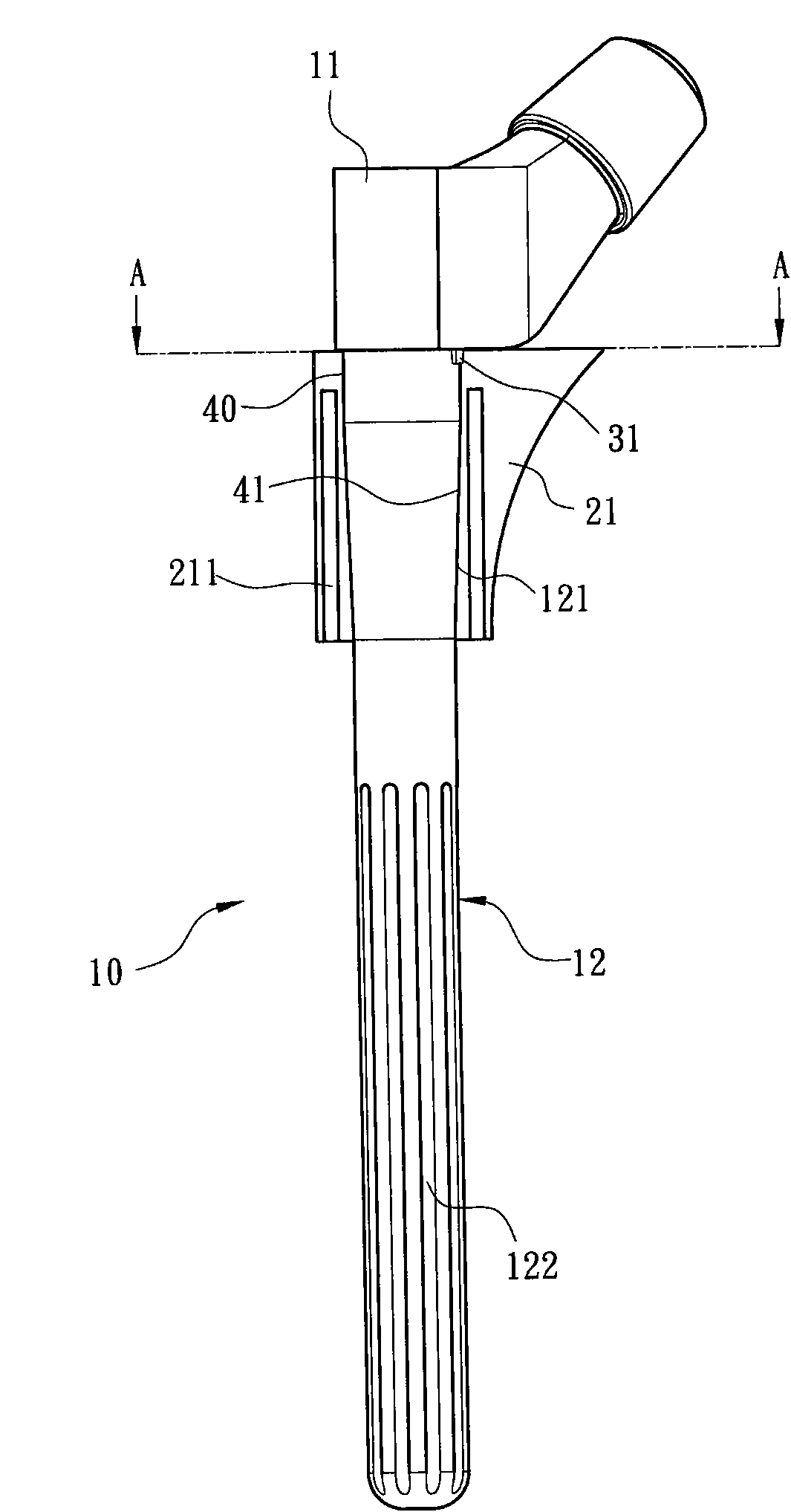
[0035] see figure 1 , figure 2 and Figure 6 As shown, they are respectively the first exploded appearance schematic diagram, the second appearance exploded schematic diagram and the first use state schematic diagram of a preferred embodiment of the modular artificial hip joint femoral stem of the present invention. The modular artificial hip joint femoral stem of the preferred embodiment of the present invention includes a seat body 20, which is used for embedding into the proximal femoral medullary cavity 51 and is provided with a perforation 40 with a taper 41, and the perforation 40 penetrates A support handle 10 is provided, wherein the seat body 20 and the support ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com