ARMS-PCR method for mtDNA allelic gene typing and point mutation detecting
An allele and point mutation technology, applied in the field of molecular genetics, can solve the problems of high utility and difference in PCR amplification efficiency, etc., and achieve the effect of highly reliable results, simple operation and practicability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
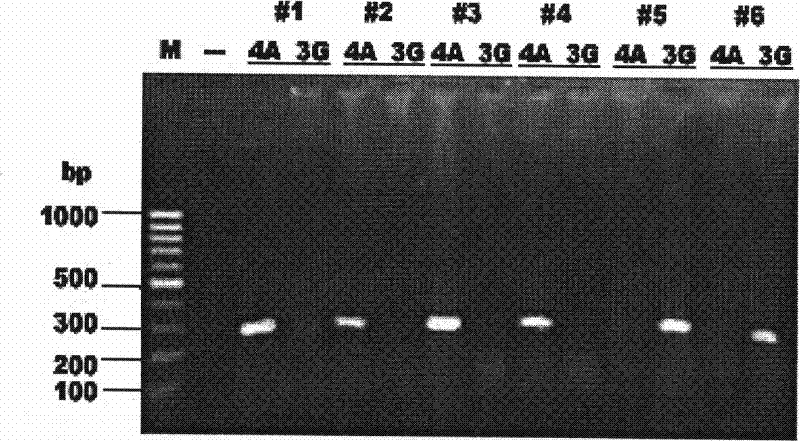
[0013] Example 1 Detection of mtSNP 8701A / G by the method of the present invention
[0014] Taking the individual genotyping of mtSNP 8701A / G as an example, aiming at the alternating changes of A and G nucleotides in different individuals, mismatched primers were designed in accordance with the principle of ARMS-PCR amplification, and the optimized 200 cases of DNA samples were tested for genotyping under amplification conditions, and the results were consistent with the results of sequence analysis and typing.
[0015] (1). Design ARMS-PCR amplification primers
[0016] Six pairs of ARMS-PCR amplification primers were designed in the experiment, such as figure 1 shown. The common upstream primer is ATF1 (np8466-8587). The 3' ends of the 6 downstream ARMS primers are fixedly terminated at the mtDNAnp8701 site, and 6 downstream primers that differ from each other at the 3' ends are designed for the nucleotide substitution of G and A between the two SNP alleles .
[0017] S...
Embodiment 2
[0025] Example 2: Detection of mt10398A / G
[0026] Taking the aforementioned individual genotyping of mtSNP10398A / G, which can be detected by Bgl I enzyme digestion, as an example, aiming at the alternating changes of A and G nucleotides in different individuals, an error in accordance with the principle of ARMS-PCR amplification was carried out. Design primers and use optimized amplification conditions for genotyping of DNA samples.
[0027] The inventor designed two pairs of primers, the shared downstream primer is (10398R):
[0028] 5'-GGTGTTGAGGGTTATGAGAGTA-3';
[0029] The two upstream primers are mismatched ARMS primers. The upstream ARMS primer 1 is (10398FG):
[0030] 5'-GACTACAAAAAGGATTAGAC AC AG-3';
[0031] The upstream ARMS primer 2 is (10398FA):
[0032] 5'-GACTACAAAAAGGATTAGAC AC AA-3'.
[0033] The bases at the 3' end of the upstream primer are complementary to A or G respectively, and consecutive mismatched bases are also added at the penultimate 3-4 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com