3D segmentation by voxel classification based on intensity histogram thresholding intialised by K-means clustering
一种聚类、体素的技术,应用在图像分析、涉及3D图像数据的细节、图像增强等方向,能够解决不能聚类数据等问题
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
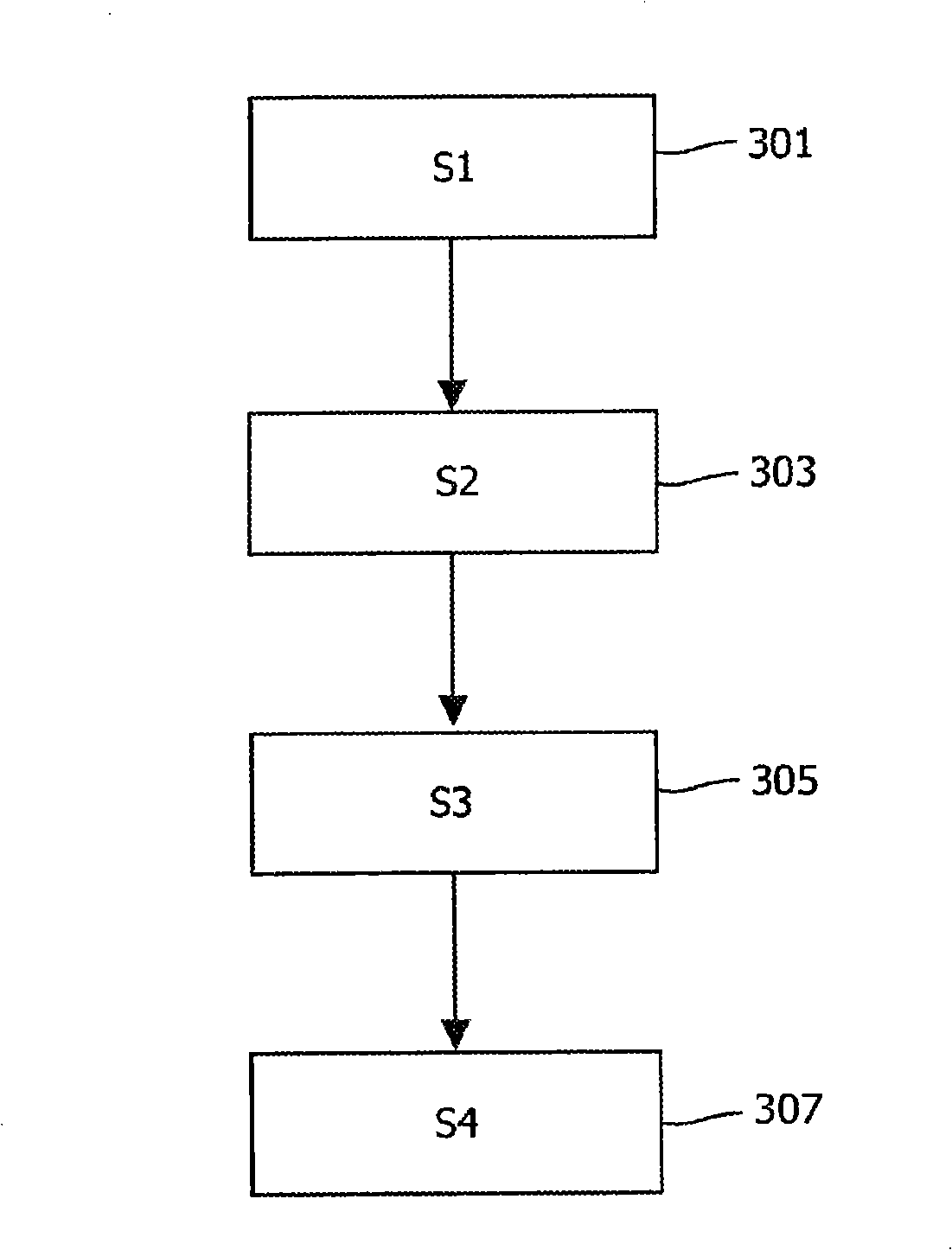
[0029] image 3 A flowchart is shown illustrating a method for interactively evaluating and rearranging a cluster map of voxels in an image in accordance with the present invention.
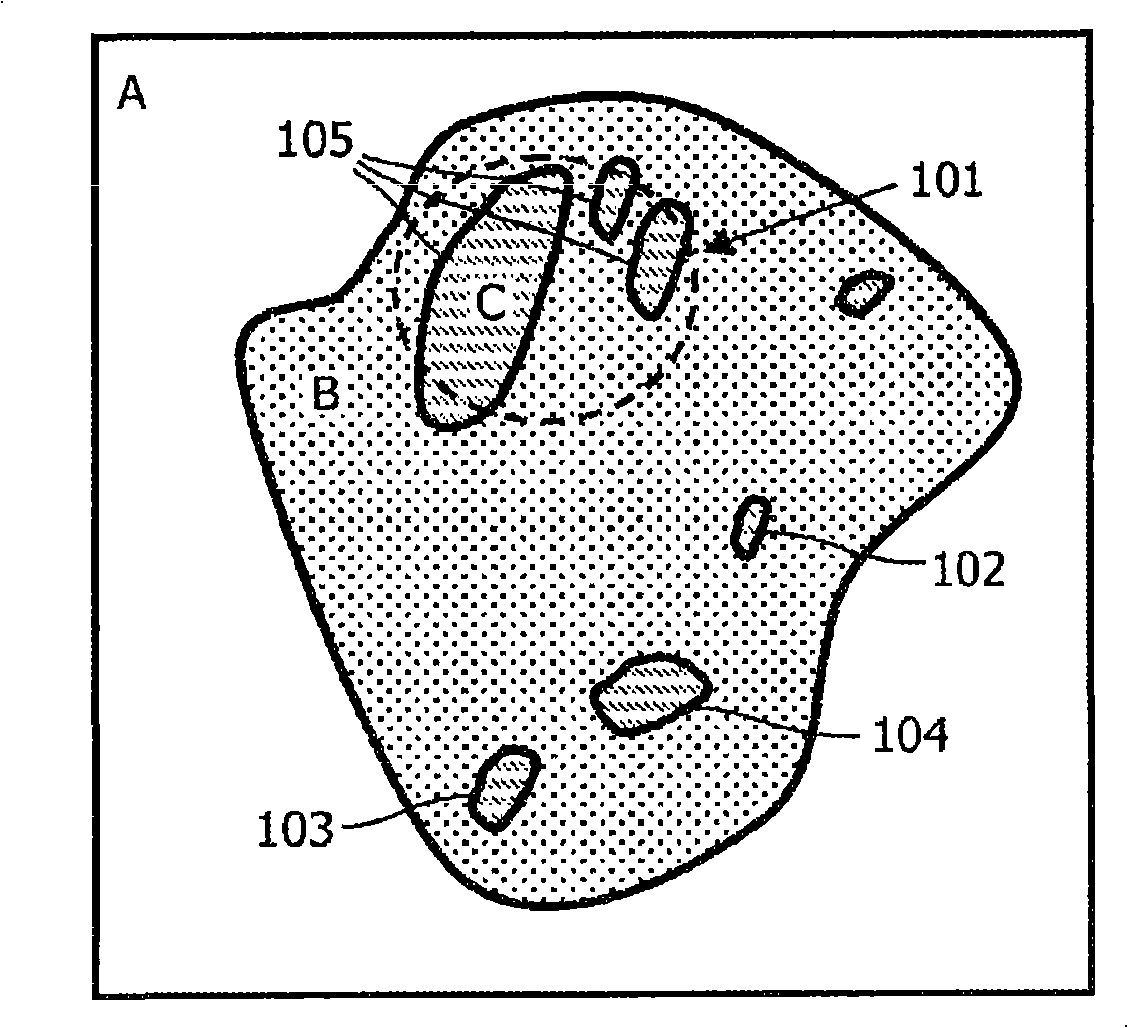
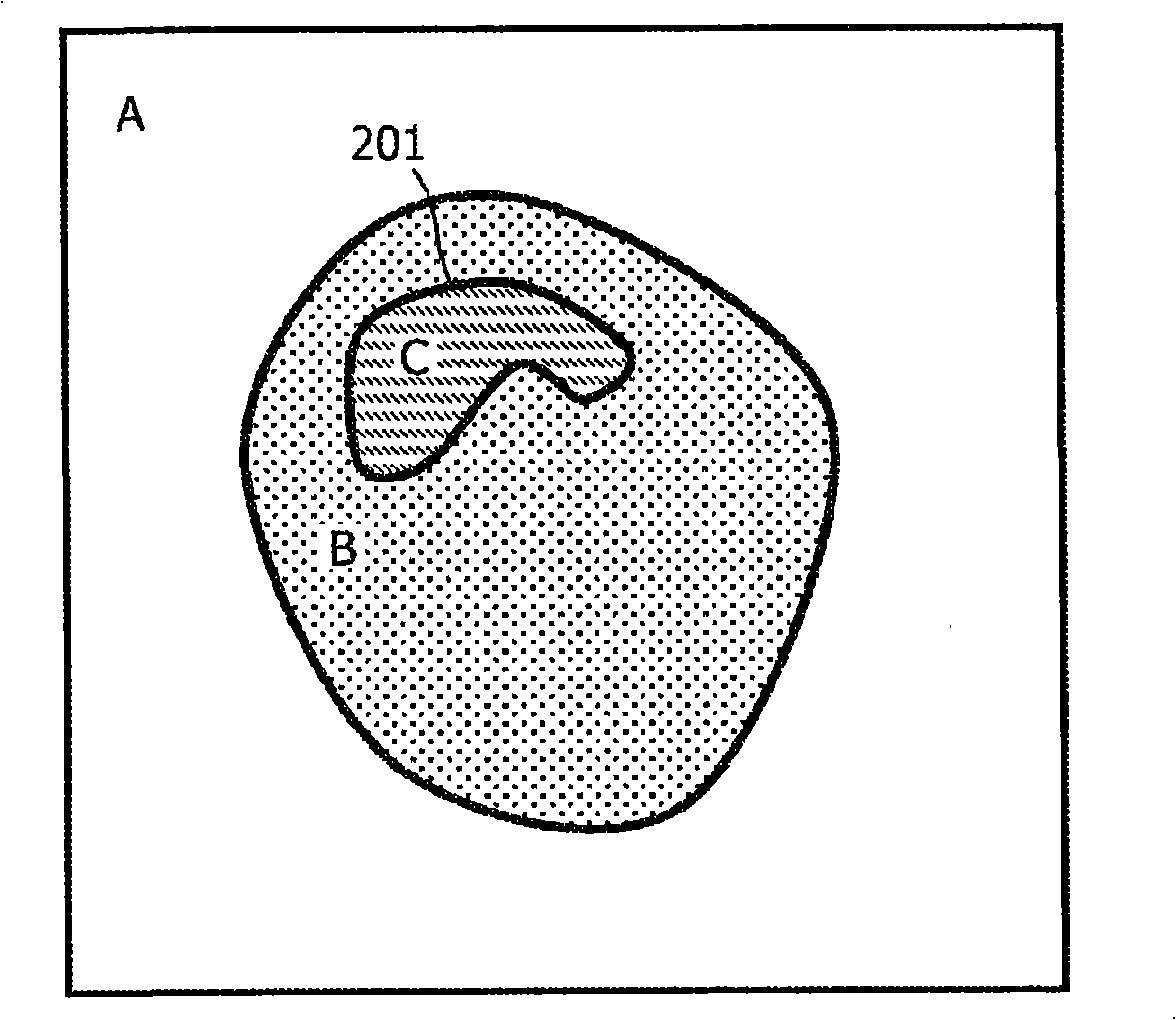
[0030] Such clustering graphs are realized by clustering algorithms such as K-means, QT clustering, fuzzy c-means clustering and other types of algorithms already mentioned in the literature, See Milan Sonka and J. Michael Fitzpatrick, Handbook of Medical Imaging, Volume 2. As previously mentioned in the background, implementing a cluster map by such an algorithm typically results in fragmented clusters 105 ( figure 1 shown in region 101) and separate clusters 102-104. like figure 1 The clusters shown are voxels that share some common property, usually based on proximity, ie a predefined distance metric. The areas labeled A, B, and C are clustering levels, where each clustering level is assigned a specific color, e.g. A might be black, B might be blue, and C might be red.
[0031]For example...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com