Identification of a novel type of sucrose synthase and use thereof in fiber modification
A sucrose synthase, fiber technology, applied in the agricultural field, can solve problems such as development that have not been described
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
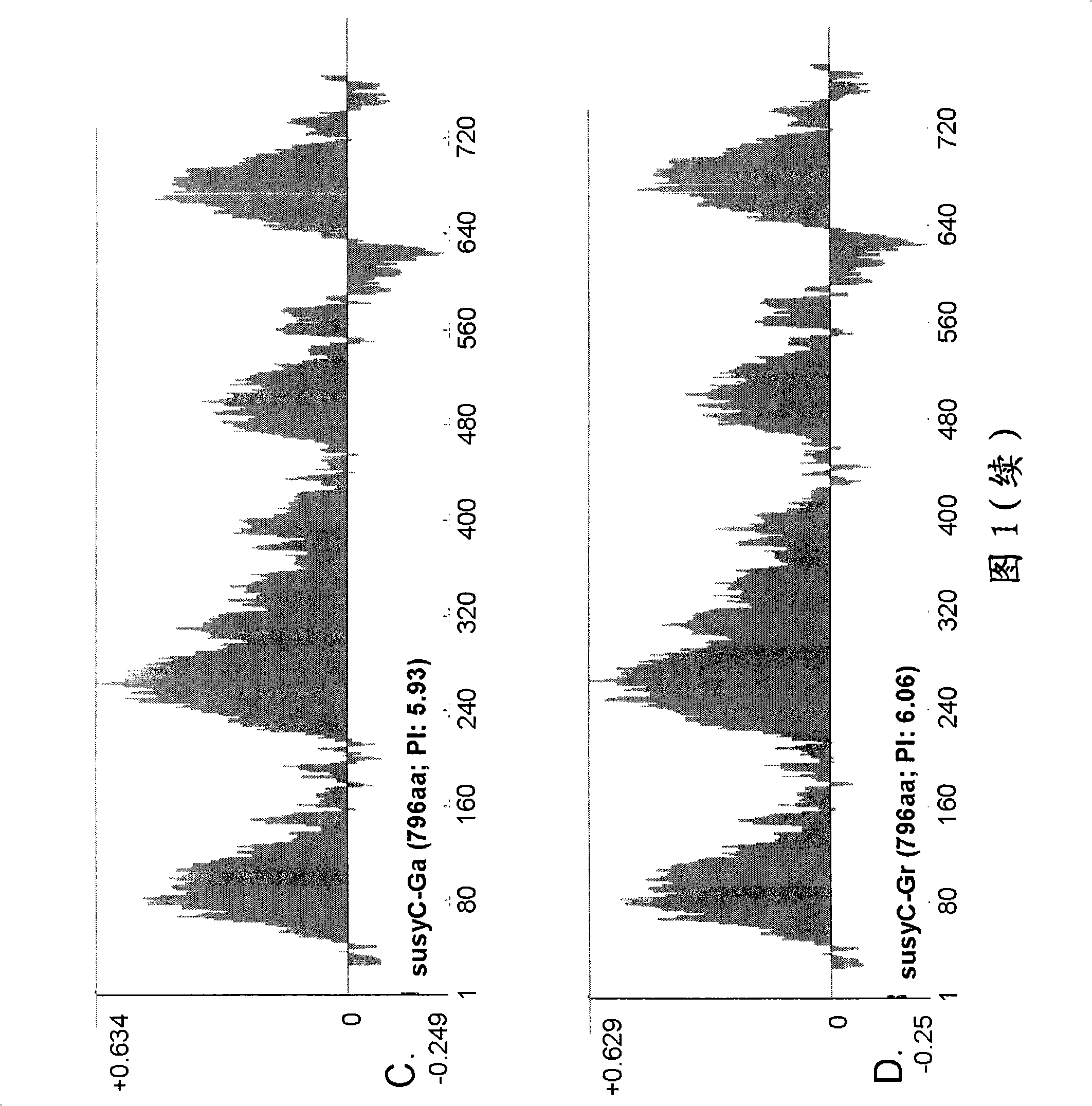
[0149] Example 1. Identification of Type C Sucrose Synthase in Gossypium Species
[0150]Identification of SusC. It has been confirmed that there are at least three types of Sus genes expressed in cotton fibers during development, called types A, B and C. The A / D-type is homologous to the previously reported sequence (accession number U73588), and the B-type shows strong sequence similarity with the published sequence. The C-type sequence provided in this specification is a new sequence and shows differential expression between the extension phase and the secondary cell wall phase. Type C is an isoform that appears in the later stages of fiber development. SusC is only 76% identical to A and B proteins at the amino acid level. By using RTPCR and Northern analysis, it has been confirmed that the developmental expression profile of type C transcripts precedes the synthesis of secondary cell walls, but shows a pattern more commensurate with their role in the development of the fiber,...
Embodiment 2
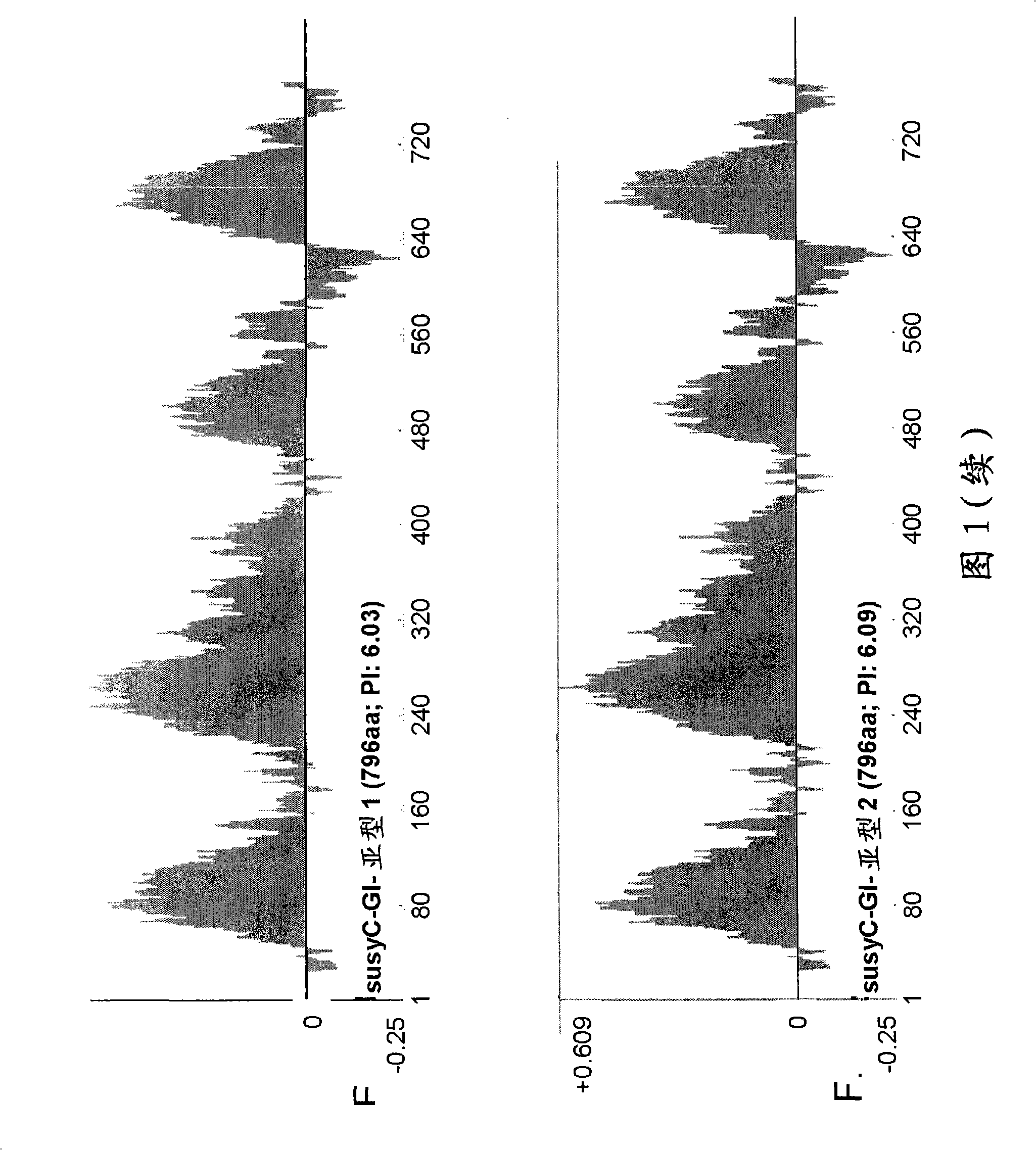
[0163] Example 2. Analysis of SusC isotypes and identification of different sucrose synthase in cotton and related species Differences between isotypes.
[0164] Phosphorylation site: A serine phosphorylation site at the N-terminus of the protein has been characterized in detail in the literature, which has a consensus sequence of RXXS. Corn (Zea mays) (has the following sites: 12 RXXS 15 The phosphorylation of this specific serine in) appears to be related to the release of the susy enzyme from the plasma membrane (Winter H et al., 1997-FEBS Letters 420, 151-155; Hardin SC et al., 2004, Plant Physiology 134, 1427-1438). At the site 8 RXXS 11 The mutation of the same serine above causes mung bean sucrose synthase to be more effective in using sucrose to produce UDP glucose (= higher Km) (Nakai T. et al., 1999, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96, 14- 18). The phosphorylation at this specific site in soybeans has also been characterized, and the phosphorylation seems to be related to...
Embodiment 3
[0180] Example 3. Overexpression of SusC in cotton.
[0181] By using standard recombinant DNA technology, the following DNA elements are effectively connected:
[0182] The cotton fiber specific promoter described in WO2004 / 066571
[0183] The DNA region encoding sucrose synthase C with the nucleotide sequence of SEQ ID No. 1
[0184] · 3'nos terminator region.
[0185] The chimeric gene is introduced into a T-DNA vector together with the bar selection gene. The T-DNA vector is introduced into Agrobacterium tumefaciens, as described in US 6,483,013 for the production of transgenic cotton plants.
[0186] Analyze the increased expression of SusC in transgenic cotton plants containing chimeric genes, especially fibers, and analyze fiber strength, fiber length, fiber maturity ratio, immature fiber content, fiber uniformity, and micronaire value. Fiber obtained from these plants. .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com