A dynamic channel allocation method based on generic algorithm
A technology of dynamic channel allocation and genetic algorithm, which is applied in the field of dynamic channel allocation, can solve problems such as difficult to predict position parameters, waste of channel resources, link requests cannot be allocated to channels, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0029] The invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
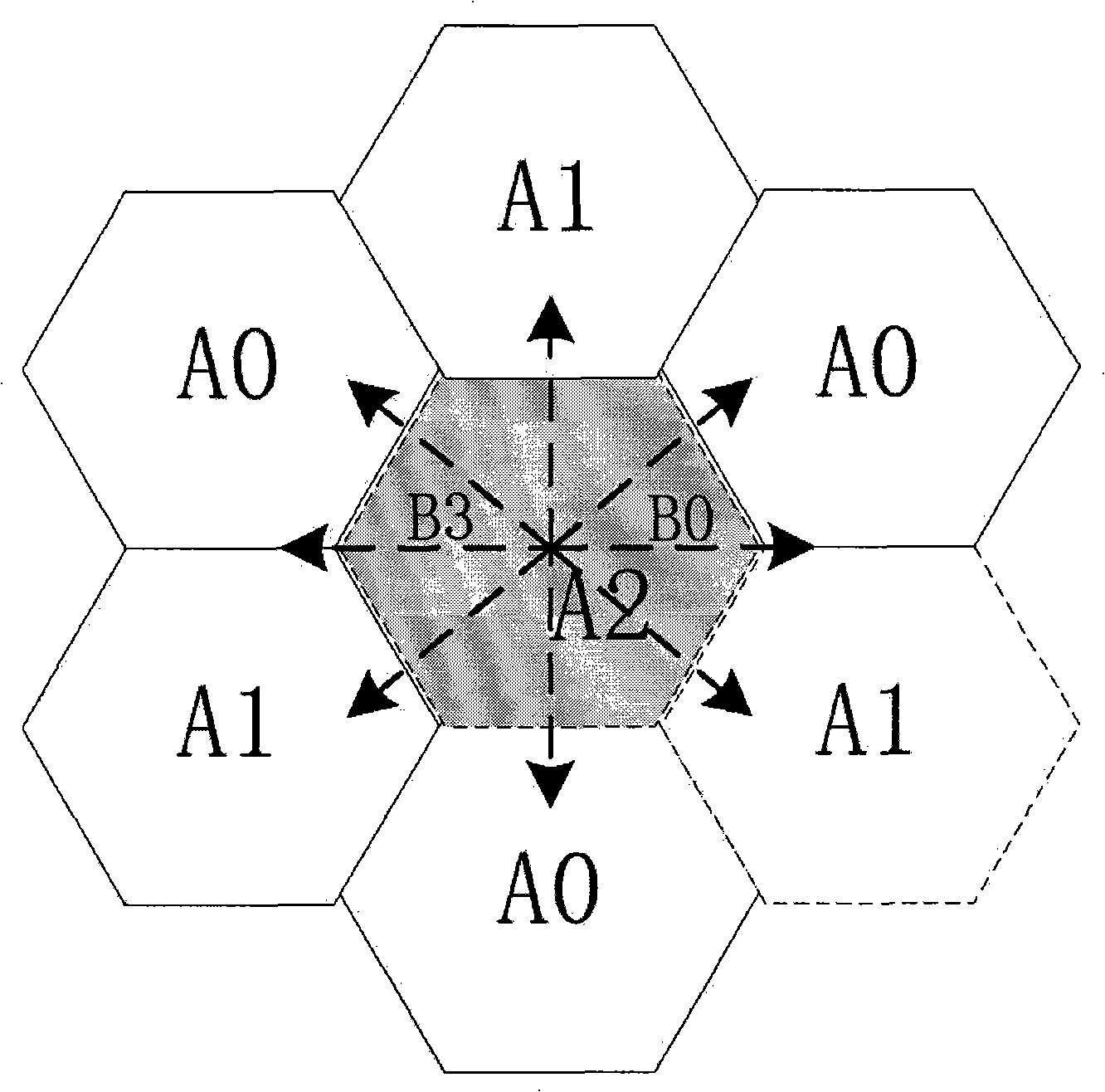
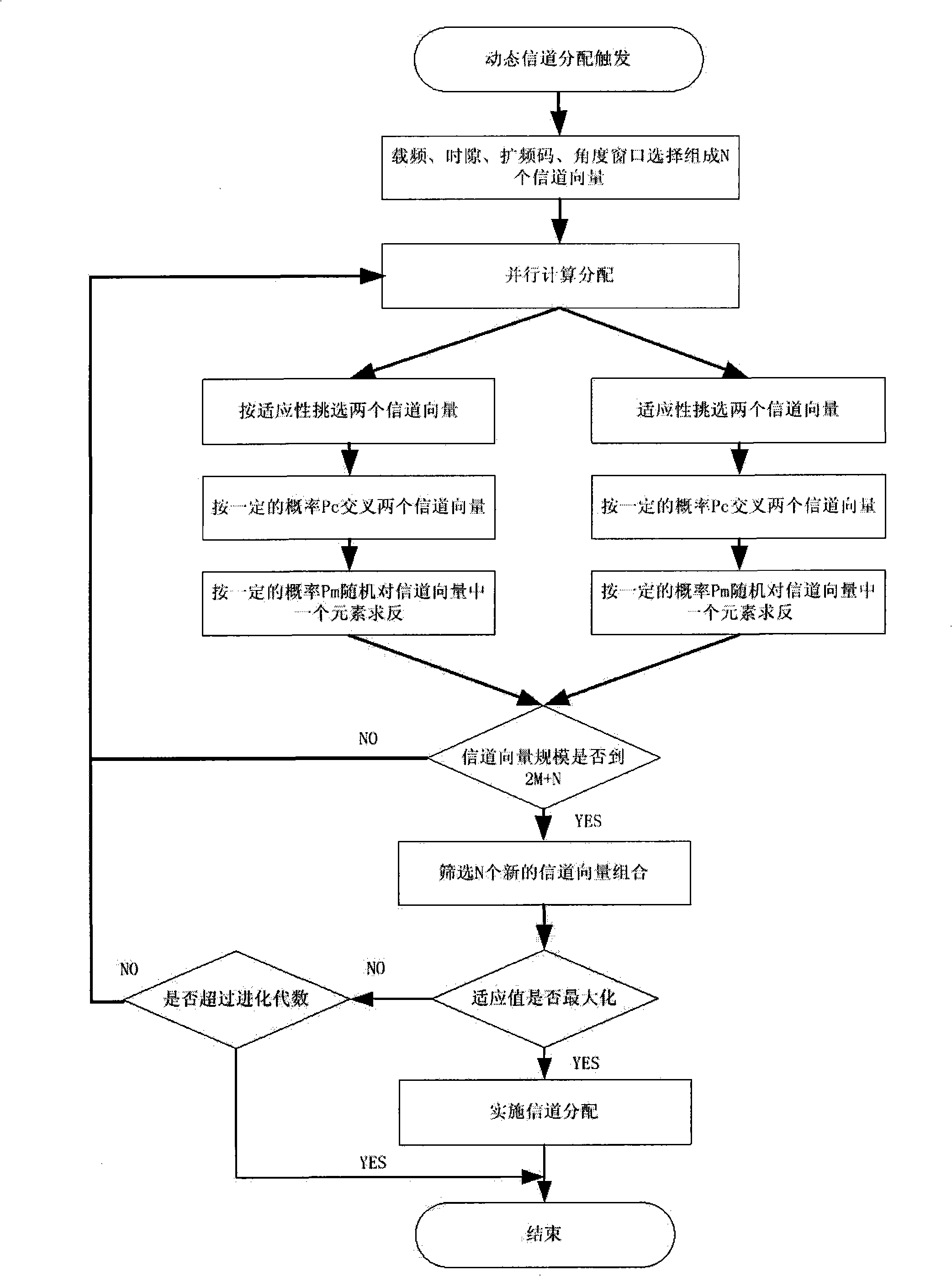
[0030] as attached figure 1 , in a multi-carrier TD-SCDMA cell cluster communication network. For ease of illustration, only seven cells are drawn, the number of carriers is N1=9, the number of service time slots is N2=6, the number of code-domain spreading N3=16, and the number of beam angles N4=8. The implementation process is attached figure 2 ,Proceed as follows:
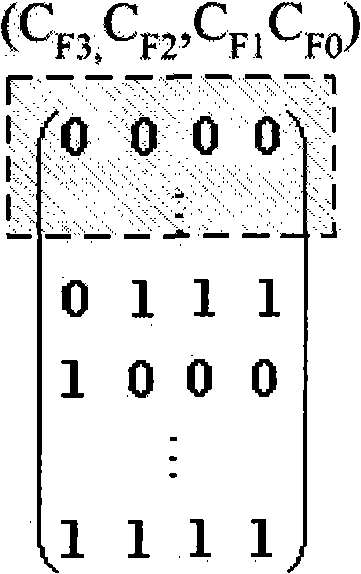
[0031] Step 1: First number the 9 carrier frequencies in the cell cluster, min(2 m >=9)=16, so 4 binary representations are required. Therefore, all carrier frequencies can form a 16×4 carrier frequency channel matrix X LF =(C F3 , C F2 , C F1 , C F0 ). In turn, the 8×3 time slot channel matrix X can be obtained TS =(T S2 ,T S1 ,T S0 ), 16×4 spread spectrum channel matrix X SF =(S F3 , S F2 , S F1 , S F0 ), 8×3 beam angle channel matrix X BF =(B F2 , B F1 , B F0 );
[0032] ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com