Semiconductor device and test mode control circuit
A test mode, semiconductor technology, applied in the direction of measuring electricity, measuring devices, measuring electrical variables, etc., can solve problems such as release, inability to ensure safety, and reduced LSI yield.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
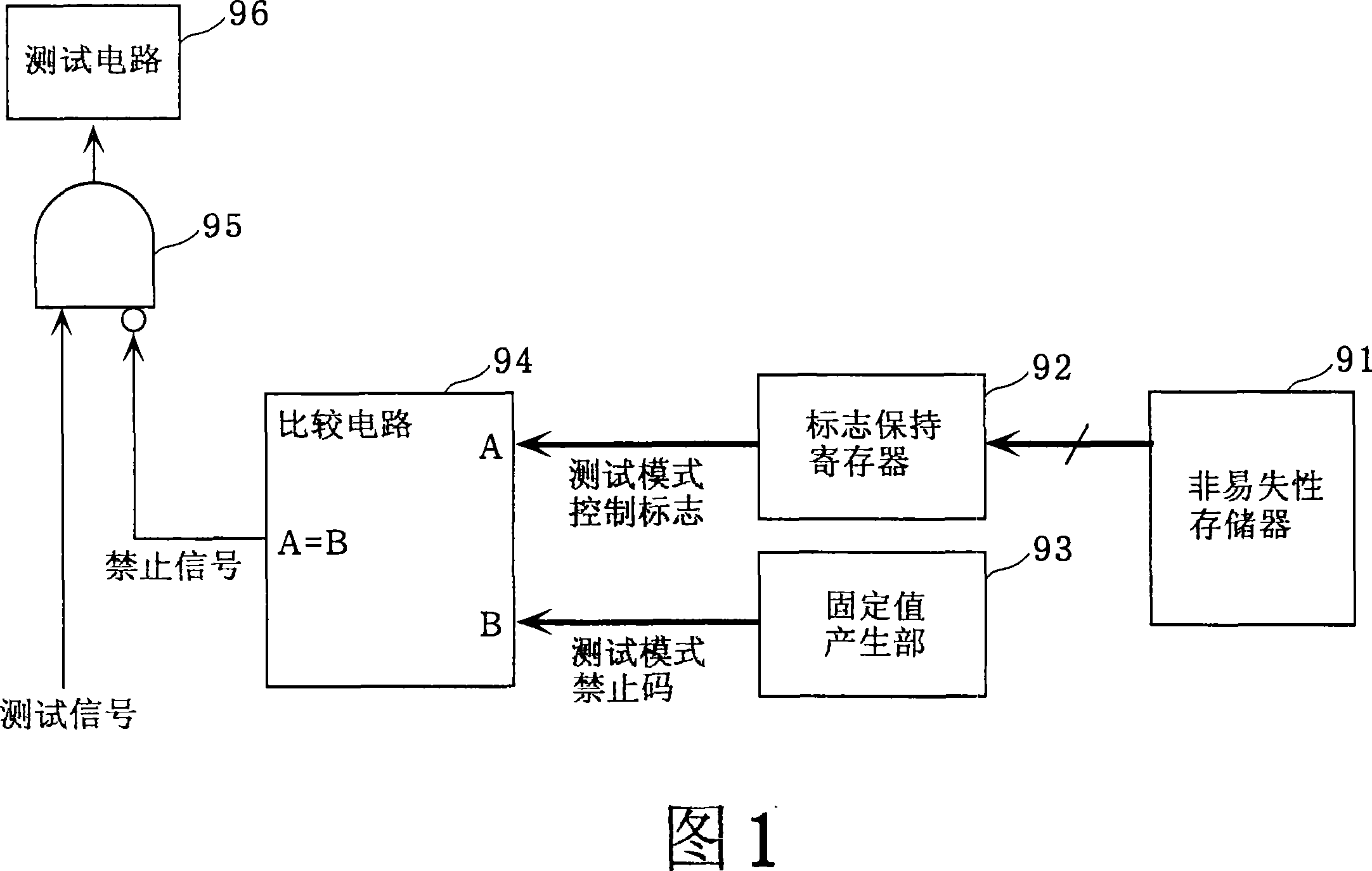
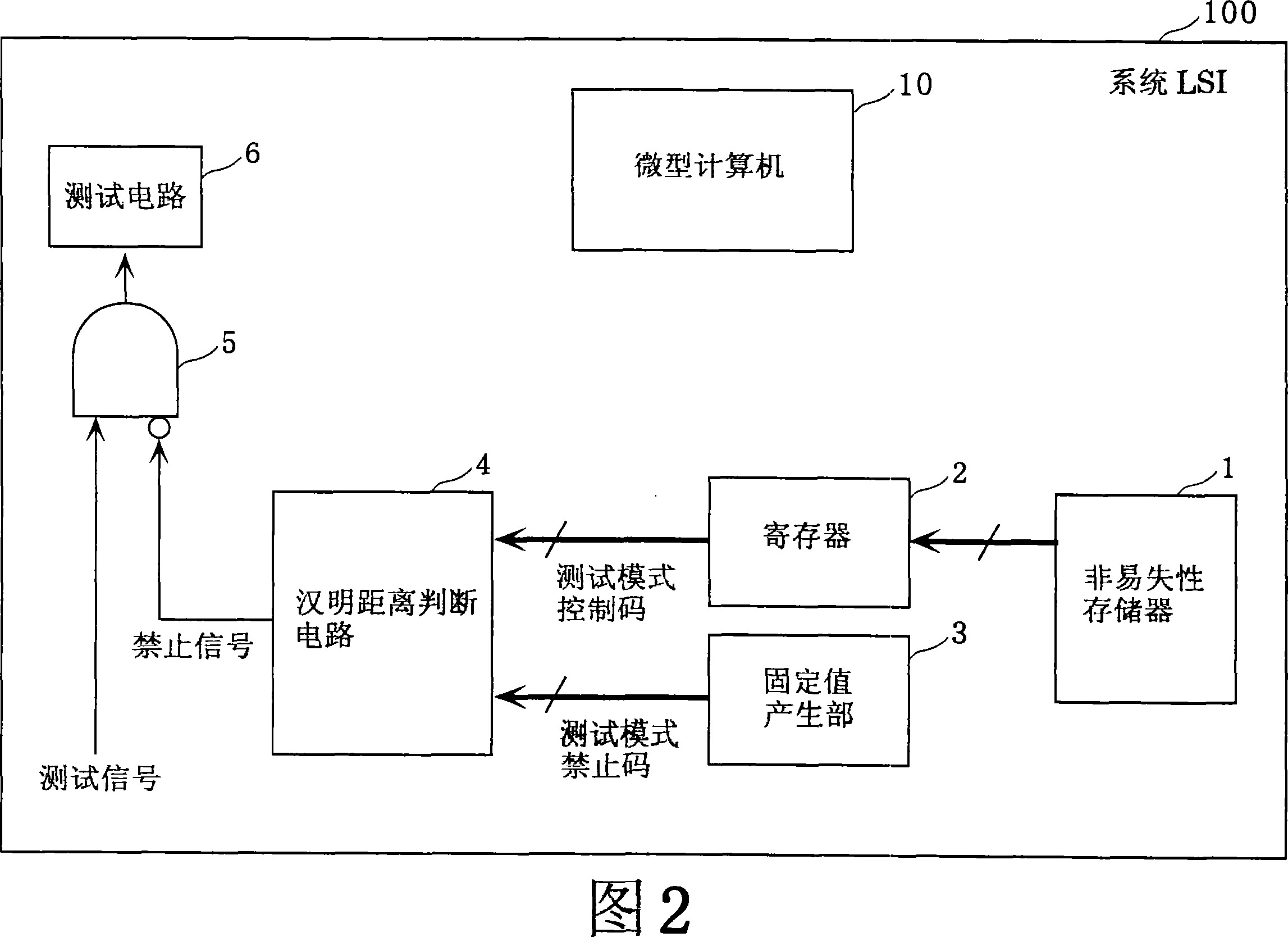
[0057] FIG. 2 is a block diagram of a system LSI having a test mode control circuit in Embodiment 1 of the present invention. In this figure, the system LSI 100 is a semiconductor device with a test mode, including a nonvolatile memory 1, a register 2, a fixed value generator 3, a Hamming distance judgment circuit 4, an AND circuit 5, a test circuit 6, and a micro computer10. Furthermore, a test mode control circuit is constituted by part of the nonvolatile memory 1 , the register 2 , the fixed value generator 3 , the Hamming distance judgment circuit 4 , and the AND circuit 5 .
[0058] The nonvolatile memory 1 stores a test mode control code for enabling or prohibiting transition to the test mode at a predetermined address. The test mode control code is set as necessary immediately after the factory manufactures or during maintenance. After shipment, a test mode control code for prohibiting transition to the test mode is set.
[0059] The register 2 holds the test mode in...
Embodiment 2
[0086] 8 is a block diagram showing the structure of a semiconductor device in Embodiment 2 of the present invention. This figure is different from FIG. 2 in that a selector 7 is added, and an output signal from the selector 7 is input to the register 2 . Hereinafter, the difference will be mainly explained, and the same point will be omitted.
[0087]The selector 7 receives the test mode control code from the nonvolatile memory 1 and the fixed value from the fixed value generator 3, selects the test mode control code when the reset signal is active, and selects the fixed value when the reset signal is invalid.
[0088] The selector 7 holds a fixed value as an initial value when the semiconductor device is reset, and holds the test mode control code from the nonvolatile memory 1 after the reset.
[0089] According to this, the Hamming distance judging circuit 4 asserts the prohibition signal during the period from reset until the test mode control code is set in the register,...
Embodiment 3
[0092] 9 is a block diagram showing the structure of a semiconductor device in Embodiment 3 of the present invention. This figure is different from FIG. 2 in that an access circuit 8 is added. Hereinafter, the difference will be mainly explained, and the same point will be omitted.
[0093] The flag access circuit 8 is a hardware circuit that performs the work shown in FIG. 4 or FIG. 7 . That is, the access circuit 8 automatically generates a read signal for the address storing the test mode control code of the nonvolatile memory 1 after the reset signal is input, and writes it into the register 2 . After the writing of the test mode control code is finished, when the Hamming distance judging circuit 4 outputs a high level and the Hamming distance is 1 or more, that is, the test mode control code stored in the nonvolatile memory 1 When the Hamming distance from the test mode inhibit code is less than or equal to a predetermined number and the number of bits of the test mode ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com