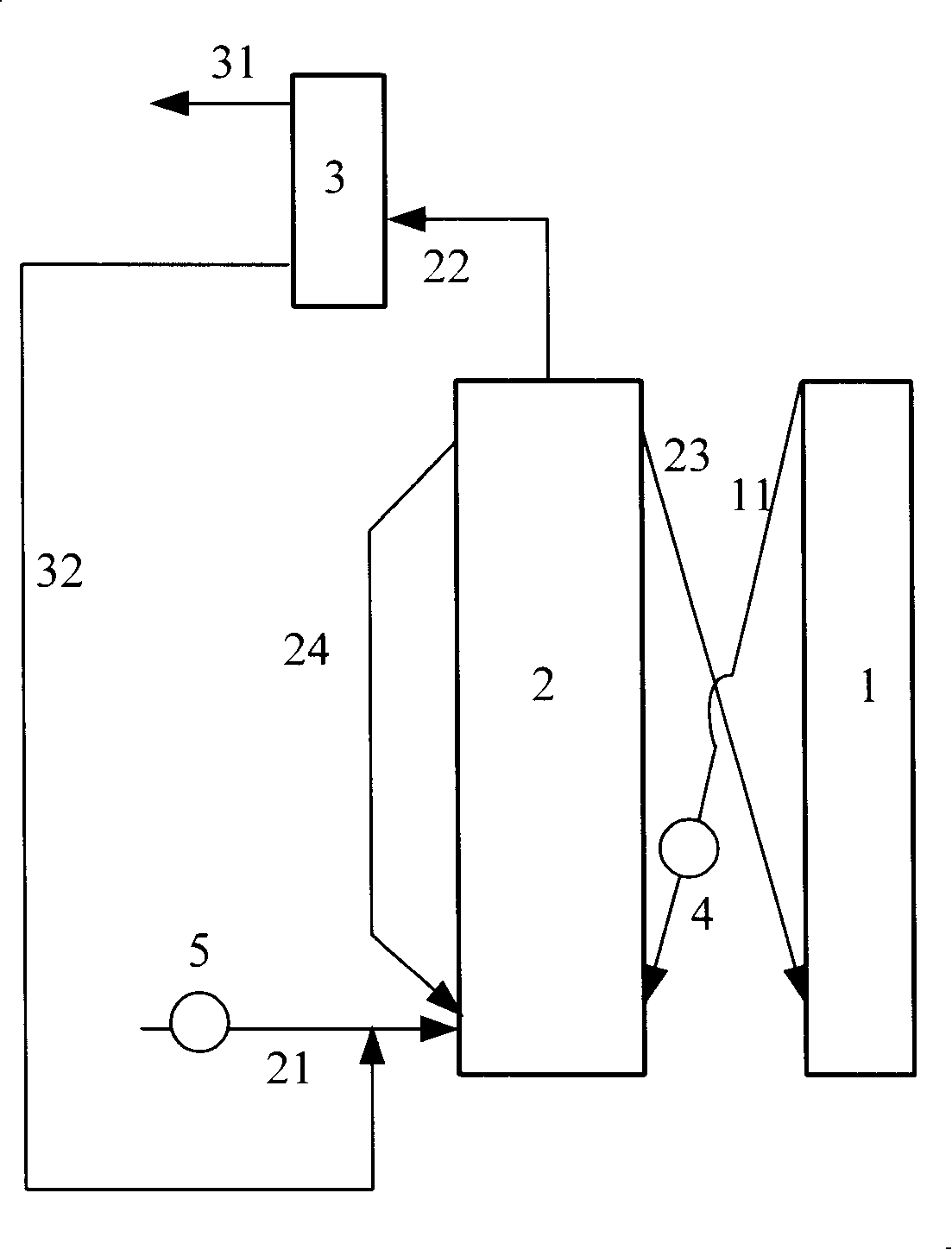
Method for producing dimethyl ether from methanol
A technology of dimethyl ether and methanol, which is applied in the field of gas-phase dehydration to produce dimethyl ether, and can solve problems such as difficult control of bed temperature
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] The code name of the catalyst used in this example is MTD-1 (containing 30% by weight of USY zeolite, 5% by weight of ZSM-5 zeolite, and the balance is carrier, all based on the total weight of the catalyst).
[0036] The gaseous methanol raw material enters the fluidized bed reactor and contacts with the MTD-1 catalyst. At a temperature of 280°C and a pressure (gauge pressure) of 0.1 MPa, the weight ratio of the catalyst to the methanol raw material (agent-alcohol ratio) is 2.5, and the weight hourly space velocity is 3.0h -1 Reaction under the condition of reacting, reactant flows through separation and obtains carbon deposition catalyst and product flow, and this product flow further separates and obtains target product dimethyl ether, and product distribution is as shown in table 2, and unreacted methyl alcohol returns fluidized bed reactor; The catalyst is divided into two parts, wherein 50% by weight of the carbon-deposited catalyst is sent to the regenerator for c...
Embodiment 2
[0039] The code name of the catalyst used in this example is MTD-2 (containing 35% by weight of USY zeolite, and the balance is a carrier, all based on the total weight of the catalyst)
[0040] The liquid methanol raw material enters the fluidized bed reactor and contacts with the MTD-2 catalyst. At a temperature of 380°C and a pressure (gauge pressure) of 0.1MPa, the weight ratio of the catalyst to the methanol raw material (agent-alcohol ratio) is 40, and the weight hourly space velocity is 50h -1 Reaction under the condition of condition, reactant flow obtains coke catalyst and product flow through separation, and this product flow further separates and obtains target product dimethyl ether, and product distribution is as shown in table 2, and excessive methyl alcohol returns fluidized bed reactor; Coke catalyst All go to the regenerator for scorched regeneration.
[0041] After all the carbon-deposited catalysts are regenerated, the regenerated catalysts are cooled to 410...
Embodiment 3
[0043] The code name of the catalyst used in this example is MTD-3 (containing 30% by weight of USY zeolite, 5% by weight of Beta zeolite, and the balance being carrier, all based on the total weight of the catalyst).
[0044] The liquid methanol raw material enters the fluidized bed reactor and contacts with the MTD-3 catalyst. At a temperature of 150°C and a pressure (gauge pressure) of 0.1MPa, the weight ratio of the catalyst to the methanol raw material (agent-alcohol ratio) is 6, and the weight hourly space velocity is 0.1h -1 Reaction under the condition of condition, reactant flow obtains coke catalyst and product flow through separation, and this product flow further separates and obtains target product dimethyl ether, and product distribution is as shown in table 2, and excessive methyl alcohol returns fluidized bed reactor; Coke catalyst It is divided into two parts, wherein 25% by weight of the carbon-deposited catalyst is sent to the regenerator for coke regeneratio...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com