Method for removing synchronous process of cheap magnetic disc redundant array apparatus
A technology of synchronization process and equipment, applied in the fields of instruments, electrical digital data processing, memory systems, etc., can solve the problems caused by users of synchronization operation, reduce the overall efficiency of the system, long synchronization operation time, etc., to achieve a clear life cycle, eliminate Synchronization process, the effect of eliminating confusion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0050] Regarding the features and implementation of the present invention, the preferred embodiments are described in detail below in conjunction with the drawings.
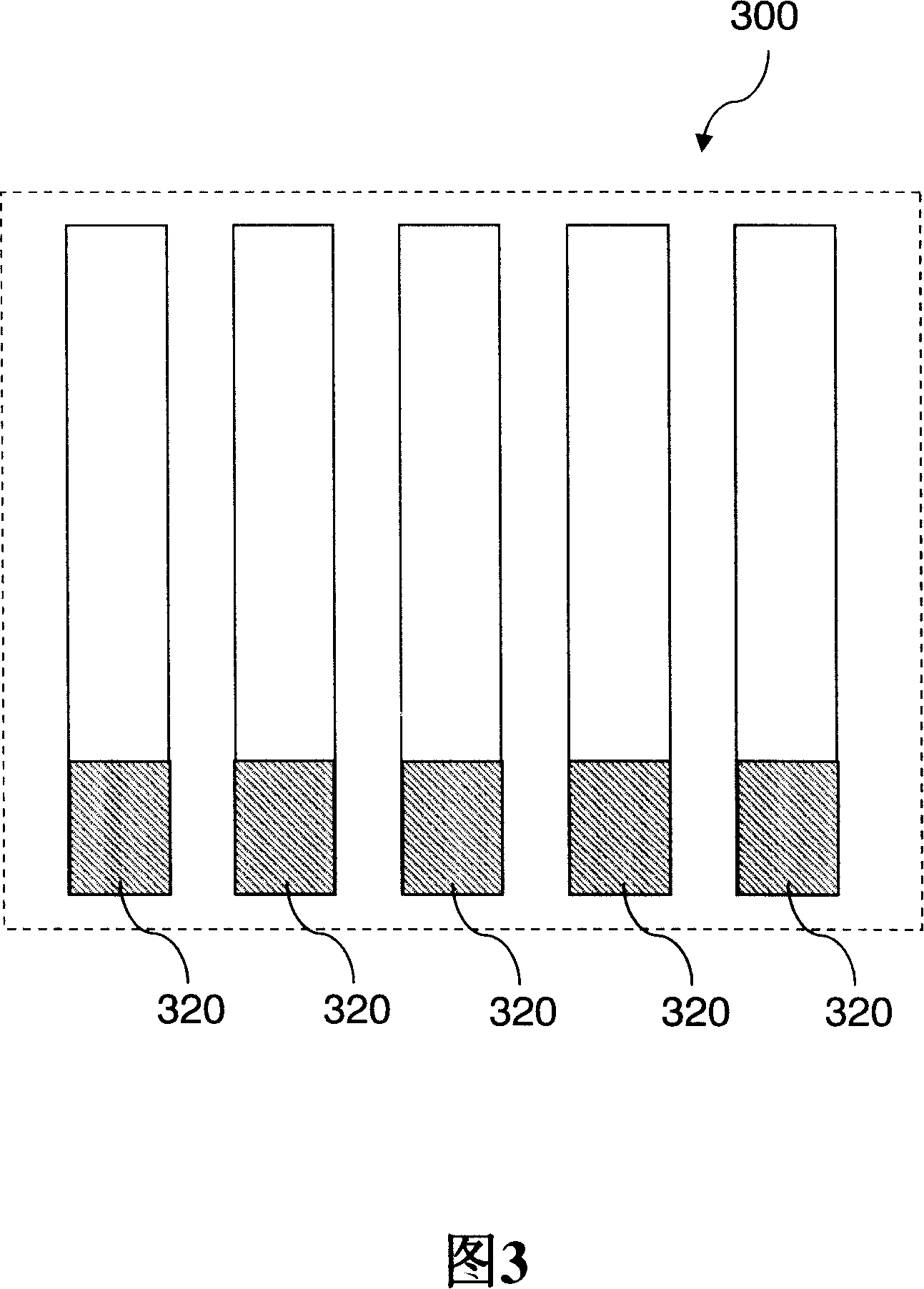
[0051] As shown in FIG. 3 , FIG. 3 is a block diagram of the data storage structure of the RAID device according to the present invention. As shown in the figure, the bitmap 320 is created in the RAID device 300 in a RAID-1 manner, that is, the bitmap 320 is located in each hard disk (hard disk 1, hard disk 2, hard disk 3, hard disk 4, and hard disk 5) of the RAID device 300 in a mirrored manner. ). Wherein, each bit of the bitmap 320 corresponds to each data block of the RAID device 300 . The size of the bitmap 320 is calculated by the following formula: size of the bitmap÷size of the RAID device=1÷(number of bytes of data blocks of the RAID device×8) (Formula 1). Assuming that the capacity of the RAID device 300 is 1T (ie, 1024×1024M), and the size of each data block is 64K, the size of the bitmap 320 is: 102...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com