Method for synthesizing lithium iron phosphate battery anode material by microwave
A technology of lithium iron phosphate and cathode material, which is applied in battery electrodes, chemical instruments and methods, circuits, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0007] (1) Preparation of precursors: Accurately weigh lithium salt, ferrous salt, phosphate and metal salt or carbon doping raw materials for doping according to the stoichiometric ratio, grind them in a mortar, and then put them into a Continue to grind in the mortar for 1 hour before use.
[0008] (2) A microwave reaction device that can provide a protective atmosphere: Dig a groove in the refractory material, put it into a heat conduction dish and fill the gap with a microwave absorbent, and put an appropriate amount of microwave air sealant in the heat conduction dish. Put the precursor into the reaction vessel, put the reaction vessel into the heat conduction vessel and cover it with the matching cover of the reaction vessel, which can cover the edge of the reaction vessel and contact the inner wall of the heat conduction vessel. Cover the lid of the reaction vessel with a microwave air sealant, and at this time turn the air seal vessel upside down on the heat-resistant ...
Embodiment 1
[0012] Using microwave reaction to form pure phase lithium iron phosphate
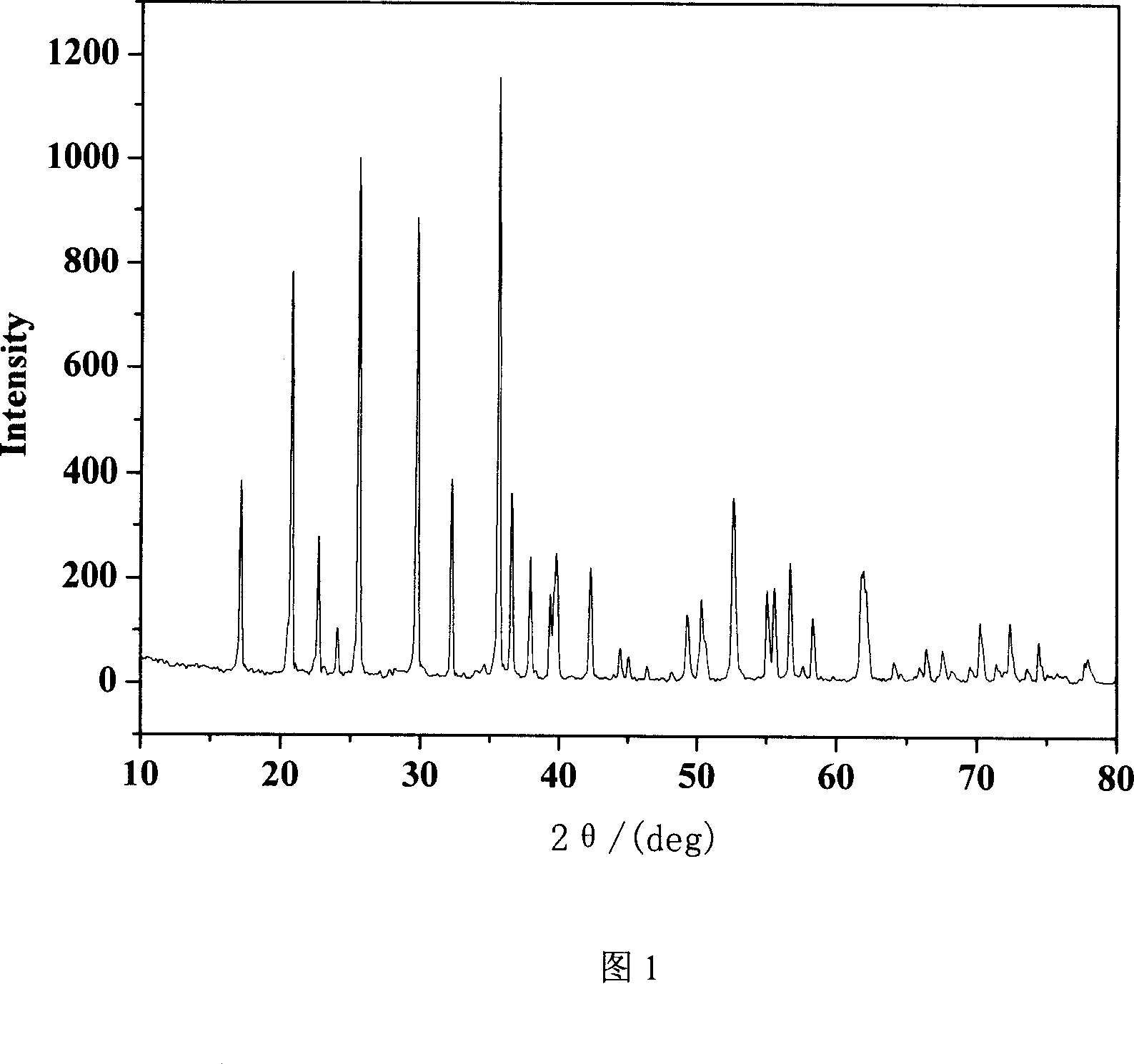
[0013] Accurately weigh lithium acetate, ferrous oxalate, and ammonium dihydrogen phosphate according to the stoichiometric ratio, grind them evenly in a mortar, place them in a reaction device, heat them in a household microwave oven for 15 minutes, and then use an X-ray diffractometer to determine the structure of the product. The XRD pattern of the product is consistent with the peak position of lithium iron phosphate (JCPDS No.40-1499), indicating that the product is lithium iron phosphate. The product was placed in hydrochloric acid with a concentration of 10M, and the solid was completely dissolved without precipitation, which proved that the final product contained no carbon. It is proved that pure-phase lithium ferrous phosphate can be obtained by adopting the method of the present invention, which overcomes the defect that carbonaceous materials must be mixed in the method for synthesizing lit...
Embodiment 2
[0015] Synthesis of Lithium Iron Phosphate Doped with Copper Ions by Microwave Reaction
[0016] Accurately weigh lithium acetate, ferrous oxalate, ammonium dihydrogen phosphate, and copper acetate according to the stoichiometric ratio, grind them evenly in a mortar, place them in a reaction device, heat them in a household microwave oven for 15 minutes, and then test the products with an X-ray diffractometer. Structure determination. The XRD pattern of the product is consistent with the peak position of lithium ferrous phosphate (JCPDS No.40-1499), and there is no impurity peak of copper ions, indicating that copper ions enter the crystal phase of lithium ferrous phosphate, and the doped and undoped products have the same Crystal structure.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com