Method for making optical fibre with low E-waveband and L-waveband loss wave peak
A wave band, optical fiber technology, applied in the field of optical fiber
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
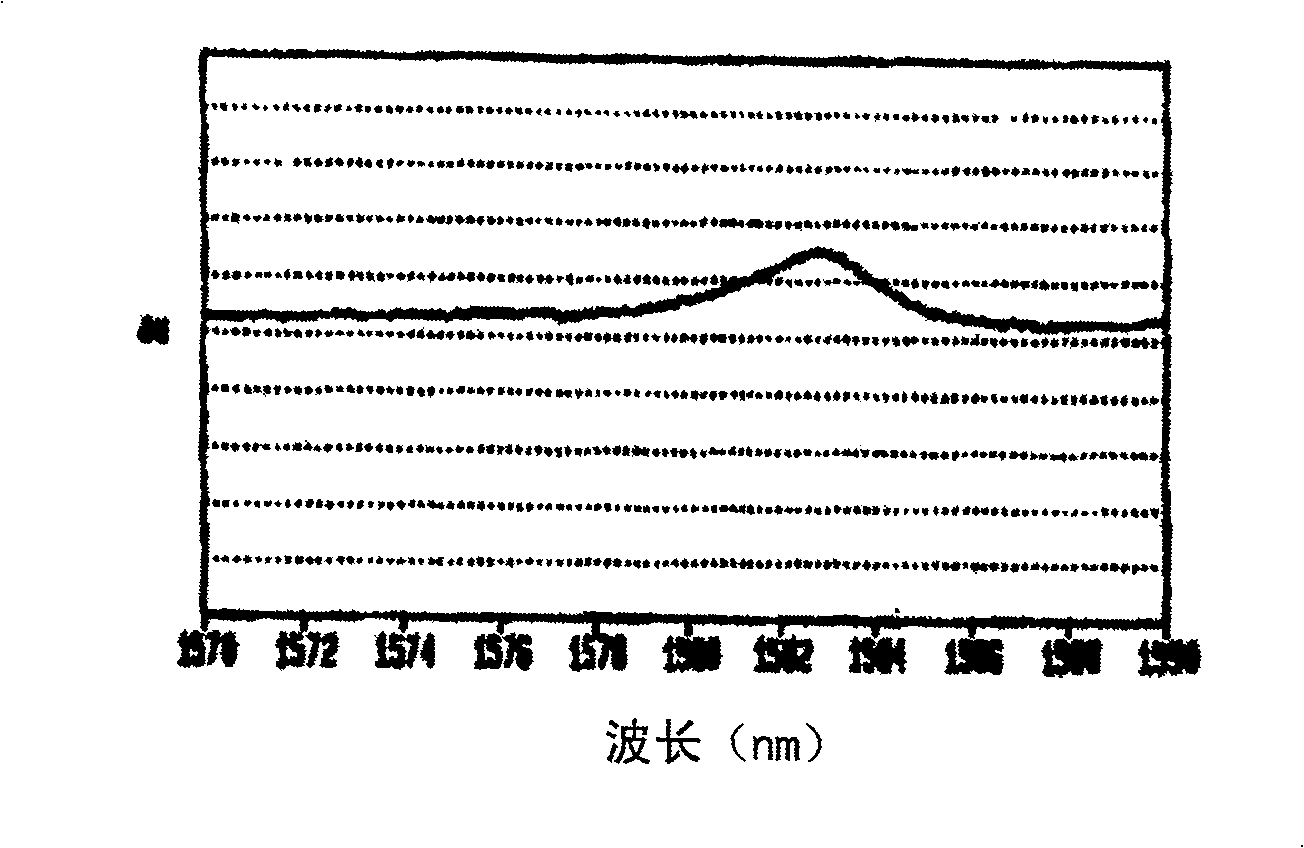
[0022] In the process of researching long-distance optical fiber transmission systems using light channels in the E-band (1360nm-1460nm) and L-band (1565nm-1625nm), the applicant found that there are previously unknown wavelengths at 1440nm, 1583nm and 1614nm. Known narrow and relatively small loss peak. figure 1 A typical loss peak at a wavelength of 1583nm is illustrated. The loss peaks at 1440nm and 1614nm are very similar in width and magnitude. Since these peaks are very narrow in width, they are difficult to be removed by gain equalizers in long-distance transmission systems. And while being relatively small, the loss is sufficient to cause signal dropouts in transmission channels of E-band and L-band long-distance DWDM optical fiber transmission systems. Applicants have further determined that these loss peaks are due to carbon contamination of the fiber.
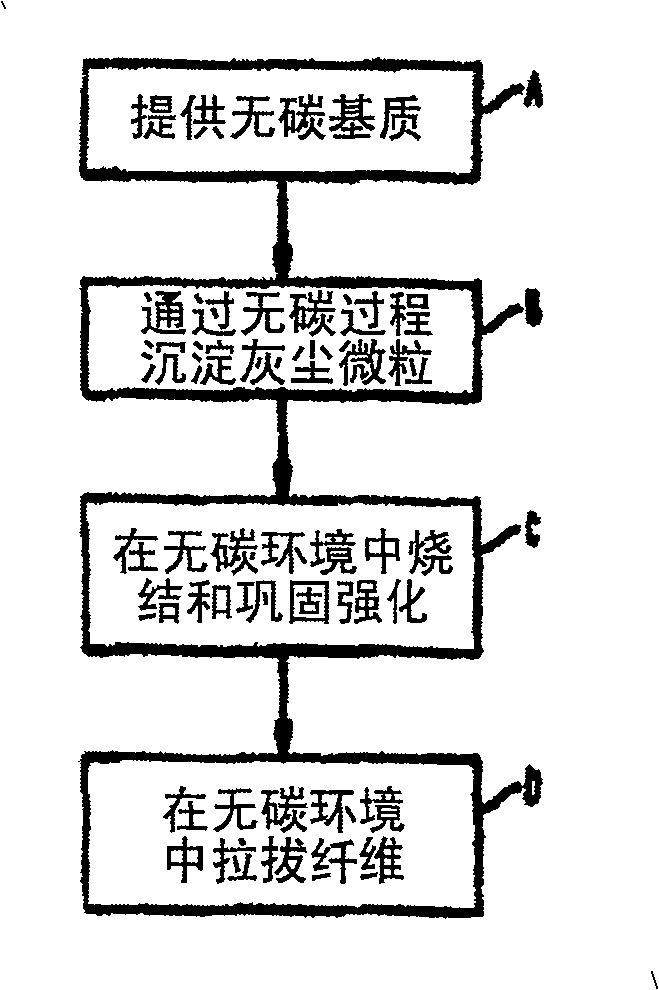
[0023] According to the present invention, optical fibers are manufactured by a process that strictly avoids ca...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com