Optical fibre with chromatic dispersion compensation
A dispersion compensating optical fiber and dispersion technology, which is applied to the required dispersion optical fiber, clad optical fiber, multi-layer core/clad optical fiber, etc., can solve the problems of ineffective compensation, low ratio of optical fiber dispersion and dispersion slope, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
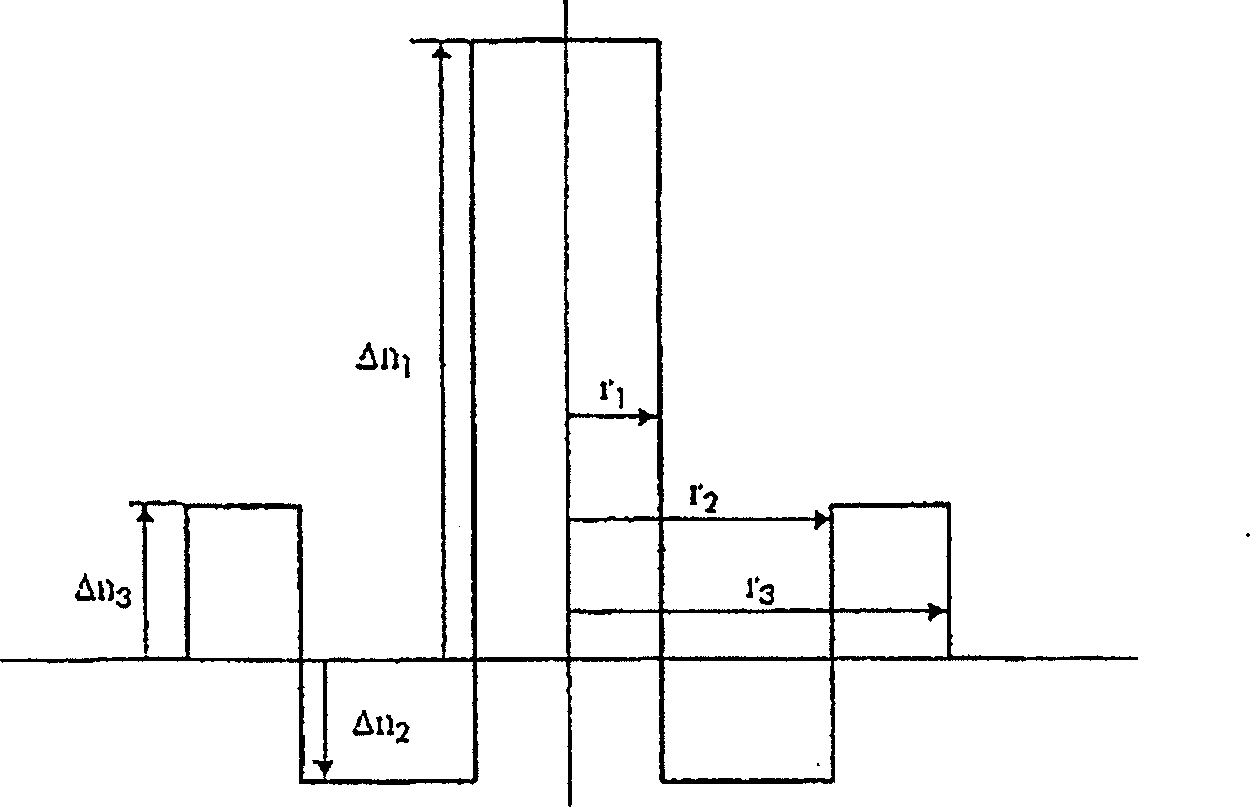
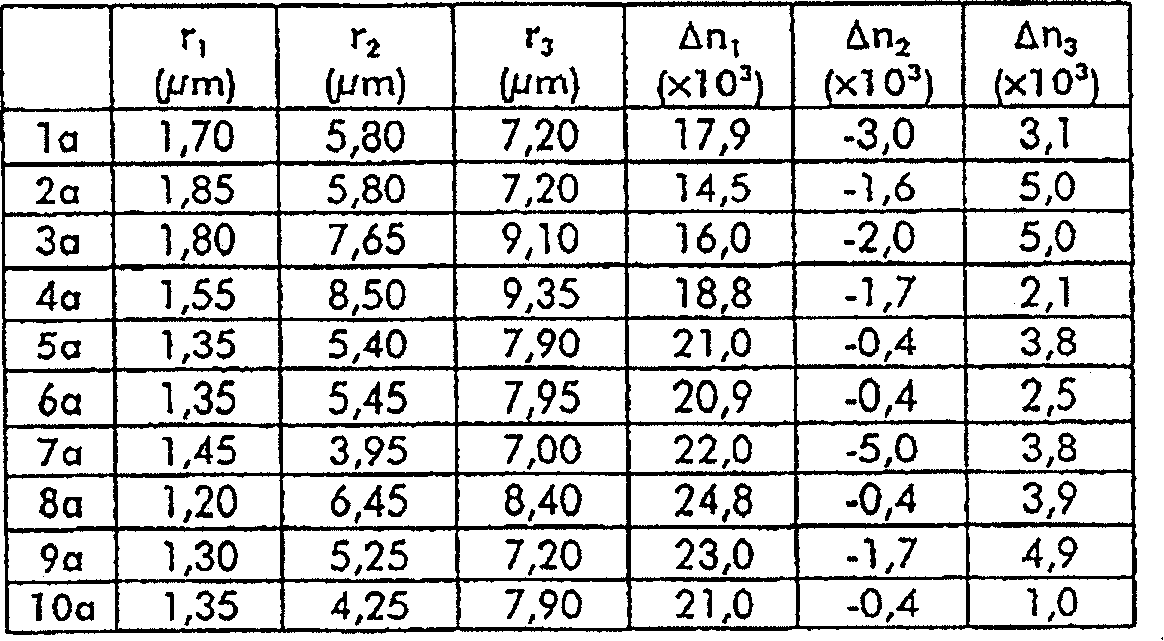
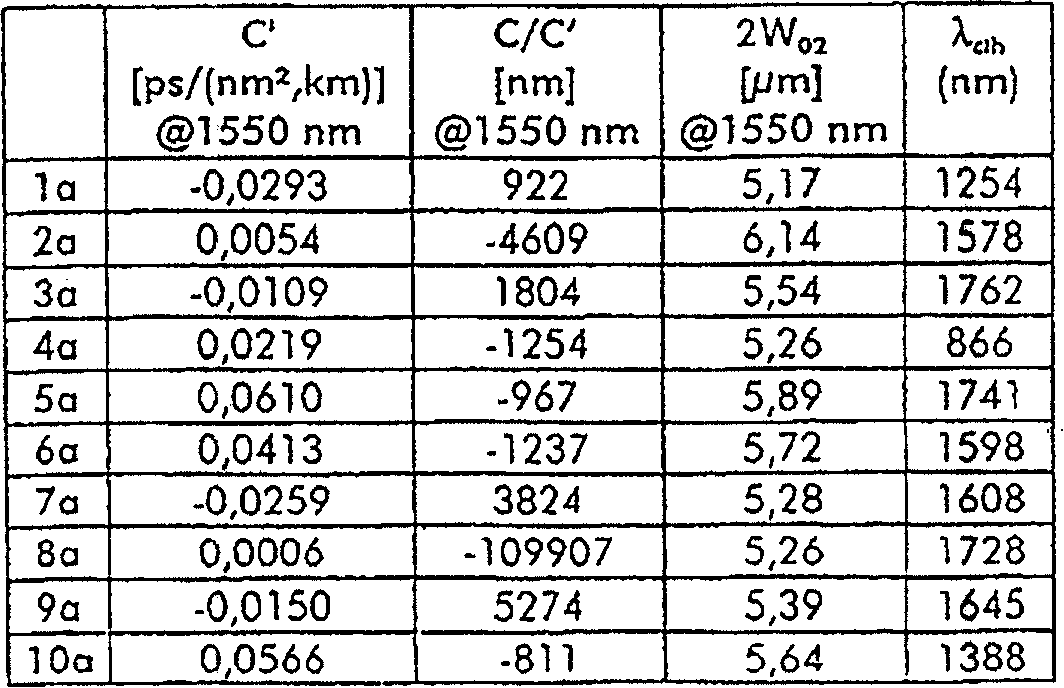
[0052] figure 1 An embodiment of a first type of profile having three layers of a dispersion compensating optical fiber according to the invention is schematically shown. The first layer, called the central layer, has a maximum refractive index difference Δn relative to the constant refractive index of the cladding 1 and the outer radius r 1 . The maximum refractive index difference Δn 1 is positive. The refractive index is preferably constant and is zero for radius with radius r 1 the maximum value between. The second layer, called the depressed layer, has a maximum refractive index difference Δn relative to the constant refractive index of the cladding 2 and the outer radius r 2 . The maximum refractive index difference Δn 2 is negative. The refractive index at radius r 1 with radius r 2 is preferably constant. The third layer, called the annular layer, has a maximum refractive index difference Δn relative to the constant refractive index of the cladding 3 and ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com