Process of Preparing mRNA-Loaded Lipid Nanoparticles
a technology of lipid nanoparticles and lipid nanoparticles, which is applied in the direction of transferases, peptide/protein ingredients, drug compositions, etc., can solve the problems of time-consuming, unpredictable, and expensive existing approaches, and achieve the effect of efficient in vivo delivery and potent protein expression
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
oparticle Formulation Process A
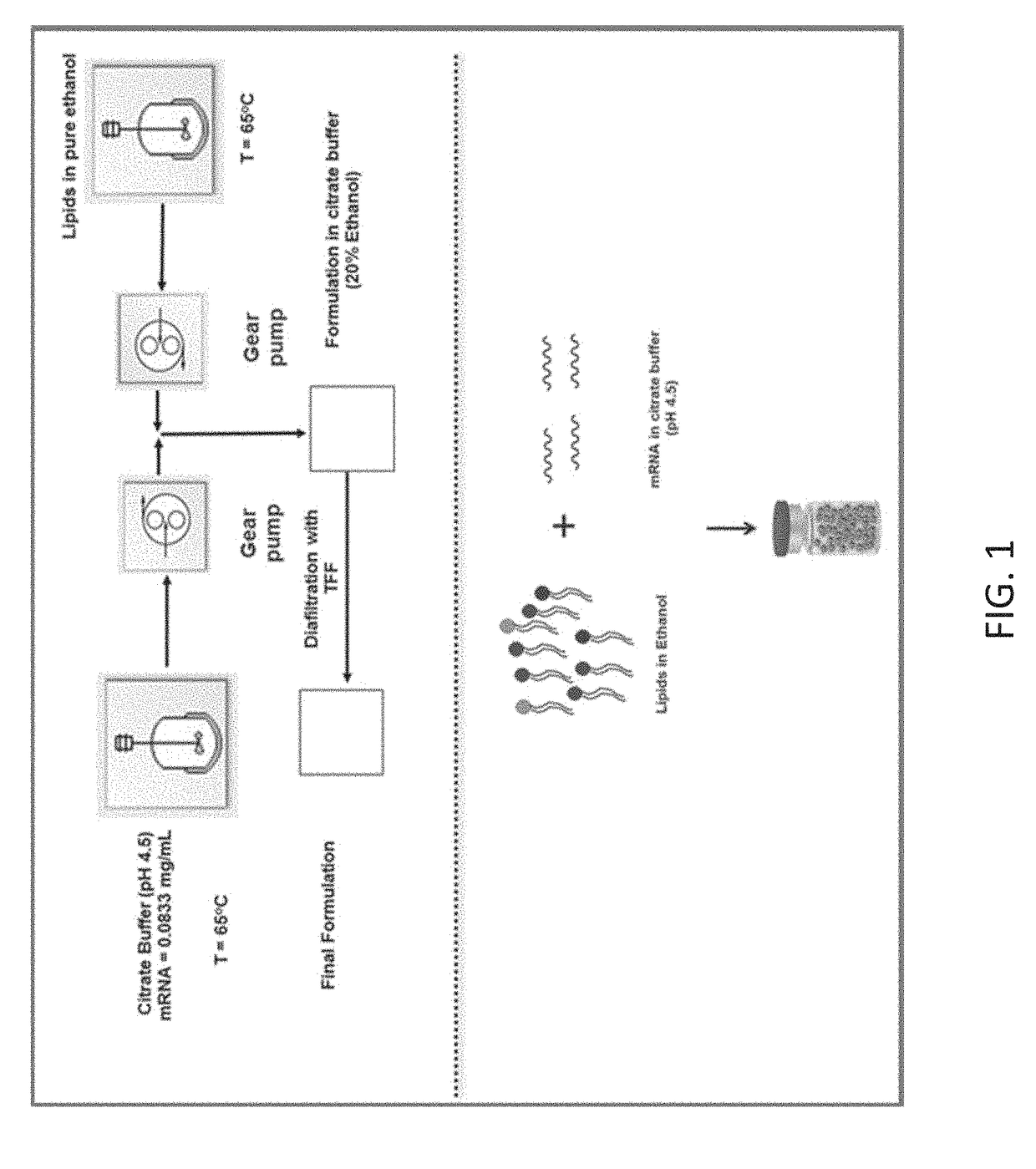
[0200]This example illustrates an exemplary lipid nanoparticle formulation process for encapsulating mRNA. As used herein, Process A refers to a conventional method of encapsulating mRNA by mixing mRNA with a mixture of lipids, without first pre-forming the lipids into lipid nanoparticles. As compared to Process B described below, Process A does not involve pre-formation of lipid nanoparticles.
[0201]An exemplary formulation Process A is shown in FIG. 1. In this process, in some embodiments, the ethanol lipid solution and the aqueous buffered solution of mRNA were prepared separately. A solution of mixture of lipids (cationic lipid, helper lipids, zwitterionic lipids, PEG lipids etc.) was prepared by dissolving lipids in ethanol. The mRNA solution was prepared by dissolving the mRNA in citrate buffer, resulting in mRNA at a concentration of 0.0833 mg / ml in citrate buffer with a pH of 4.5. As shown in FIG. 1, the mixtures were then both heated to 65° C. ...
example 2
oparticle Formulation Process B with Pre-Formed Lipid Nanoparticles
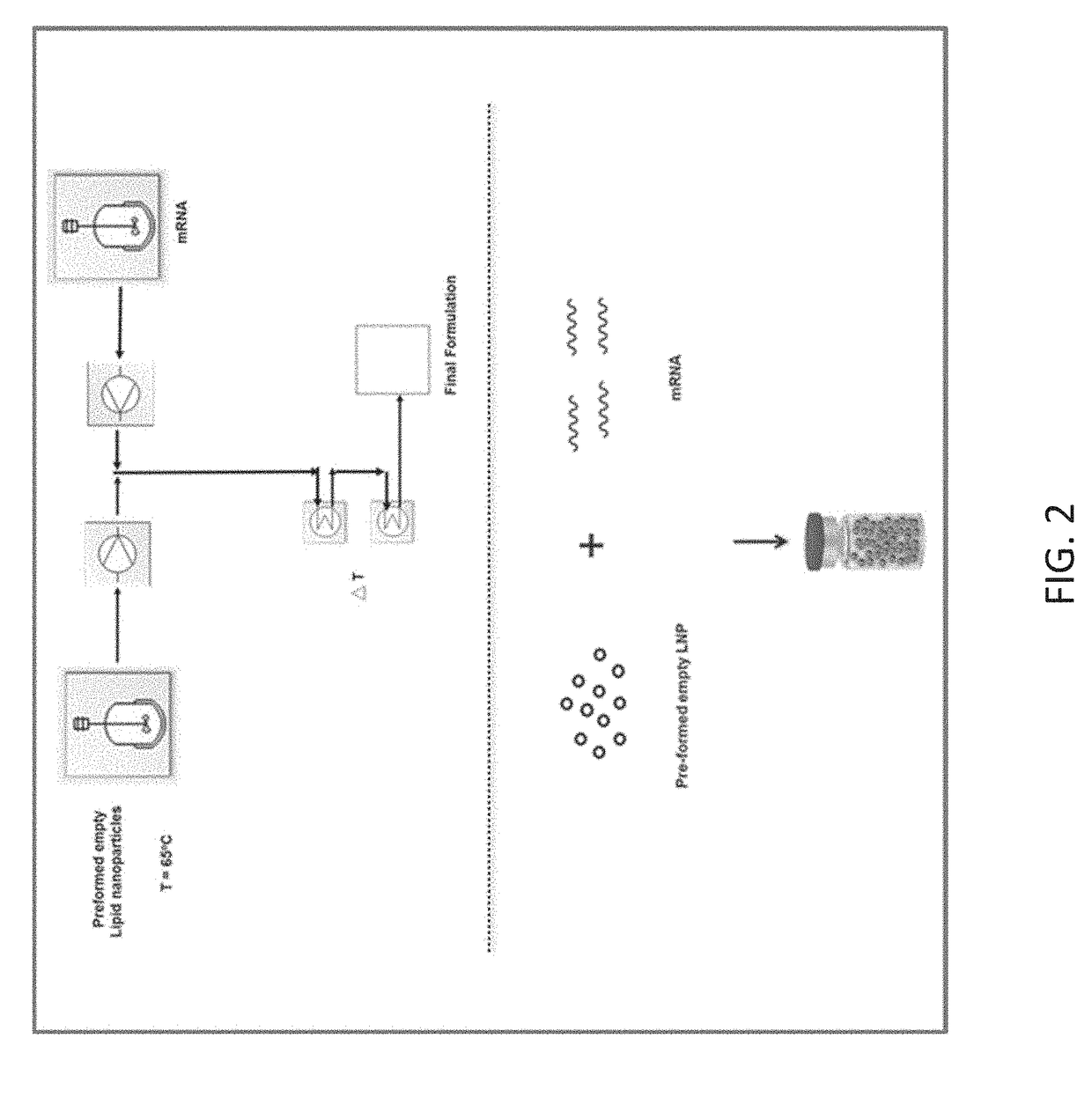
[0202]This example illustrates an exemplary Process B for encapsulating mRNA. As used herein, Process B refers to a process of encapsulating messenger RNA (mRNA) by mixing pre-formed lipid nanoparticles with mRNA. A range of different conditions, such as varying temperatures (i.e., heating or not heating the mixture), buffers, and concentrations, may be employed in Process B. The exemplary conditions described in this and other examples are for illustration purposes only.
[0203]An exemplary formulation Process B is shown in FIG. 2. In this process, in some embodiments, lipids dissolved in ethanol and citrate buffer were mixed using a pump system. The instantaneous mixing of the two streams resulted in the formation of empty lipid nanoparticles, which was a self-assembly process. The resultant formulation mixture was empty lipid nanoparticles in citrate buffer containing alcohol. The formulation was then subjected to a...
example 5
ASS1 Expression in 293T Cells
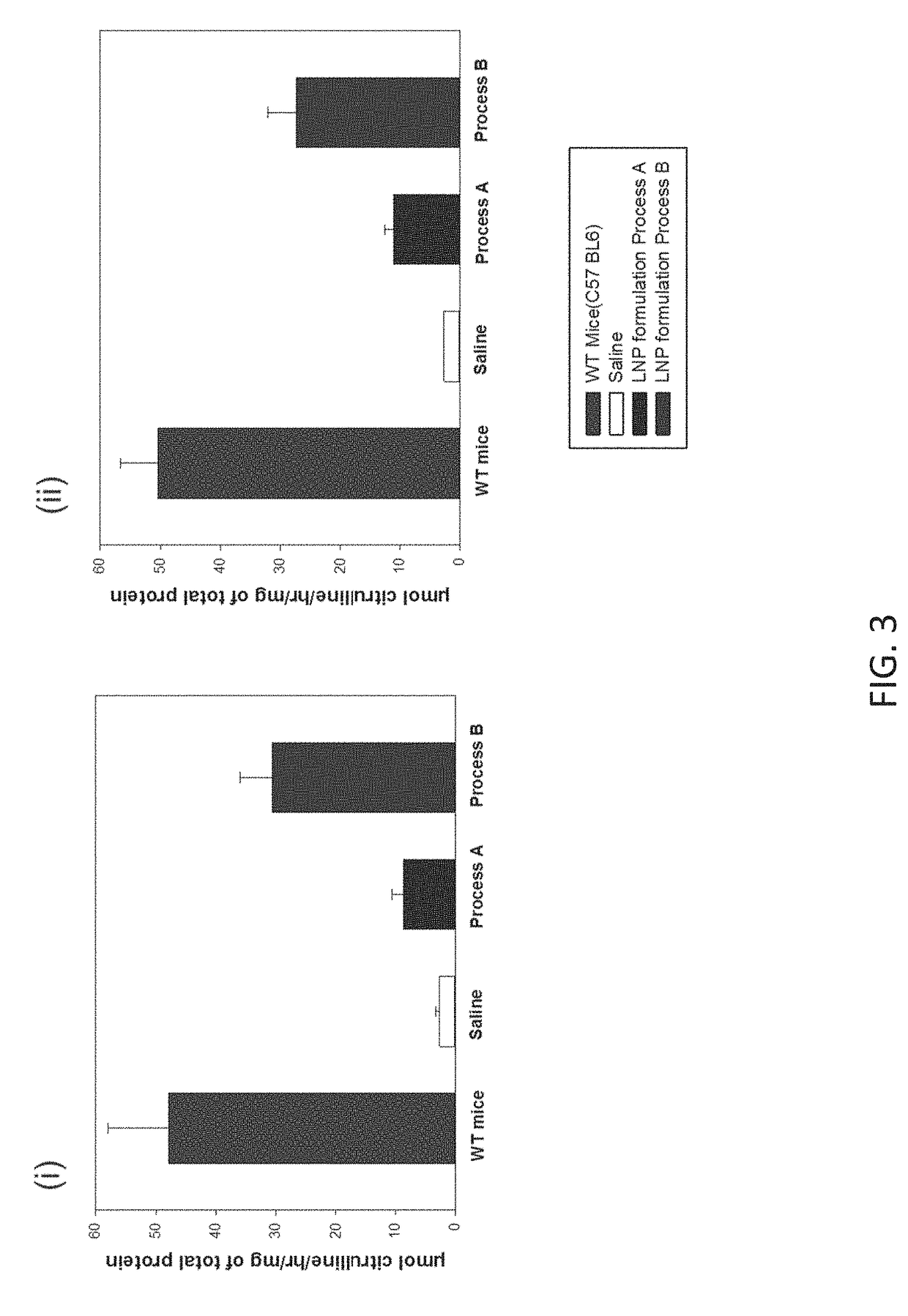
[0217]This example illustrates that the lipid nanoparticles prepared by Process B resulted in unexpectedly high protein expression in transfected cells.
[0218]FIG. 5 depicts exemplary human ASS1 protein expression in 293T cells 16 hours post-transfection with either naked hASS1 mRNA (with lipofectamine) or hASS1 mRNA-encapsulated lipid nanoparticles (without lipofectamine) produced by Process A or Process B.
[0219]In this example, 293T cells were transfected with ASS1 mRNA lipid nanoparticle formulations prepared by Process A or by Process B. Either 1 μg of ASS1 mRNA was transfected using lipofectamine or 10 μg of ASS1 mRNA encapsulated in lipid nanoparticle formulations were transfected per 106 cells for 24 hours. ASS1 protein expression was determined by ELISA.
[0220]As shown in FIG. 5, the lipid nanoparticle formulation prepared by Process B lead to much higher levels of ASS1 protein expression than the formulation prepared by Process A. The levels of AS...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com