Highly flexible stent
a stent and flexible technology, applied in the field of high-flexible stents, can solve the problems of inability to adapt to the needs of patients, lack of flexibility of the structure, and inability to inhibit the flow of liquid, so as to achieve high flexibility and suppress the amount of deformation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
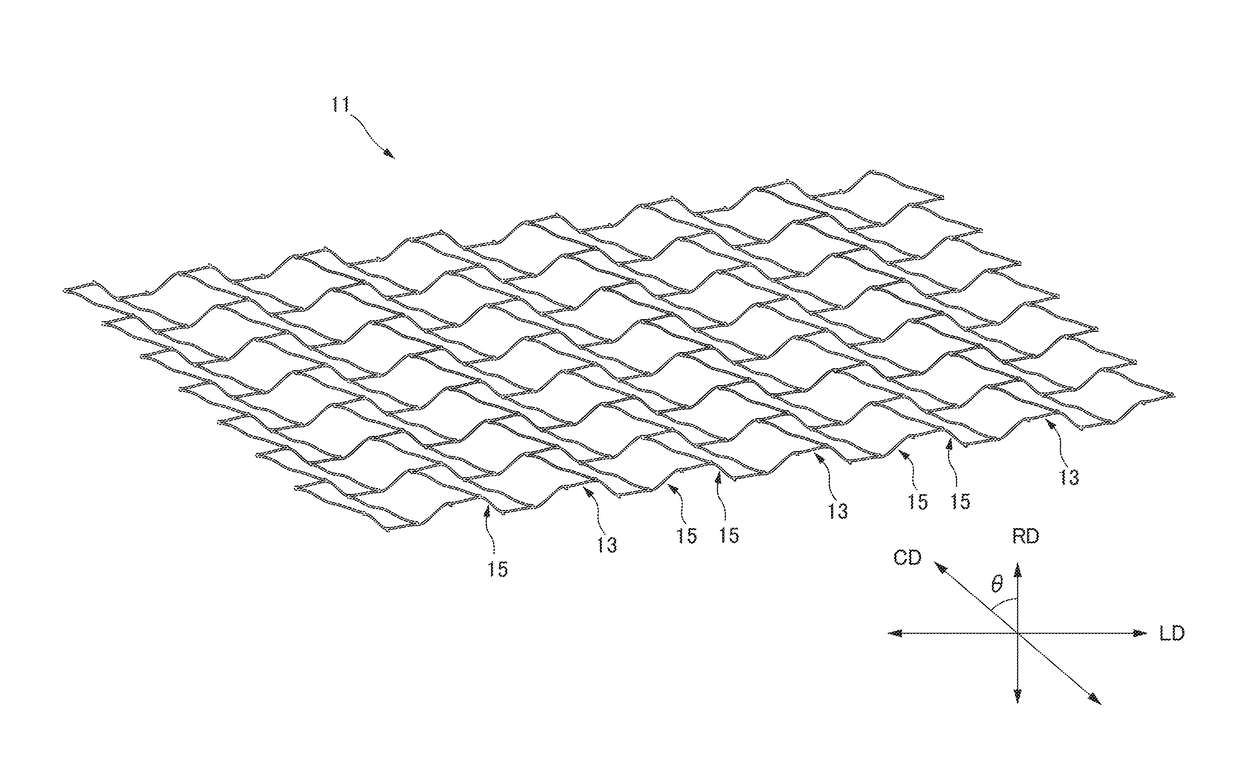
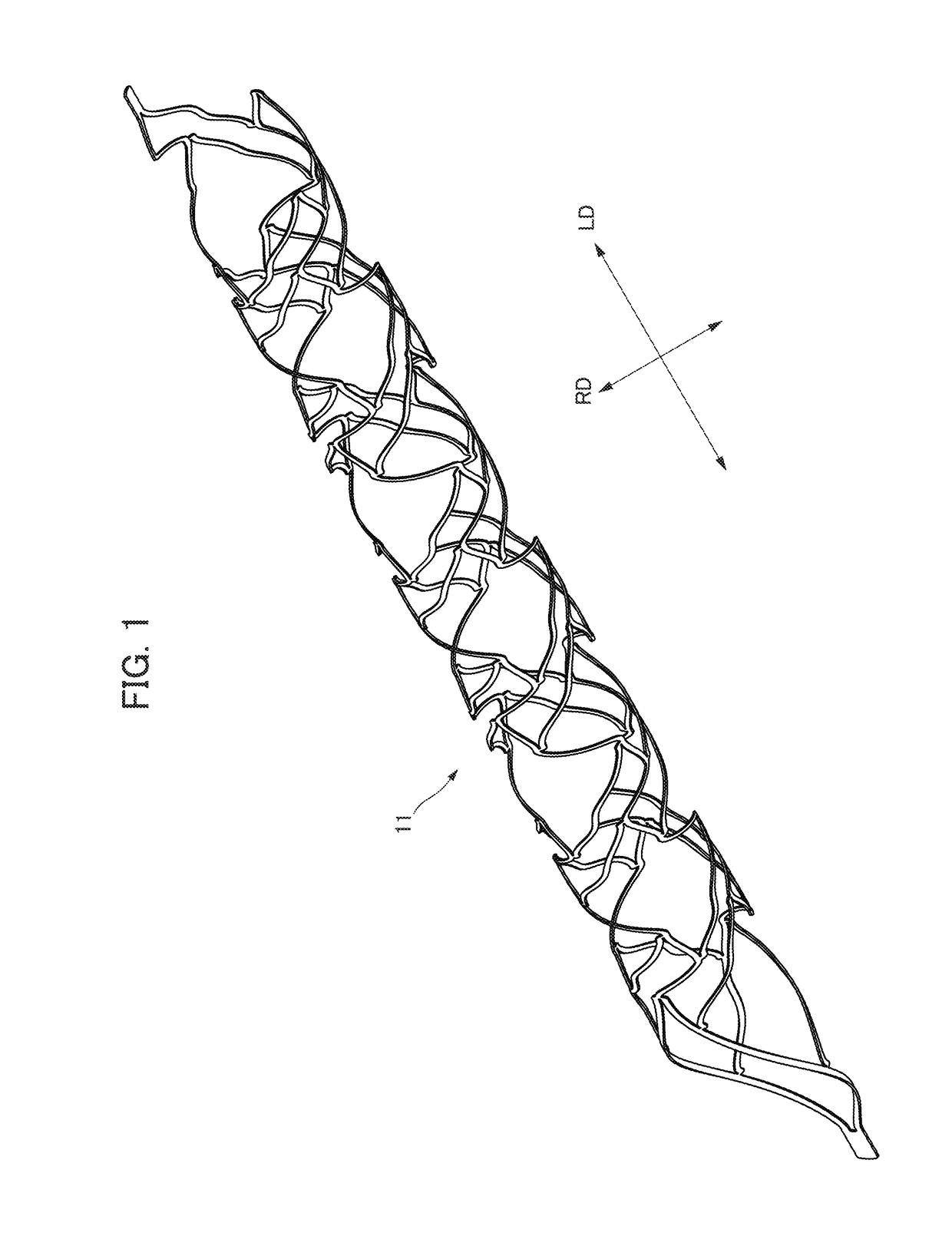
[0115]FIG. 11A shows a central axis of a cross section of the stent and a side view of a blood vessel. FIG. 11B is a schematic view of a cross section of the stent where the central axis is not displaced. FIG. 11C is a schematic view of a cross section of the stent where the central axis is displaced. FIG. 12 is a schematic view showing a malapposition. FIG. 13 is a schematic view of a developed view of a highly flexible stent in an unloaded state according to the present invention. FIG. 14 is a schematic view showing the behavior of a coiled element and the center of the figure when the stent shown in FIG. 13 is bent. FIG. 15 is a schematic view showing a behavior of the center of the figure of a cross section of the stent bent. FIG. 16 is a schematic view showing a behavior in a case in which a distortion in a right-hand direction is applied to the stent shown in FIG. 13. FIG. 17 is a schematic view showing a behavior in a case in which a distortion in a left-hand direction is app...
second embodiment
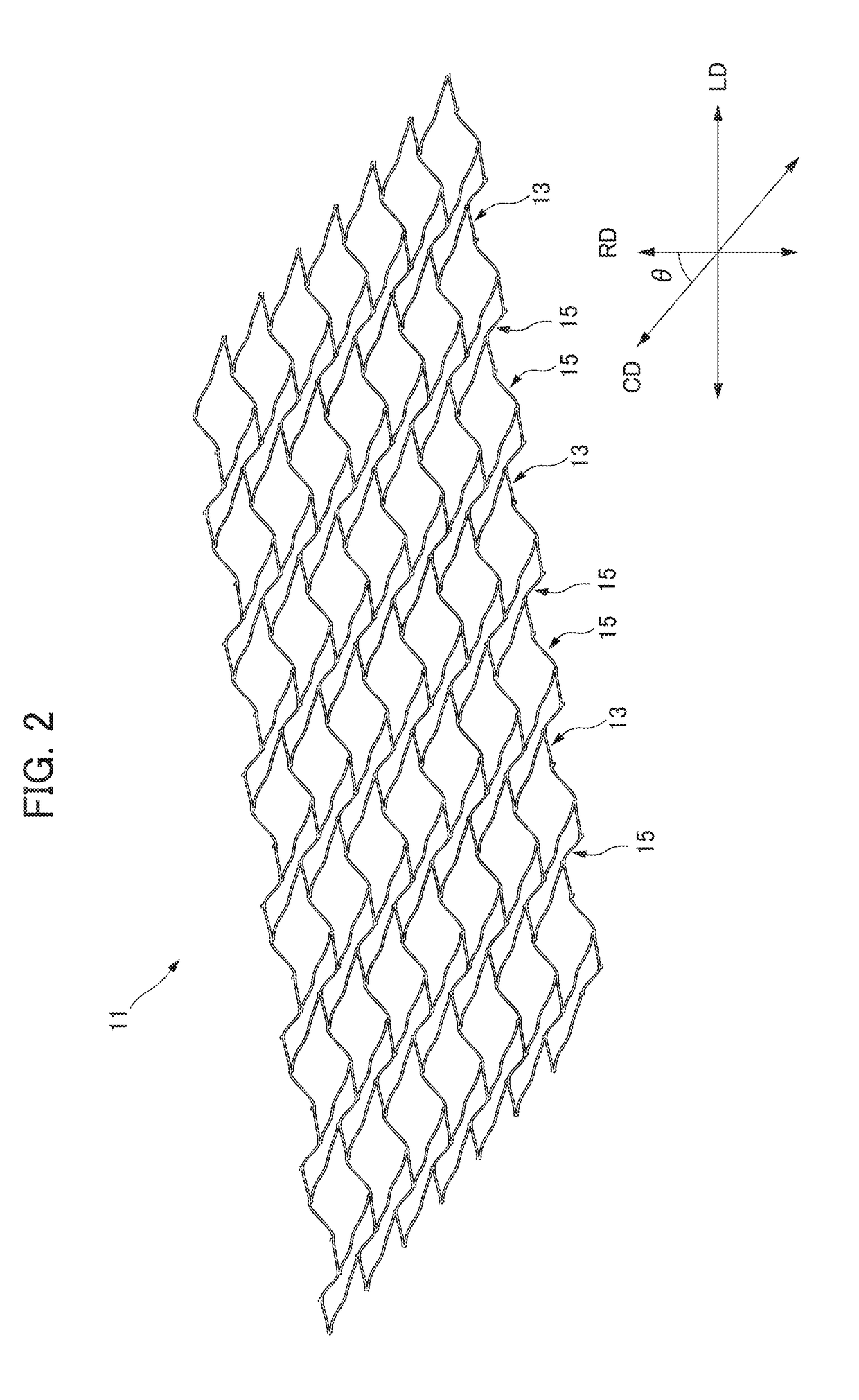
[0143]The stent 11A has a single spiral structure. As shown in FIG. 21, the single spiral structure is a structure in which there is a single spiral L28 between the joining points Δ (triangle) in the reference line L20 extending in the radial direction RD. The wavy-line pattern of a circular body 13 is a zigzagged shape. A virtual line L29 passing through a plurality of apices 17b on the same side of the zigzagged shape is linear.
[0144]It should be noted that the stent 11A according to the second embodiment shown in FIG. 21 and the stent 11 according to the first embodiment shown in FIG. 2 are in a mirror image relationship in the axial direction LD. X(1), X(2), X(3), and X(4) in FIG. 21 are used for explaining modified examples described later.
[0145]In the stent 11 according to the first embodiment shown in FIG. 2 and the stent 11A according to the second embodiment shown in FIG. 21, the wavy-line pattern body 13 forms a circular body. On the other hand, in the present invention, ...
fourth embodiment
[0156]FIG. 30 is a developed view showing a stent 11C according to the present invention to be virtually expanded into a plane.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com