Systems and Methods for Switch-Controlled VAR Sources Coupled to a Power Grid
a technology of switch-controlled var sources and power grids, applied in adaptive control, process and machine control, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of high complexity and high cost of systems to implement improved effective voltage control, limited switching speed and life of electromechanical switches, and reduce semiconductor device conduction losses, reduce switching stress on relays, and prevent infighting
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
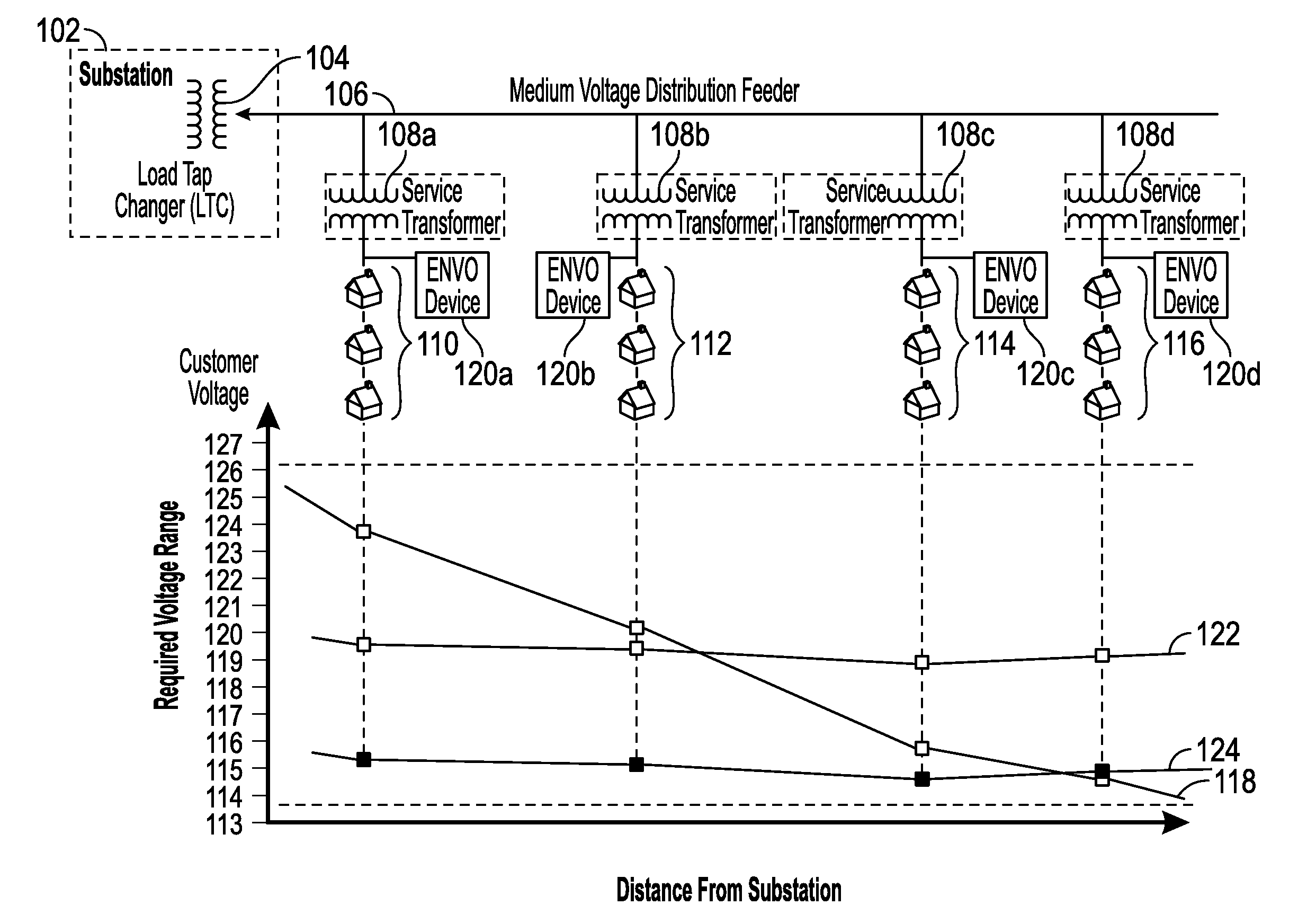
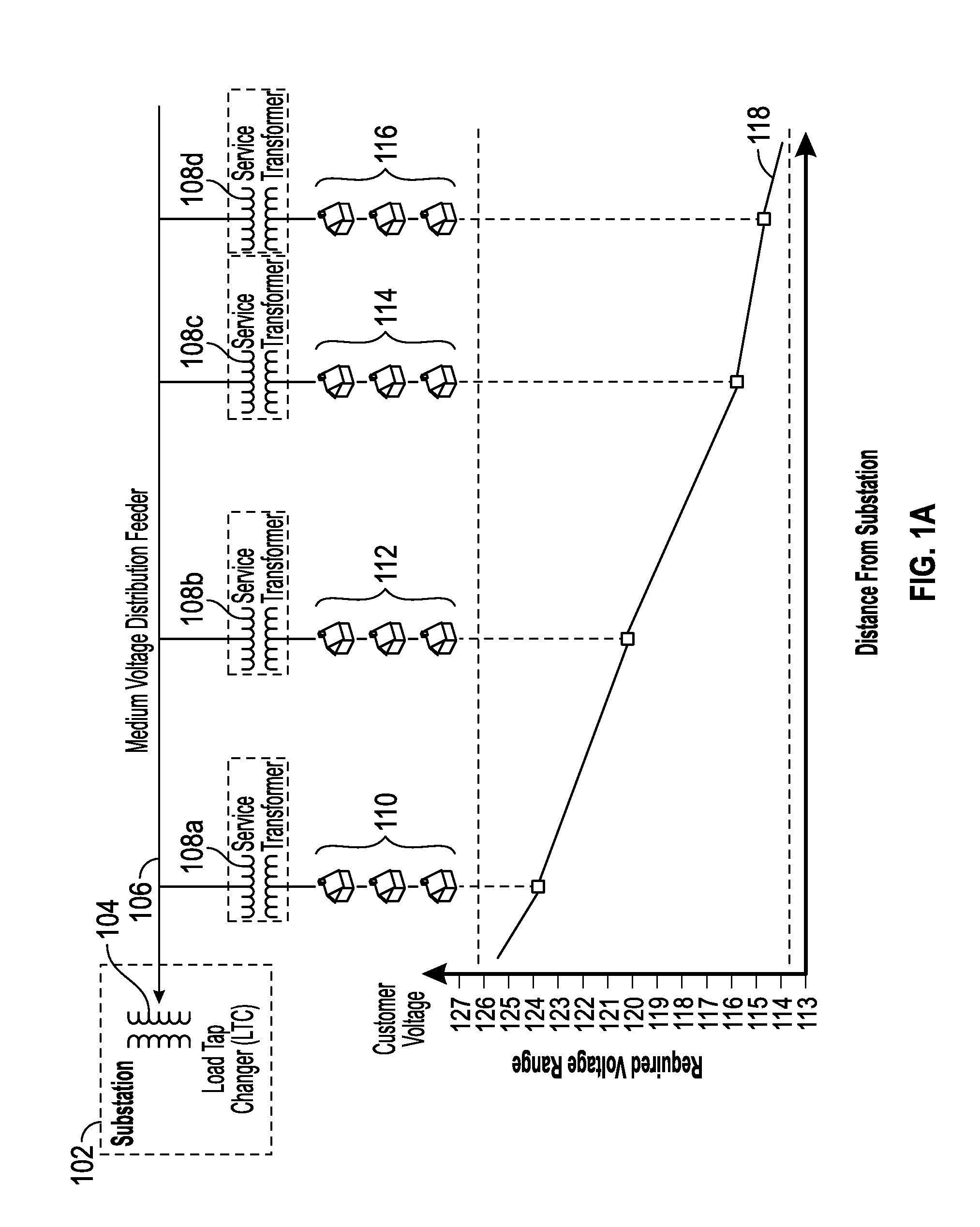
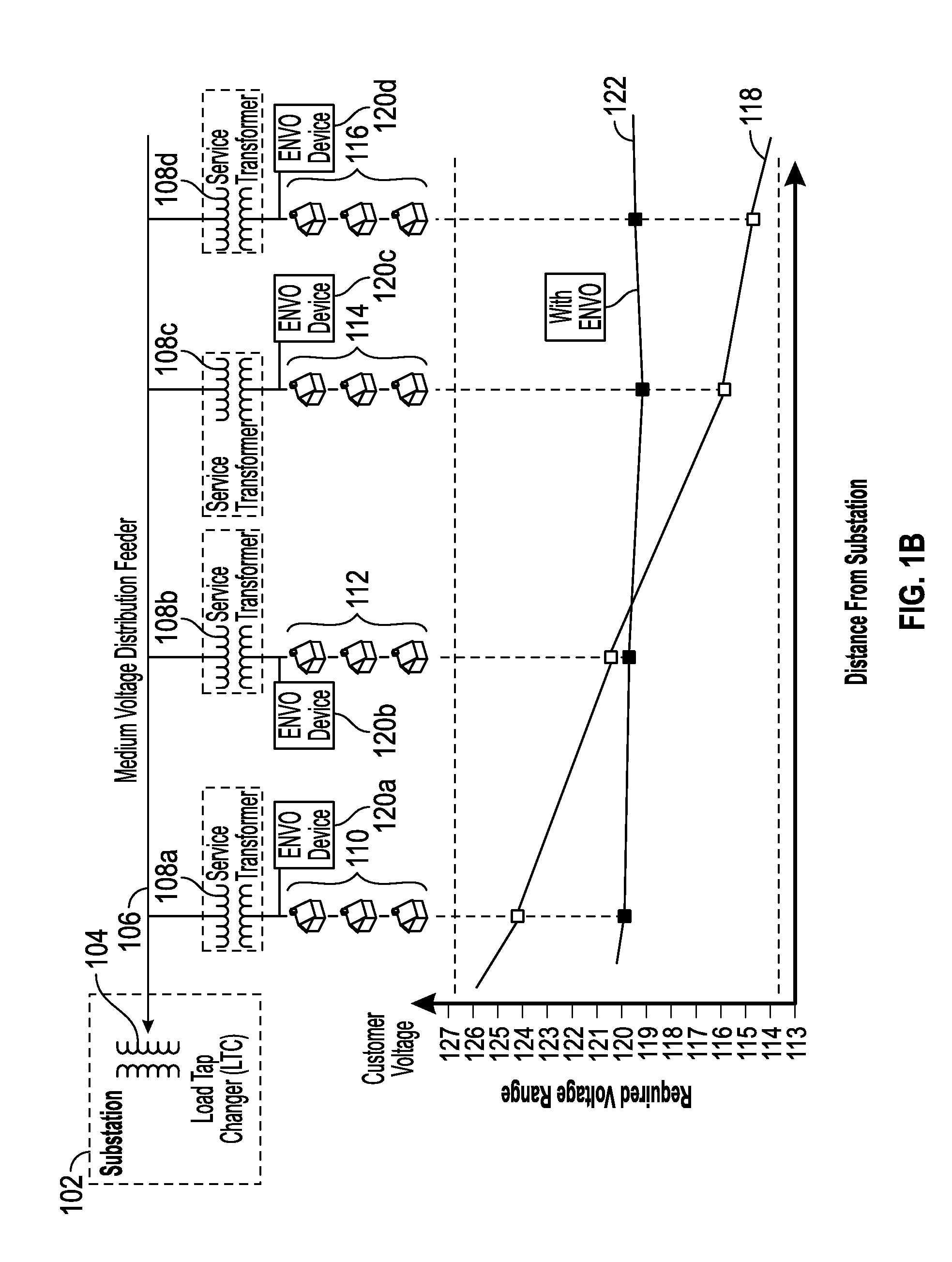
[0065]New requirements for distribution dynamic voltage control are emerging, driven by distribution renewable energy penetration and the need to increase grid capacity without building new lines or infrastructure. Applications such as Conservation Voltage Reduction (CVR) and Volt VAR Optimization (VVO) promise 3-5% increase in system capacity, simply by lowering and flattening the voltage profile along a distribution grid. To achieve CVR and VVO in the prior art, improvements to the power grid are slow in operation, difficult to model due to increased complexity of the overall system, require considerable back end infrastructure (e.g., modeling, and a centralized, computation and communication facility), are expensive to install in sufficient numbers to improve performance, and difficult to maintain. Further, conventional VVO schemes realize poor voltage regulation due to few control elements and poor granular response.
[0066]In various embodiments discussed herein, line voltage may...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com