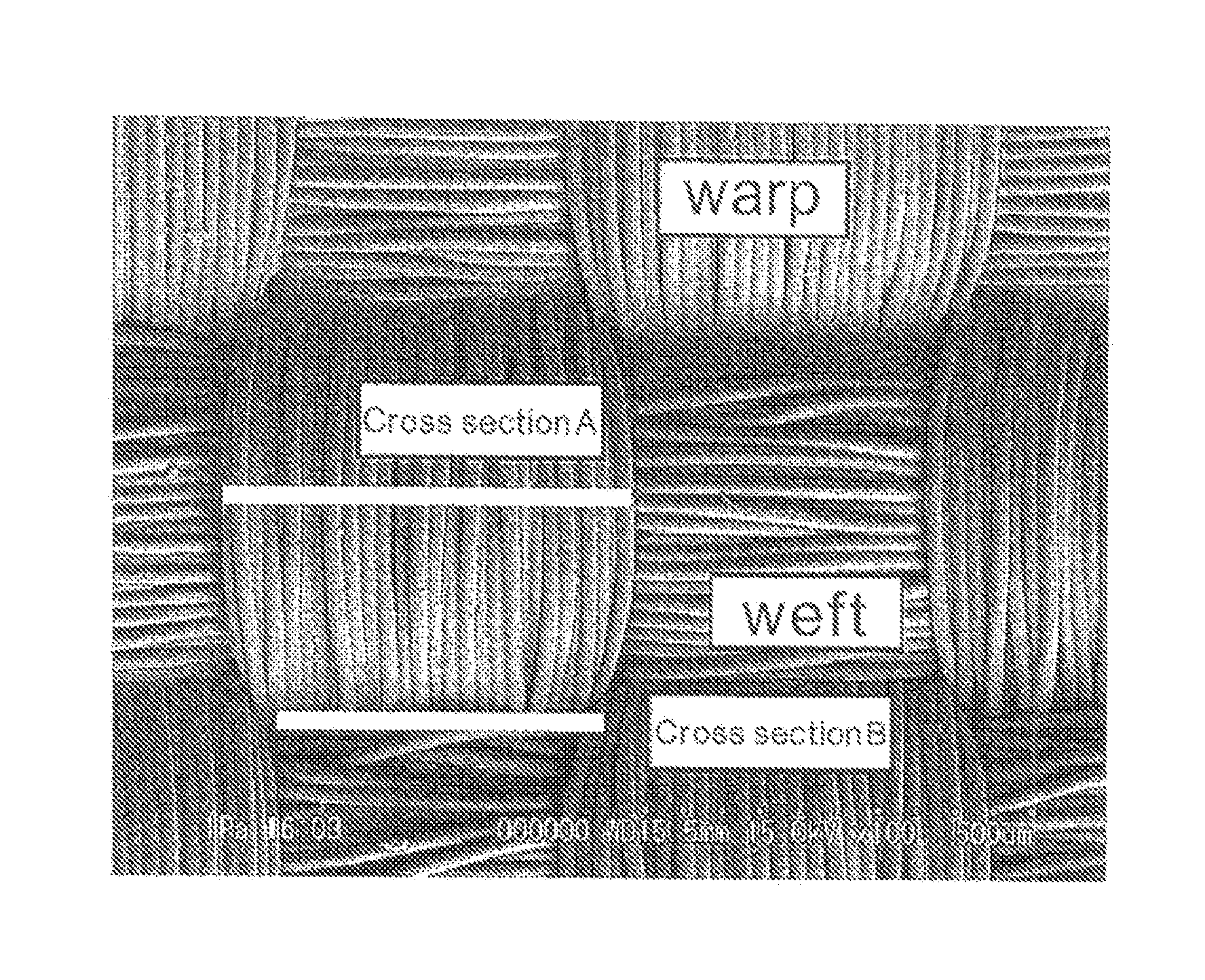
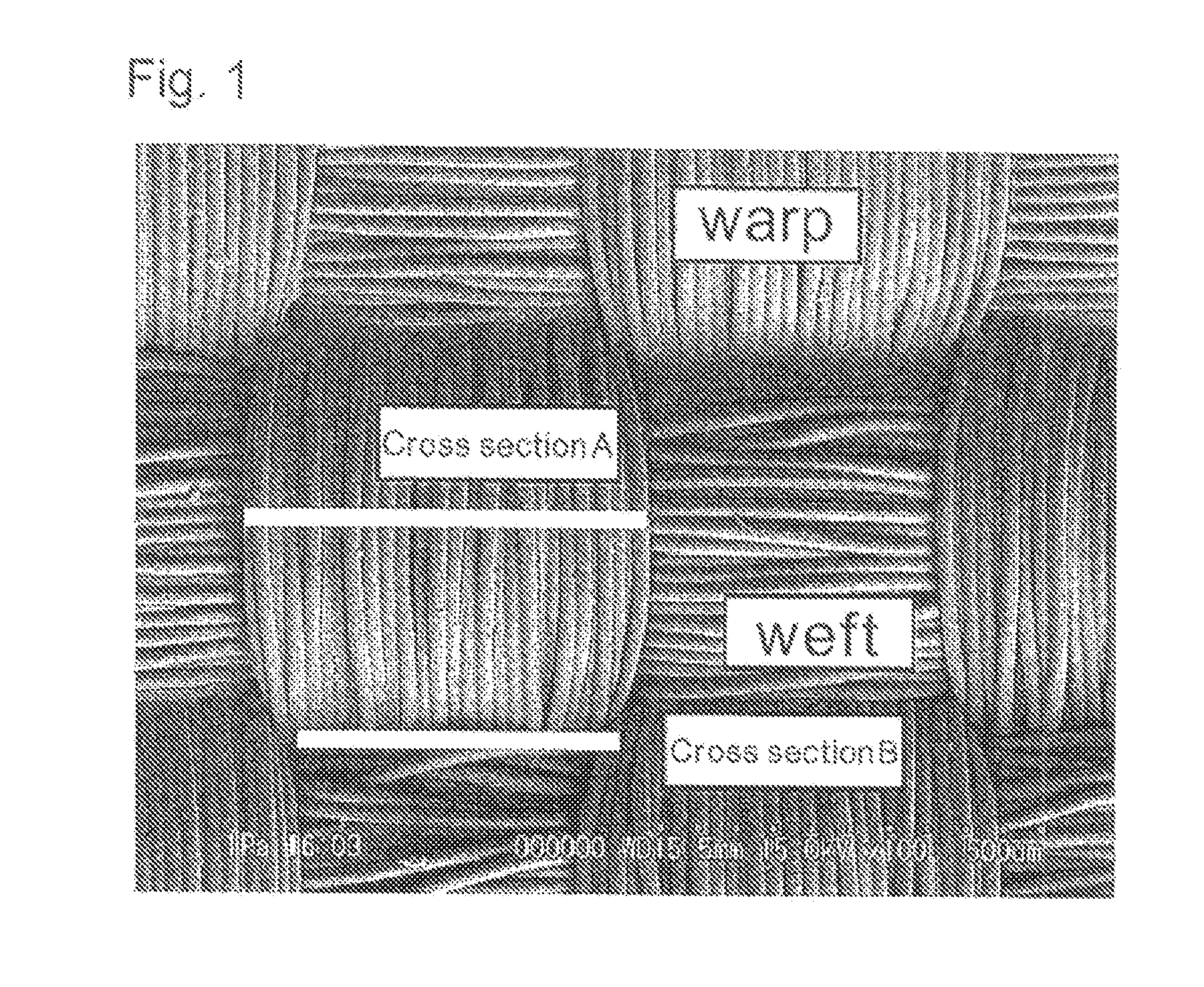
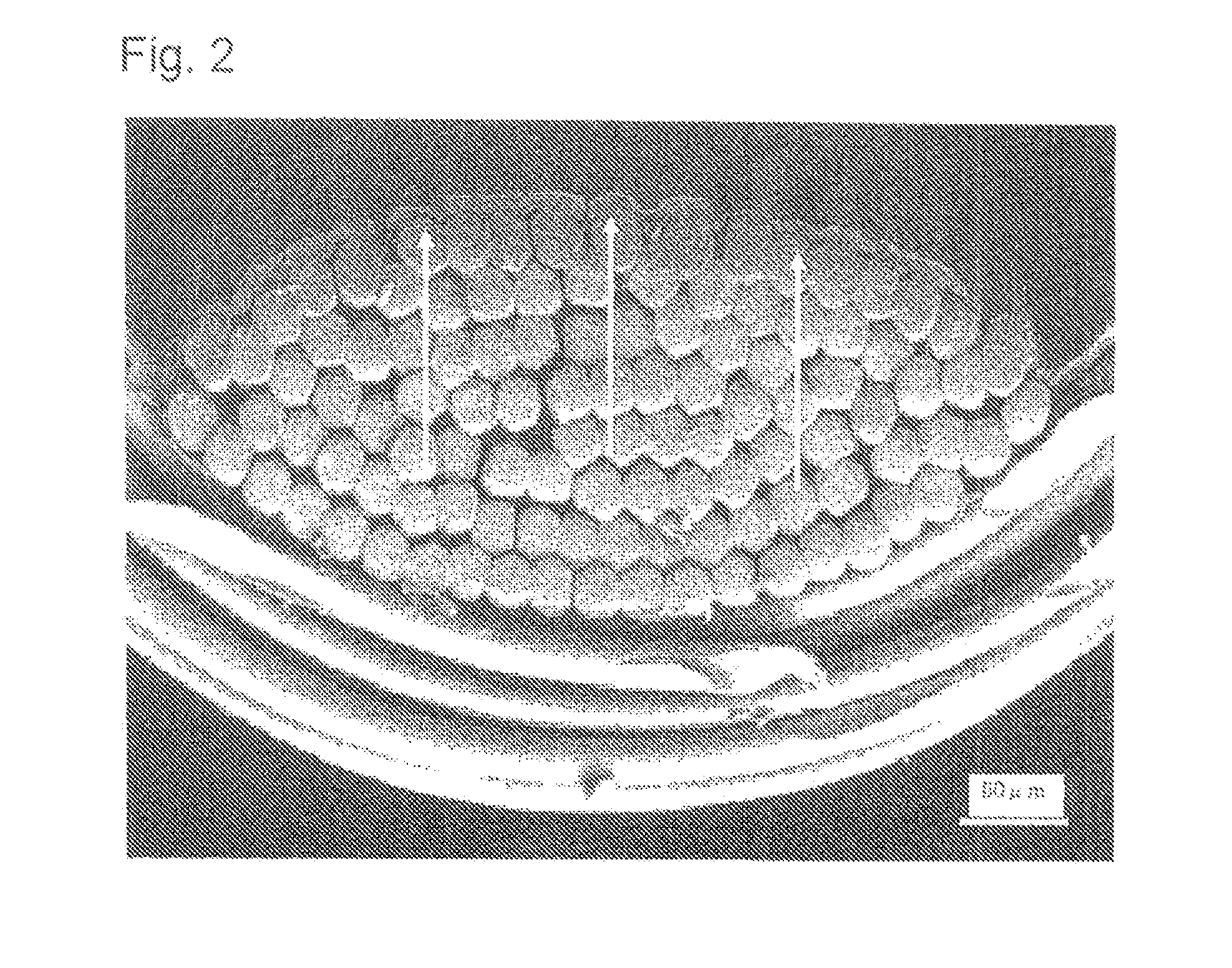
Woven fabric for airbag
a technology of woven fabric and airbag, which is applied in the direction of weaving, pedestrian/occupant safety arrangement, vehicular safety arrangement, etc., can solve the problems of increased mass of woven fabric coated with synthetic rubber, high manufacturing cost, and inability to meet the needs of passengers, etc., and achieve excellent accommodation and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0073]A polyamide 66 fiber of a total fineness of 400 dtex, and 72 filaments was woven in a water jet room in a plain weaving manner, shrinkage-processed with boiling water, and drying-finished at 110° C. to obtain a woven fabric having a warp density of 58 / 2.54 cm and a weft density of 56 / 2.54 cm. Using a polymer obtained by polymerizing a polyamide 6, a polyethylene glycol-propylamine adduct (number average molecular weight 600) and adipic acid at a molar ratio of 2.5:1:1, an aqueous resin dispersion having a solid matter concentration of 6% by mass was made. Then, to the aqueous dispersion was added carboxymethylcellulose sodium (1105, manufactured by Daicel Chemical Industries, Ltd.) at 10% by mass relative to the aqueous resin, and a viscosity was adjusted to 25 dPa·s. An aqueous dispersion of this resin composition was coated on the woven fabric by knife coating, at a resin amount after drying of 4 g / cm2. Properties of this woven fabric were assessed, and results are shown in ...
example 2
[0074]A polyamide 66 fiber of a total fineness of 350 dtex, and 108 filaments was woven in a water jet room in a plain weaving manner, shrinkage-processed with boiling water, and drying-finished at 110° C. to obtain a woven fabric having a warp density of 64 / 2.54 cm and a weft density of 61 / 2.54 cm. Using a polymer obtained by polymerizing a polyamide 6, a polypropylene glycol-propylamine adduct (number average molecular weight 1000) and adipic acid at a molar ratio of 2.0:1:1, an aqueous resin dispersion having a solid matter concentration of 10% by mass was made. Then, to the aqueous dispersion was added carboxyethylcellulose (SP200, manufactured by Daicel Chemical Industries, Ltd.) at 8% by mass relative to the aqueous resin, and a viscosity was adjusted to 20 dPa·s. An aqueous dispersion of this resin composition was coated on the woven fabric by knife coating, at a resin amount after drying of 10 g / cm2. Properties of this woven fabric were assessed, and results are shown in Tab...
example 3
[0075]A polyamide 66 fiber of a total fineness of 350 dtex, and 108 filaments was woven in a water jet room in a plain weaving manner, shrinkage-processed with boiling water, and drying-finished at 110° C. to obtain a woven fabric having a warp density of 64 / 2.54 cm and a weft density of 61 / 2.54 cm. Using a polymer obtained by polymerizing a polyamide 6, adipic acid, and polyethylene glycol (number average molecular weight 600) at a molar ratio of 1.8:1:1, an aqueous resin dispersion having a solid matter concentration of 6% by mass was made. Then, to the aqueous dispersion was added carboxymethylcellulose (07326-95, manufactured by Nacalai Tesque) at 2% by mass relative to the aqueous resin, and a viscosity was adjusted to 105 dPa·s. An aqueous dispersion of this resin composition was coated on the woven fabric by knife coating, at a resin amount after drying of 8 g / cm2. Properties of this woven fabric were assessed, and results are shown in Table 1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com