Biological information monitoring apparatus
a technology of biochemical information and monitoring apparatus, which is applied in the direction of catheters, instruments, angiography, etc., can solve the problems of inconvenient use, limited site observation, and inconvenient use of monitoring apparatus comprising components arranged in a bed or a chair, and achieve the effect of smooth handling of the interface of machines
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment 1
[0022]The first embodiment of biological information monitoring apparatus according to the invention is adapted to monitor biological information at the wash basin that the family members use several times a day in order to accumulate and provide information effective to maintain the health and support the daily lives of the family members without giving them any feeling of inconvenience.
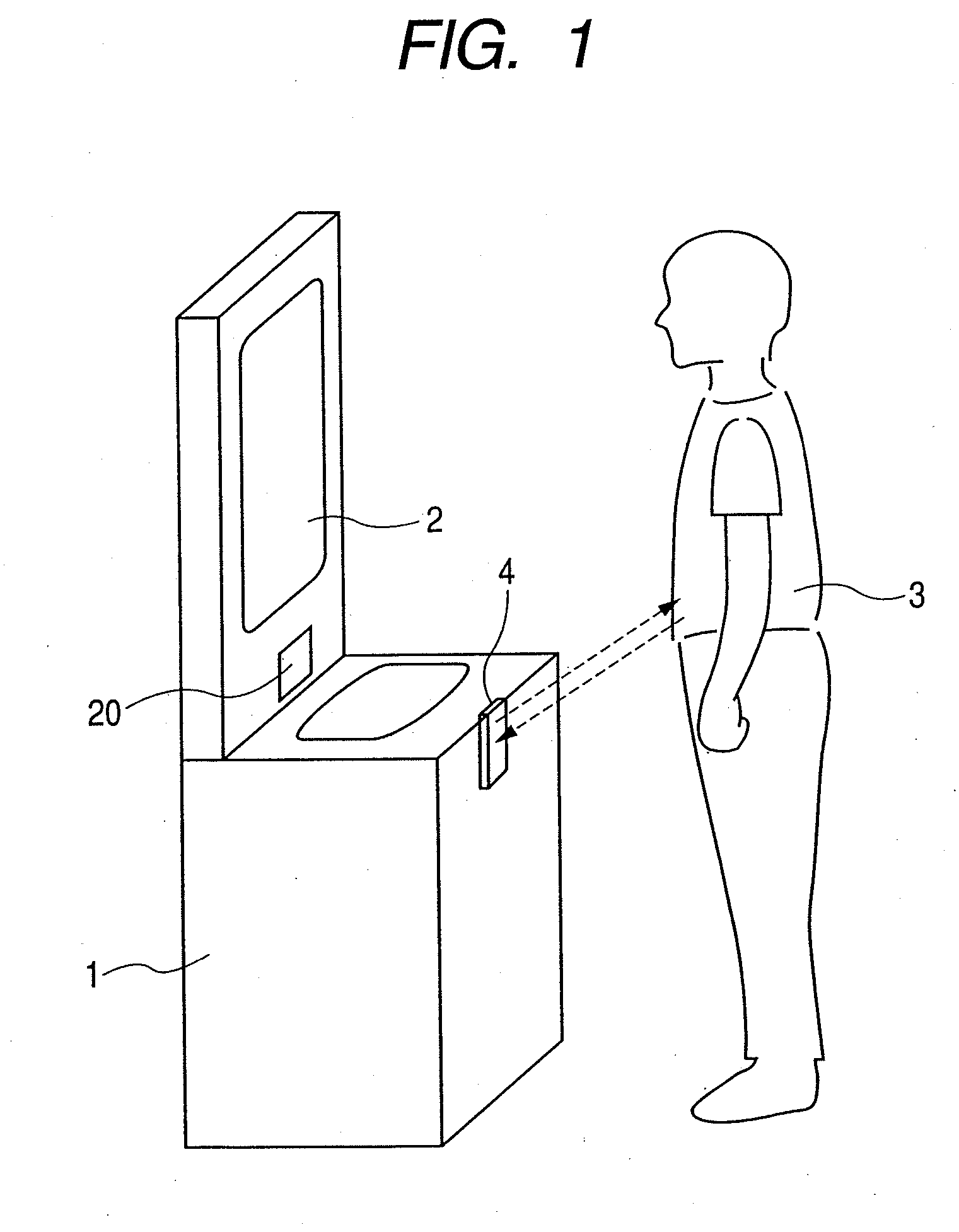
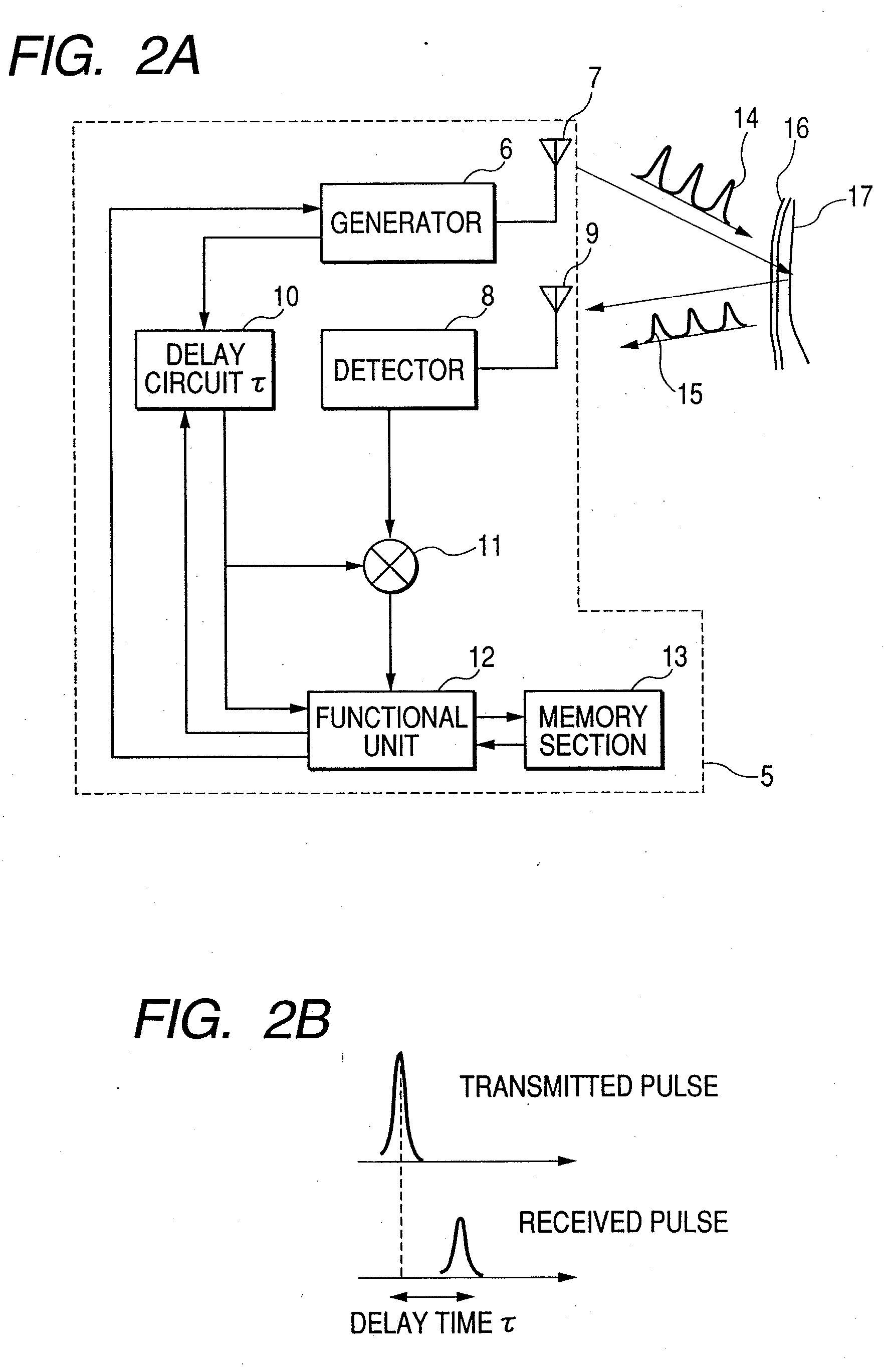
[0023]FIG. 1 illustrates a situation where a person 3 is standing in front of a wash basin 1 that is provided with a mirror 2 and doing something. A remote sensing section 4 adapted to use an electromagnetic wave is buried in the wash basin in order to remotely acquire information on the person standing in front of the wash basin typically from the abdomen of the person. A technique of irradiating an electromagnetic wave having a wavelength longer than that of infrared rays and analyzing the reflected wave so as to analyze the vibrations of the body of the person from the acquired positional fluctua...
embodiment 2
[0033]The second embodiment of the present invention is a small module of a remote sensing apparatus as described above for the first embodiment. A number of such modules may be arranged at different sites in order to simultaneously acquire biological information from a person. This arrangement is effective for accurately acquiring and correcting information on vibrations and the state of propagation of vibration in the body of the person.
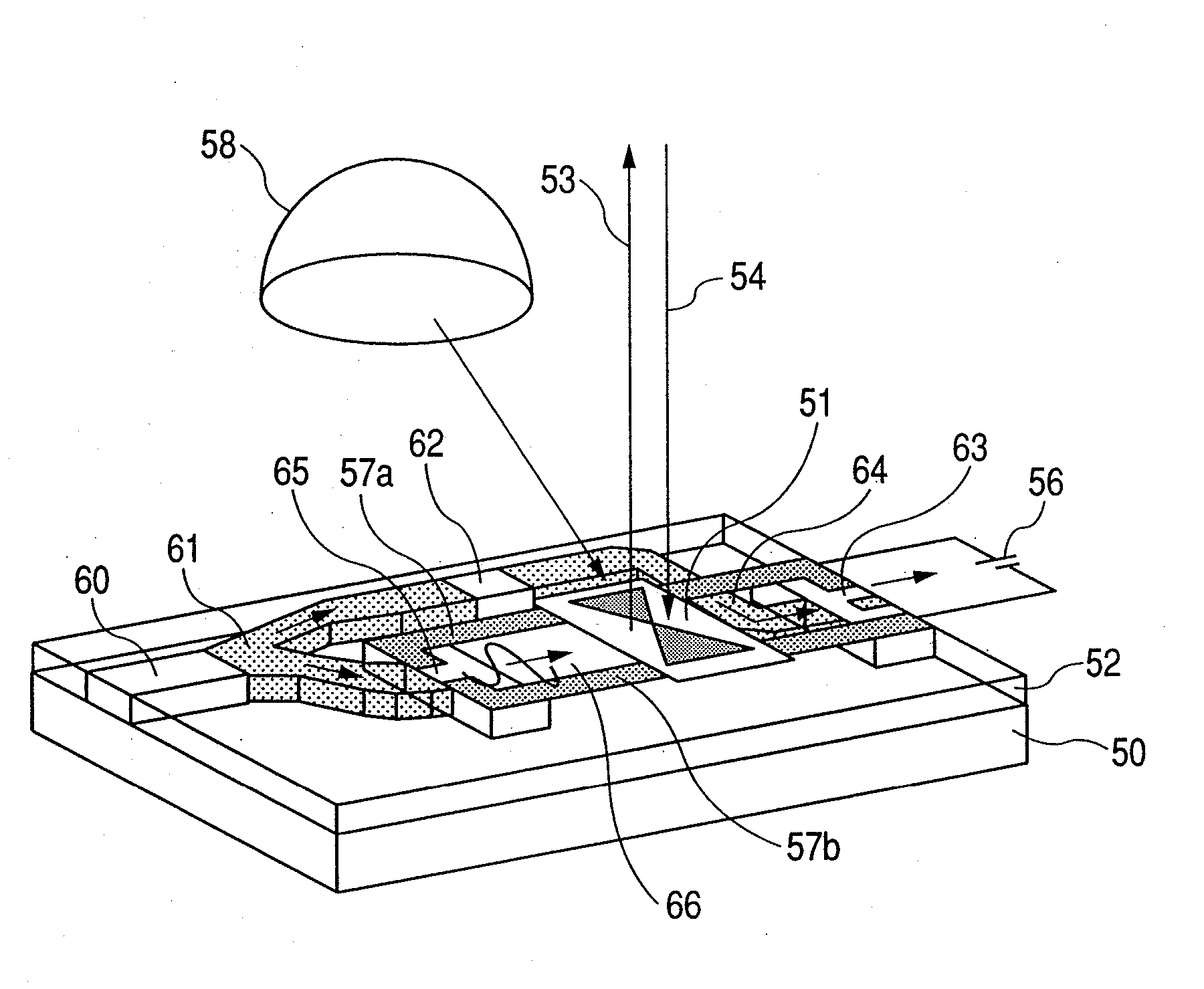
[0034]FIG. 5 schematically illustrates an integrated module according to the invention. A semiconductor mode-locked laser 60 is mounted on a substrate 50 and adapted to generate a pulse of about 0.3 psec that is coupled to an optical waveguide 61. One of the propagated laser beams branched by the optical waveguide 61 is irradiated onto a terahertz wave generator 65 and converted into an electromagnetic wave 66 having a pulse width of about 0.5 psec, which is then propagated through transmission paths 57a, 57b. The other laser beam is propagated by ...
embodiment 3
[0040]The third embodiment of the present invention is adapted to bury sensors 81a through 81d of the above described type in a chair 80 as shown in FIG. 8. Note that, in FIG. 8, the components same as or similar to those of FIG. 1 are denoted respectively by the same reference symbols.
[0041]Known vibration sensors are adapted to be arranged on or near the surface of a chair and hence are accompanied by problems particularly in terms of the appearance, the design and the comfortableness of the chair. To the contrary, electromagnetic type modular sensors according to the invention can be contained in a chair to allow a high degree of design freedom comparable to that of ordinary chairs without damaging the comfortableness of the chair. Additionally, unlike known sensors, the subject is not required to hold the back in tight contact with the back cushion of the chair and sit still. This is because the electromagnetic wave of millimeter to terahertz range to be used for observation is ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com