Small Peptides And Methods For Treatment Of Chronic Inflammatory Bowel Disease
a bowel disease and inflammatory bowel disease technology, applied in the field of small peptides, can solve the problems of increasing microvascular permeability, disrupting epithelium, stimulating neural reflexes and mucus secreting glands, etc., and preventing their further involvement in the increased inflammatory response
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
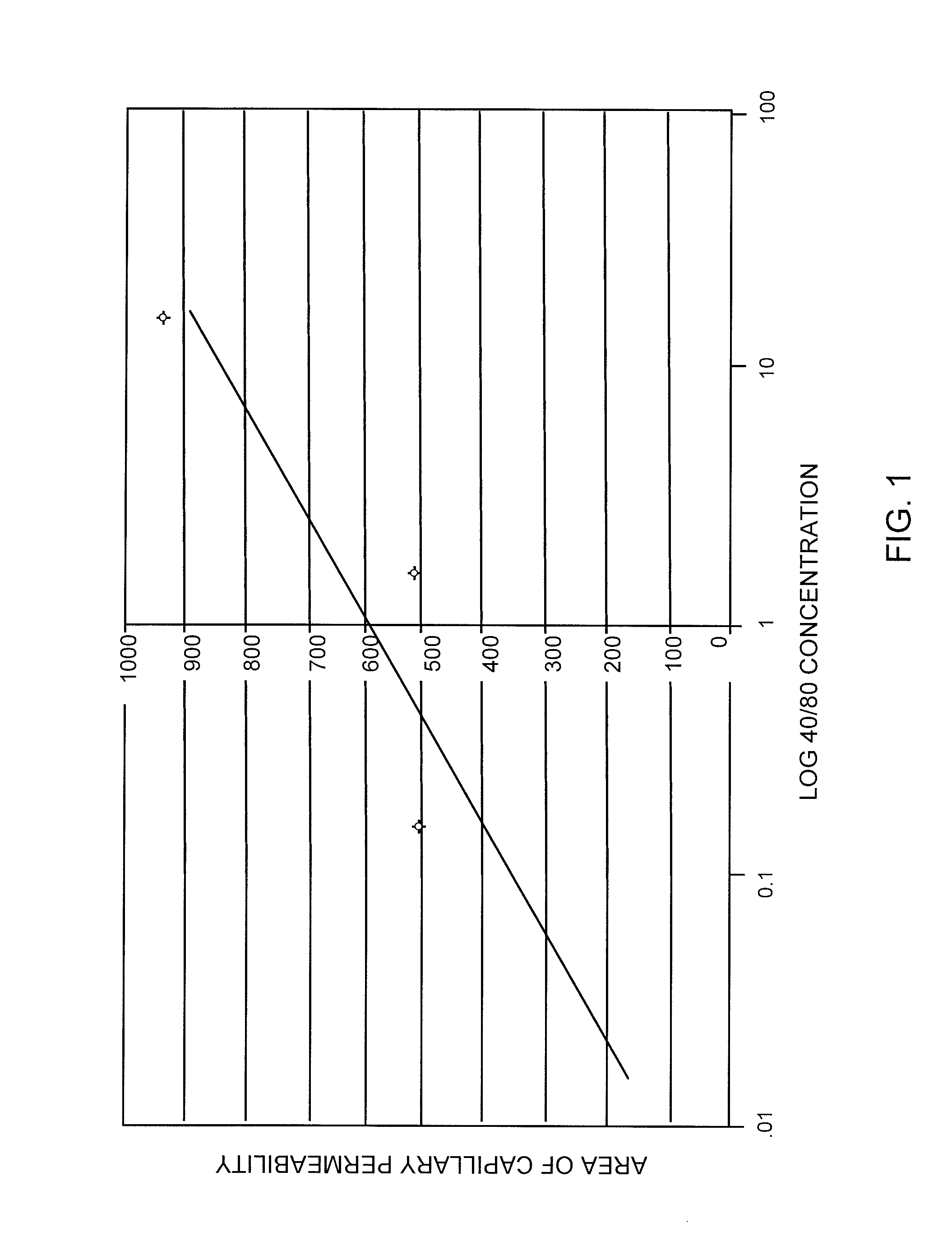
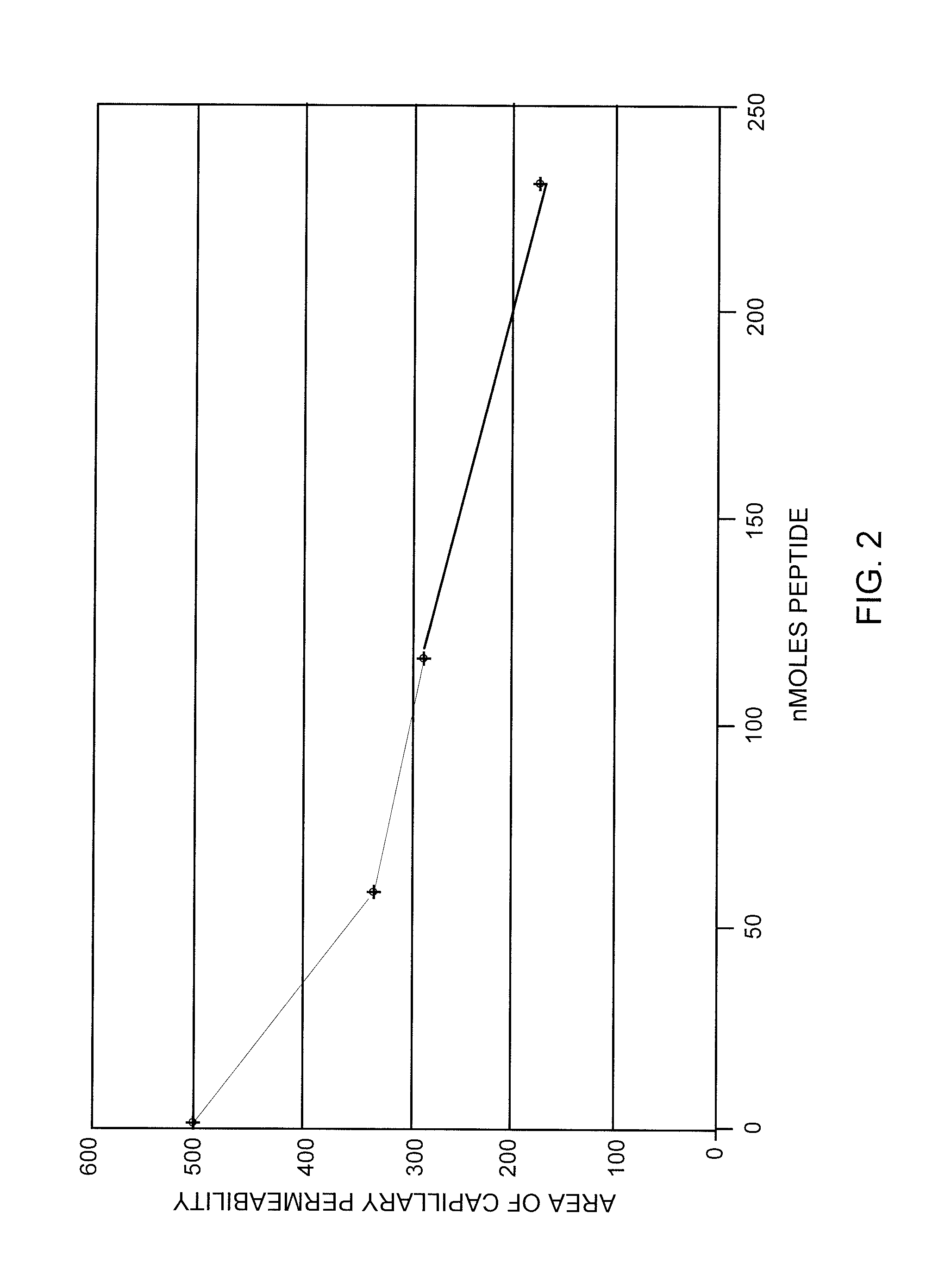
[0070]A dose response curve was prepared for the standard compound, f-Met-Leu-Phe, using the selected dose of 0.15 μg Compound 48 / 80. Doses of 0 to about 230 nM of f-Met-Leu-Phe were tested and the results are shown in FIG. 2. Inhibition of degranulation induced by Compound 48 / 80 was clearly shown.
examples 2-11
[0071]Several f-Met-Leu peptides were tested for inhibition of induced degranulation in the rat skin model using 100 nanomoles of the test peptide and a dose of 0.15 μg Compound 48 / 80. An intrinsic zero-peptide-dose 48 / 80 control was included in each rat for each experiment, and the % of inhibition was expressed in relative terms to this control (0% inhibition). The percent mast cell degranulation produced by 48 / 80 was also determined. The results are tabulated below.
TABLE 1%%SEQInhibi-Degranu-ExamplePeptideIDtionlation*2f-Met-Leu-Phe (prior3060art)3N-acetyl-Met-Leu-Phe0984N-t-BOC-Met-Leu-Phe0—5f-Met-Leu-(iodo)Phe0—6f-Met-Leu-Phe0—(benzylamide)7f-Met-Leu-Phe-Lys40—8f-Met-Leu-Phe(methyl0—ester)9f-Met-Leu-Phe-Phe21001-310f-Met-Leu-Tyr553011f-Met-Leu-Tyr-Tyr50—
example 12
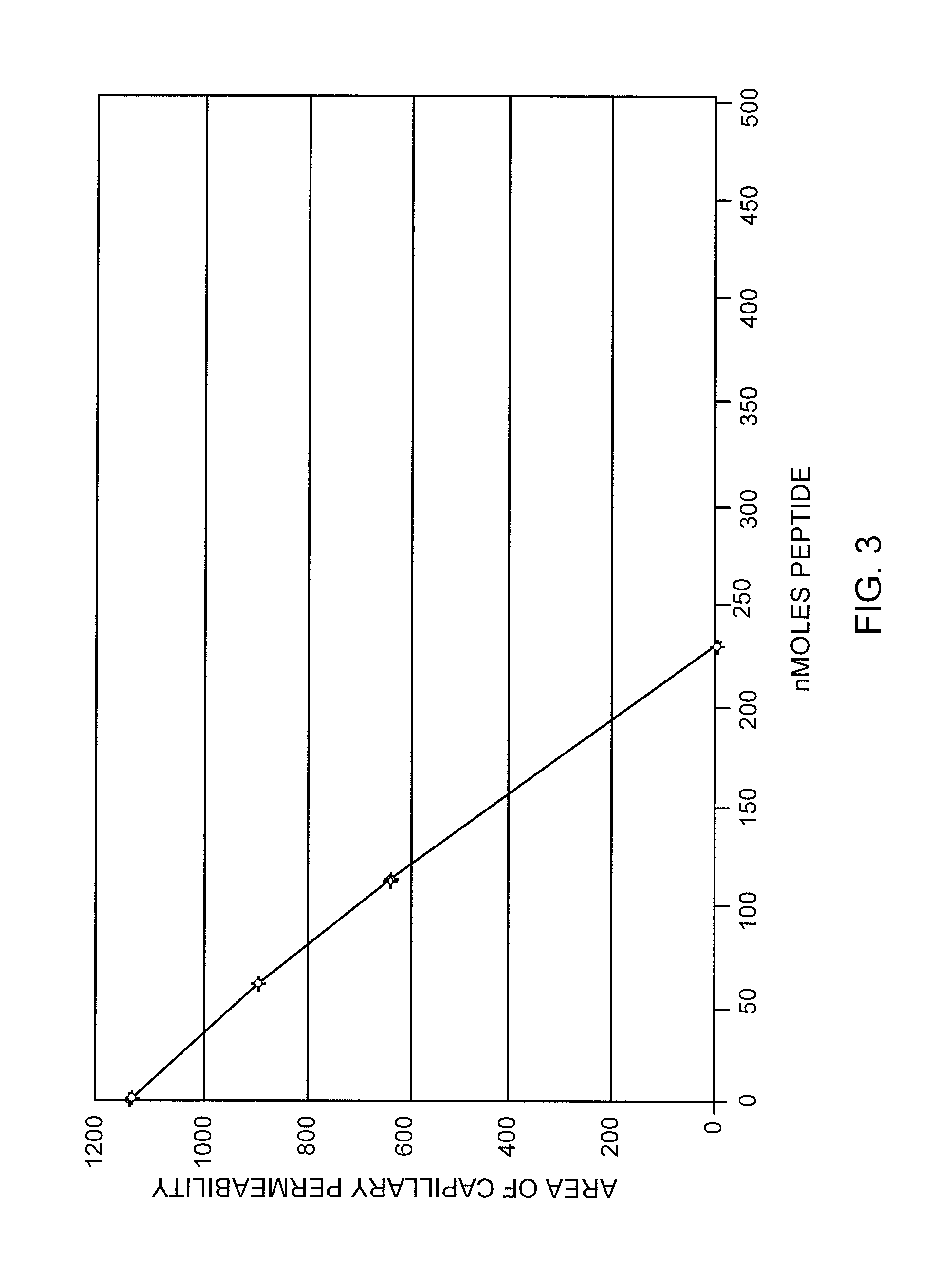
[0072]A dose response curve was prepared for f-Met-Leu-Phe-Phe using the selected dose of 0.15 μg Compound 48 / 80. Doses of 0 to about 230 nM of f-Met-Leu-Phe-Phe were tested and the results are shown in FIG. 3. Surprisingly remarkable inhibition of degranulation induced by Compound 48 / 80 was clearly shown. The inhibition of induced degranulation for f-Met-Leu-Phe-Phe was unexpectedly substantially better than that of the standard compound f-Met-Leu-Phe.
The OVA-induced Bronchial Asthma Mouse Model for Inhibition of Mast Cell Degranulation
[0073]Asthma is a complex disease, which is characterized by spontaneous exacerbation of airways obstruction and persistent bronchial hyperresponsiveness. Chronic infiltration with activated T-lymphocytes, eosinophils and macrophages / monocytes of the airway submucosa is another established feature. Inflammatory mechanisms, with expression of cytokines, and the release of inflammatory mediators, underlie the pathogenesis of bronchoconstriction and bro...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentrations | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentrations | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentrations | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com