Rapid response method for the failure of links between different routing domains
a response method and routing domain technology, applied in the field of rapid response method for the failure of a link between two routing domains, can solve the problems of complicated inter-domain routing, difficult calculation of global optimal paths, according to objective criteria
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
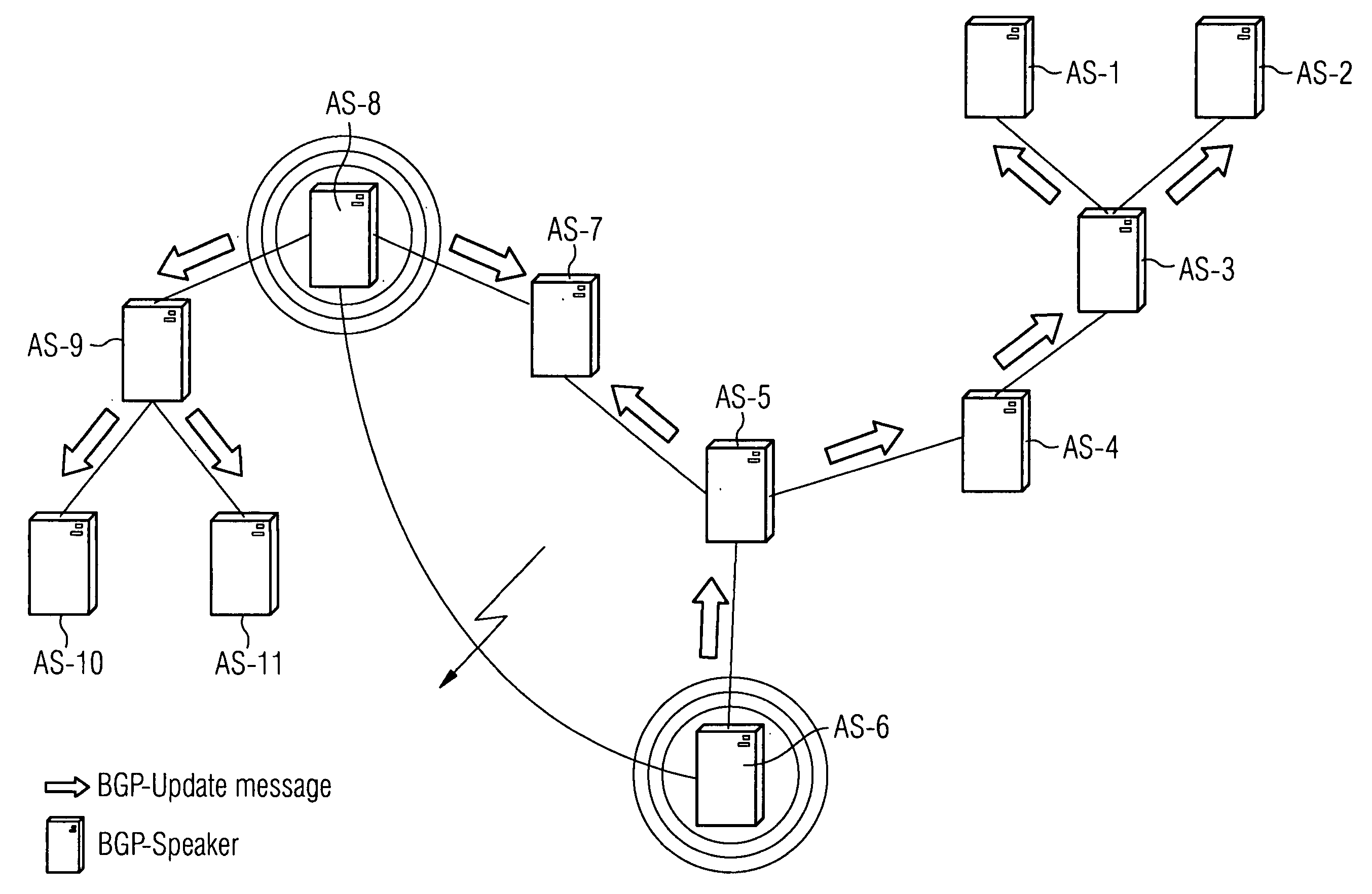
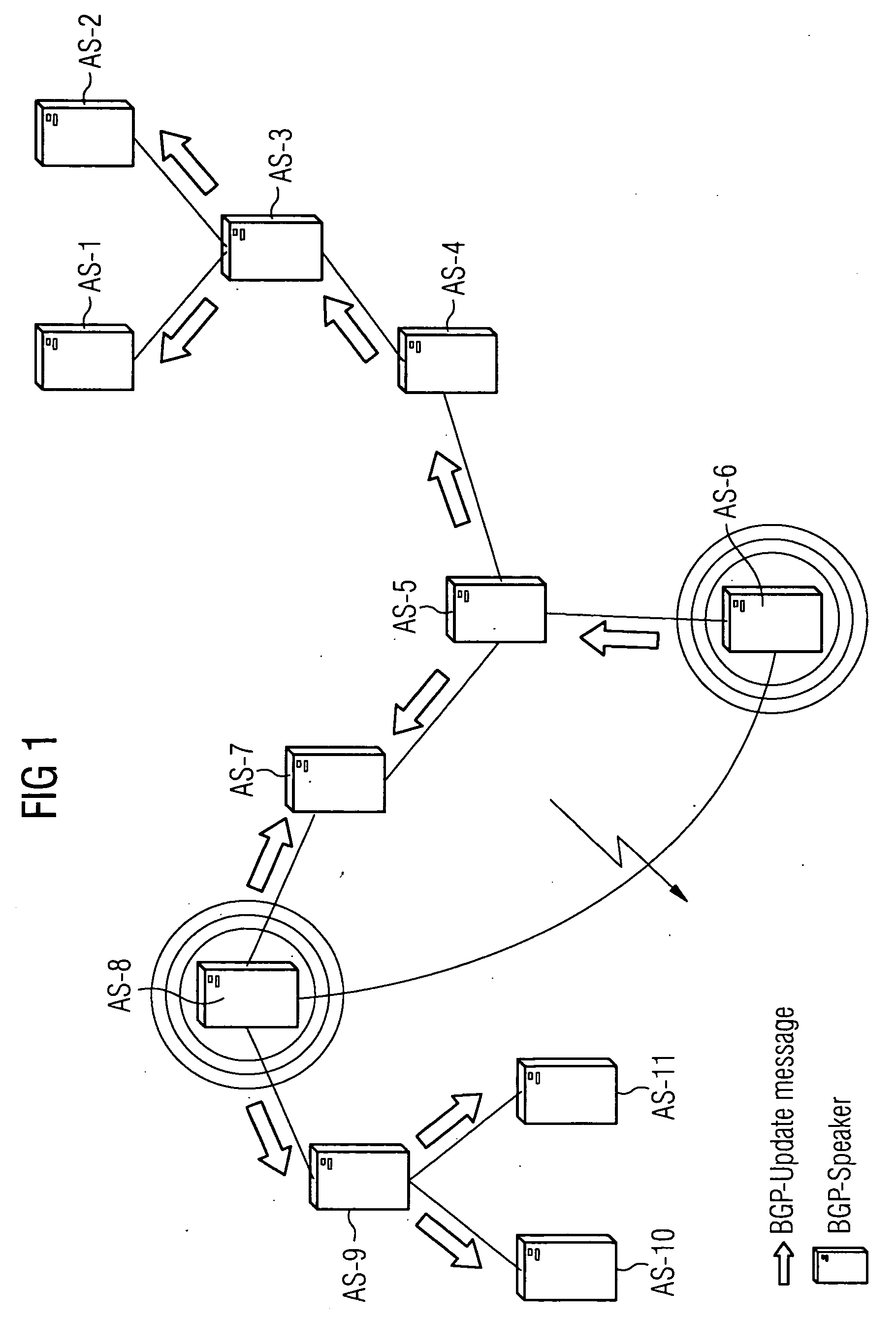
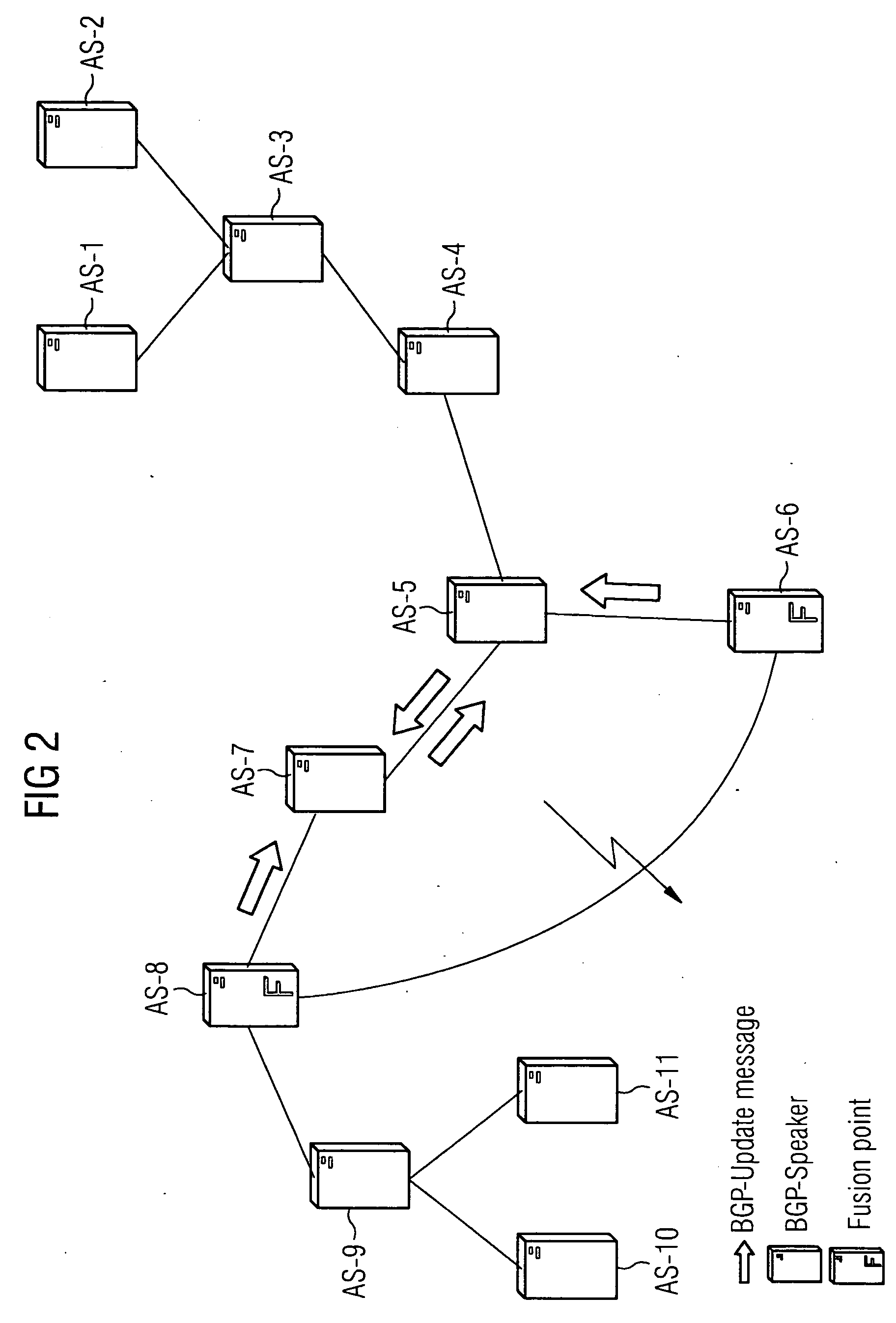
[0024]FIG. 1 shows eleven autonomous systems or routing domains AS-1 to AS-11 together with links which connect these autonomous systems to each other. The autonomous systems communicate with each other with the help of the BGP protocol, whereby individual routers in the autonomous systems are equipped with appropriate protocol capabilities. Here, we use the terms BGP speakers or BGP instances. With the help of these BGP instances, the autonomous systems exchange messages with each other, either confirming the stored state or giving information about changes which should be taken into account in routing. FIG. 1 indicates how the system responds to a link failure, under the control of the BGP protocol. In this case the link between the autonomous systems AS-6 and AS-8 is disrupted. As the response to the malfunction—the response is indicated by the arrows—so-called update messages are propagated through the whole network, or the eleven autonomous systems AS-1, . . . , AS-11 receive u...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com