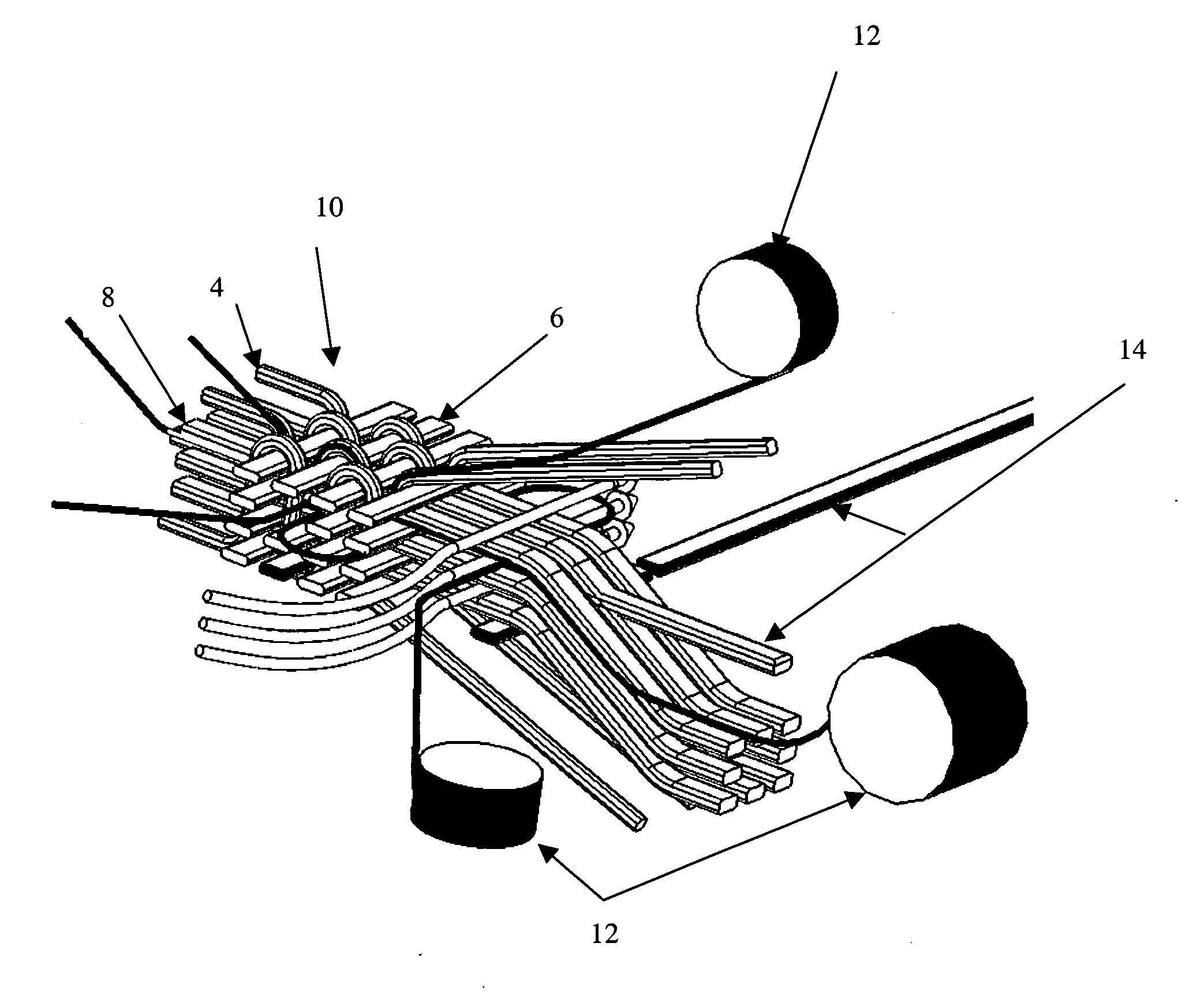
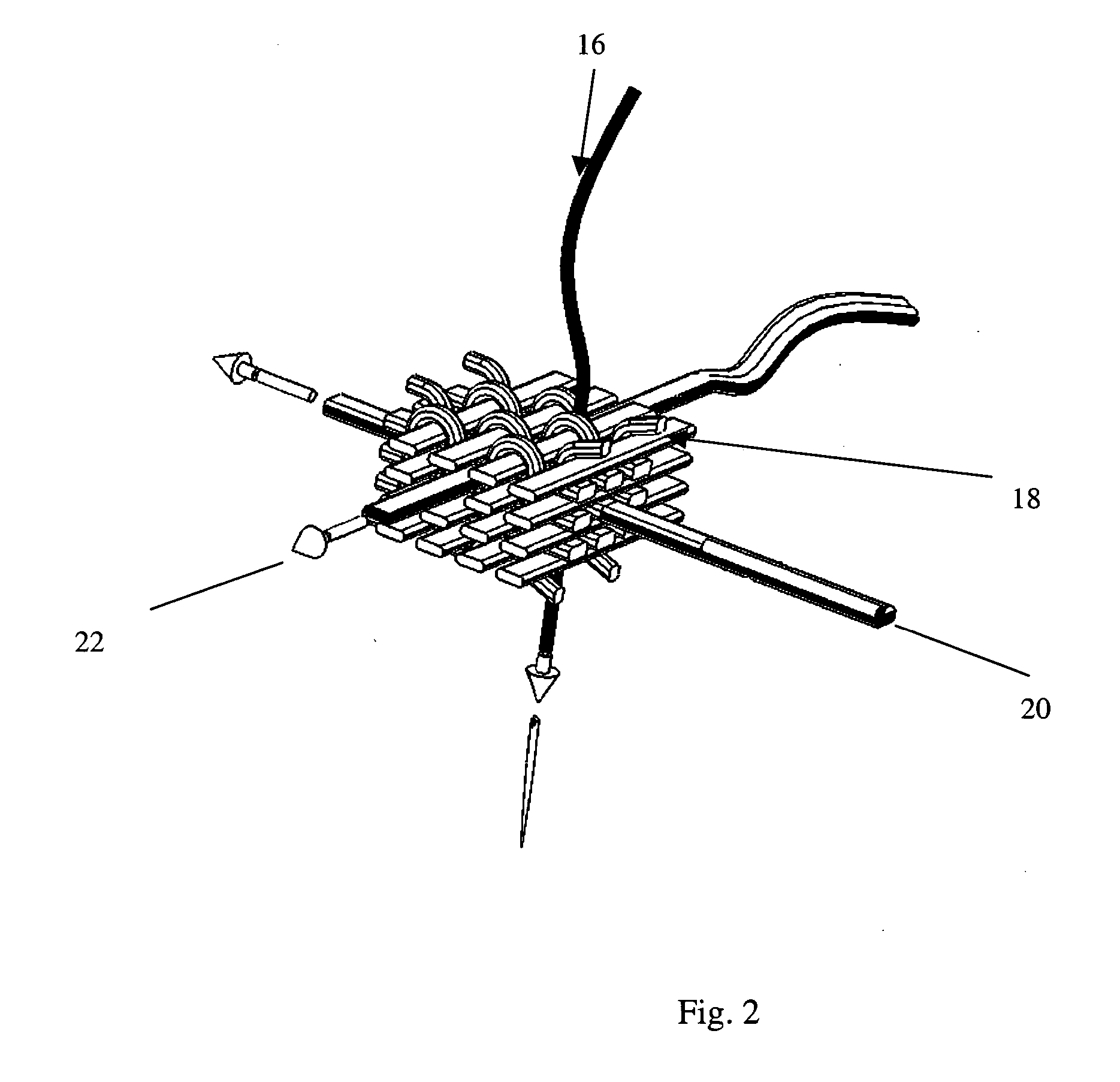
3-D fabrics and fabric preforms for composites having integrated systems, devices, and/or networks
a technology of fabric preforms and composites, applied in the field of fabric materials, can solve the problems of reducing the detectability of systems/devices, interference with on-board computers, and much higher potential to become a considerable local origin of disturbance, and all described optical fiber architectures in the invented composite are limited to two-dimensional woven architectures
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
and illustrative material do not indicate that any type of fiber architecture other than a unidirectional fiber placement or generic 2-D woven architecture, has been intended in the invention.
[0018] U.S. Pat. No. 4,836,030 describes the method of embedding a plurality of optical fibers in the composite material in pre-determined two-dimensional configuration (a serpentine pattern, specifically). Detection of light passing through any given optical fiber indicates that the composite is free of damage in the area along the extent of that optical fiber; however, integrating optical fibers within a fabric structure that is a 2-D woven structure or the like, where fiber paths are typically non-orthogonal and not substantially straight due to necessary crimping, prevents the integration of these fibers within the fabric itself. A layer of film adhesive is formed, in which optical fibers are embedded. The film adhesive layers are incorporated in composite laminate at the time of its manufa...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Electrical conductivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com