Method, system, and computer program product for trading interest rate swaps
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 3
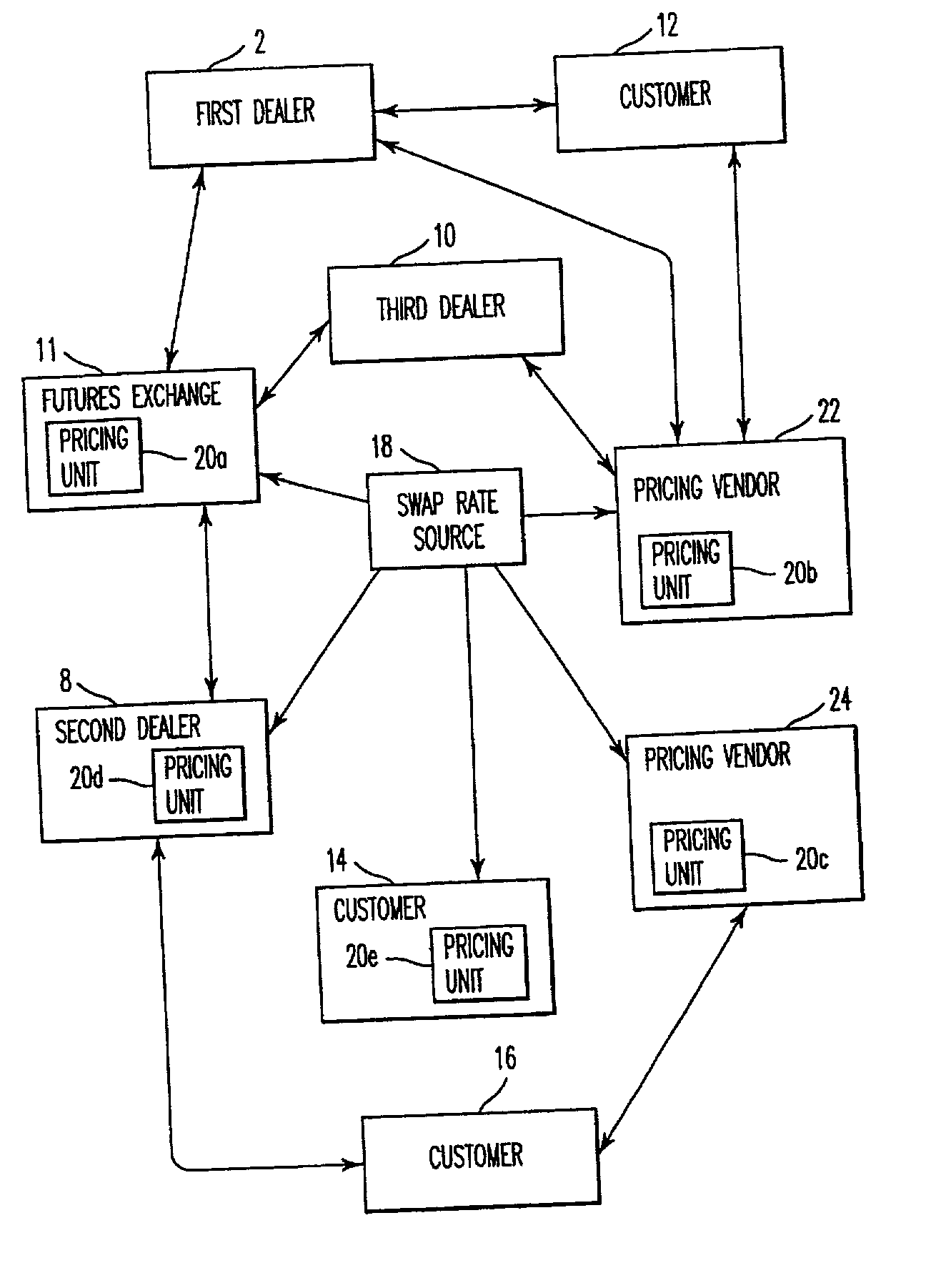
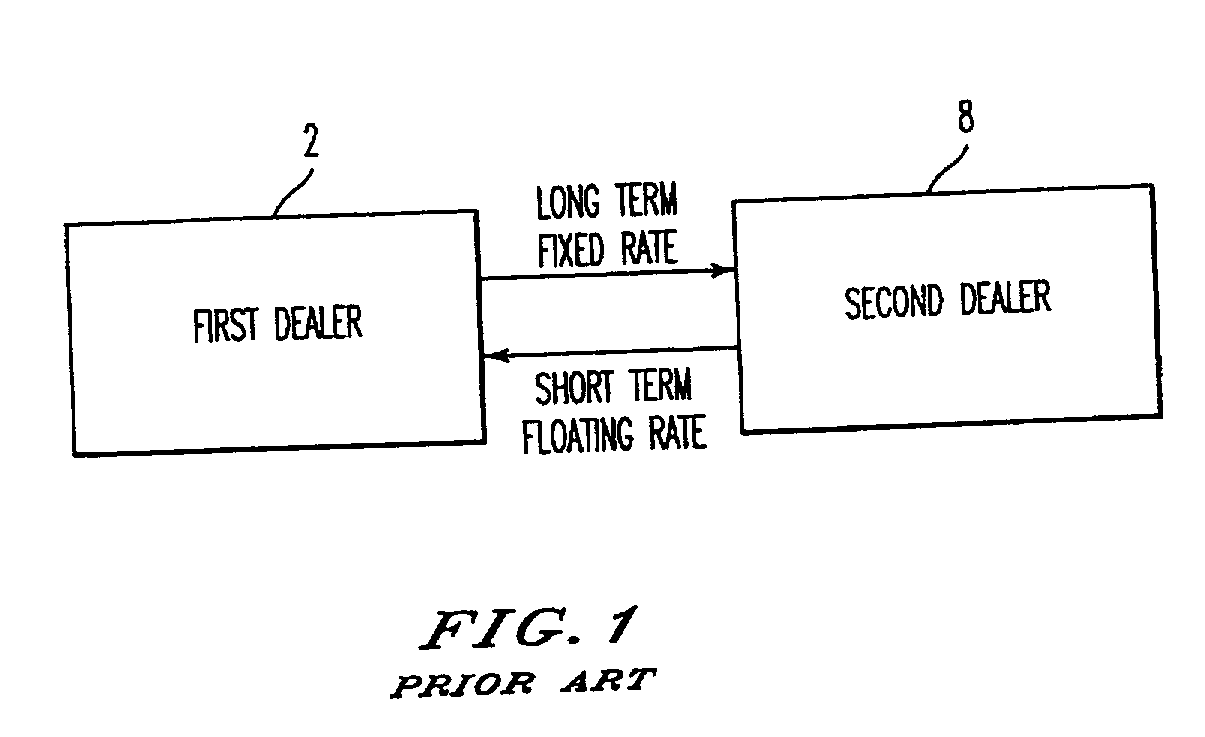
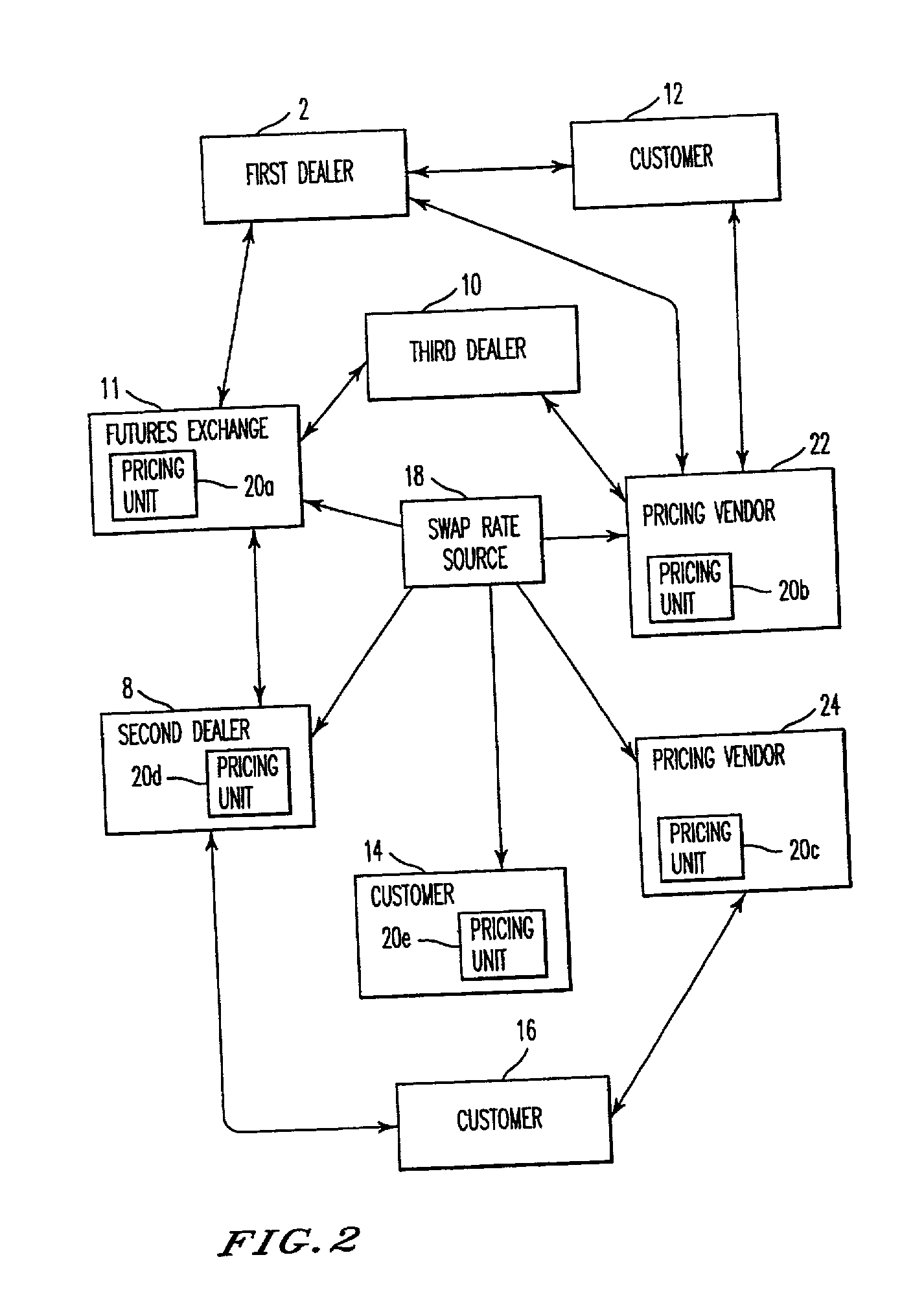
[0108] The use of the inventive contract as a swap dealer hedging instrument will now be described. With the inventive cash settled contract, swap dealers can avoid the basis risk inherent in hedging their swap books with government bonds and related futures contracts by using contracts as a hedging alternative. For example, a swap dealer receives fixed on a DM 100 million 8 year Deutschmark IRS at 4.56%. The swap has a basis point risk value of 6.578. The 10 year cash settled contract has a basis point risk value of 7.873. The swap dealer therefore uses a hedge ratio of 84.5%. As the contract has a contract value of DM 250,000, the dealer would sell 338 contract contracts ((100 million / 250,000)*0.845) against the swap position. There is a small amount of yield curve risk inherent in this hedging strategy that results from the sale of a 10 year instrument, i.e., the contract, against a long position in an 8 year instrument, i.e., the IRS. However, such risk is often present when us...
example 4
[0109] The use of the inventive contracts to hedge corporate bonds will now be described. The inventive cash settled contract can be used as a hedging instrument for both individual corporate bonds and corporate bond portfolios. Whereas customers often require exact cash flow matching of assets and liabilities in their investment portfolios, this requirement is rare in the dealer community.
[0110] Often corporate bond inventories are hedged by dealers in a manner similar to the way swap dealers have traditionally hedged their derivative portfolios, namely, by shorting government securities and related futures contracts. This has historically left both the swap dealer and the corporate bond dealer with basis risk across these different instruments. The corporate bond trader is exposed in such a hedging strategy to a widening in corporate yield spreads to the underlying government curve. This was all too evident in late August 1998 as the widening in global credit spreads has resulted ...
example 5
[0112] In Example 5 the autoroll contract embodies a contract to pay (or receive) the Treasury coupon and receive (or pay) the 3-month LIBOR rate (or any other floating rate index) until the maturity of the particular Treasury which is the subject of the respective contract. Every quarter, on the IMM effective date, all outstanding autoroll contracts will settle accrued interest and roll to the next IMM effective date without actual or physical delivery. Potentially every Treasury, domestic and foreign, would have its own autoroll contract and / or cash settled contract valued according to the present invention.
[0113] The final close the each autoroll contract of Example 5 is the IMM effective date which first occurs in the last year of a particular autoroll contract. Rather than deliver the Treasury for cash, settlement would be for cash at a price that equates the yield on the Treasury to LIBOR for the remaining days to its maturity.
[0114] For each subsequent quarter, the three mont...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com