Resolution enhancement by nearest neighbor classified filtering
An image resolution, the closest technology, applied in the field of image processing, can solve problems such as limiting performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
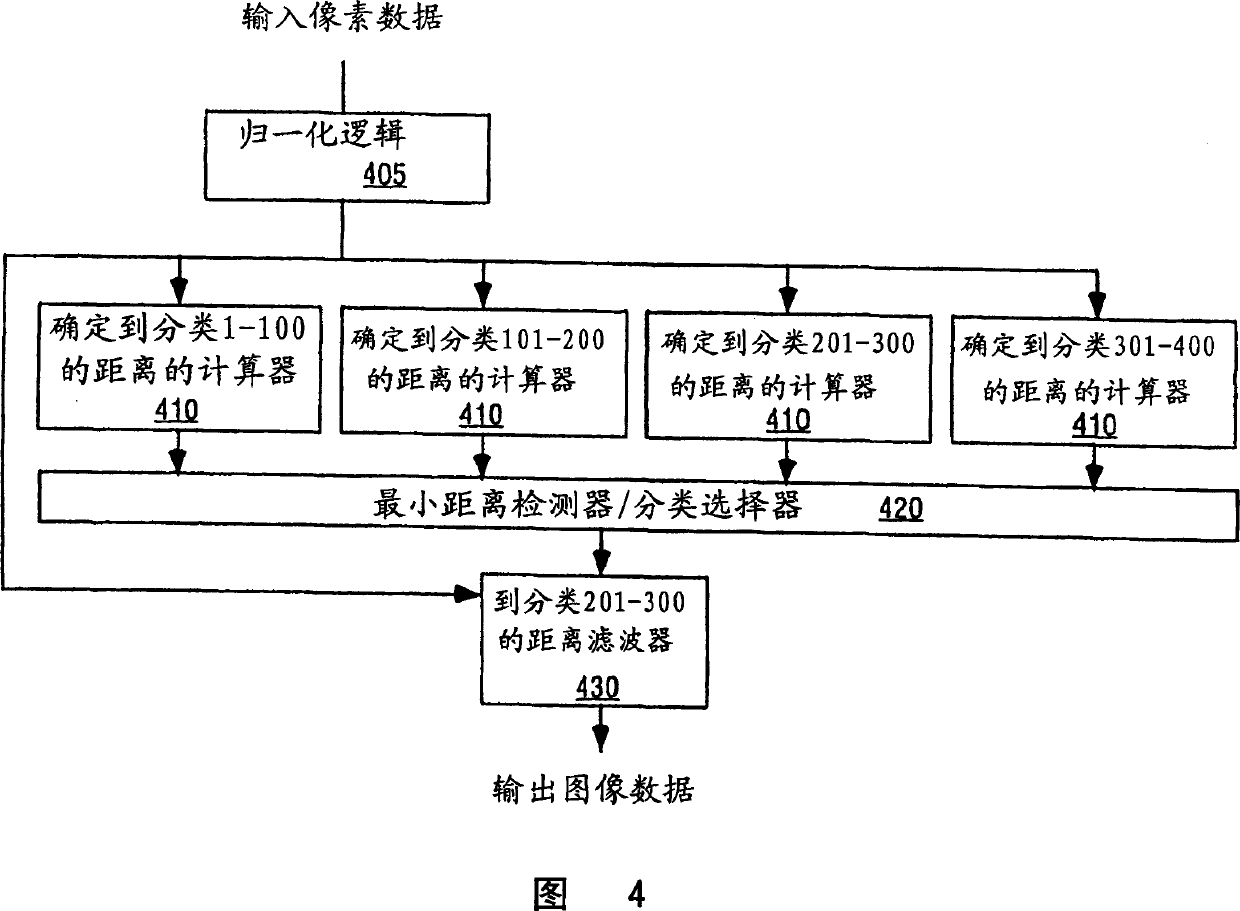
[0011] A method and device for determining the nearest neighbor classification for an input image vector from multiple spatial classifications to improve image resolution are given below. In one embodiment, the nearest neighbor class is determined by first receiving an input image vector to be classified into one of several spatial classes. Each spatial class has a corresponding normalized mean class vector. Normalizes the input image vector. Then determine the weighted distance from the normalized image vector to each normalized mean class vector. The class vectors belonging to the nearest neighboring class to the input image vector are determined on the basis of the weighted distance. Applies a filter corresponding to the nearest neighbor class to an input image vector, increasing image resolution.
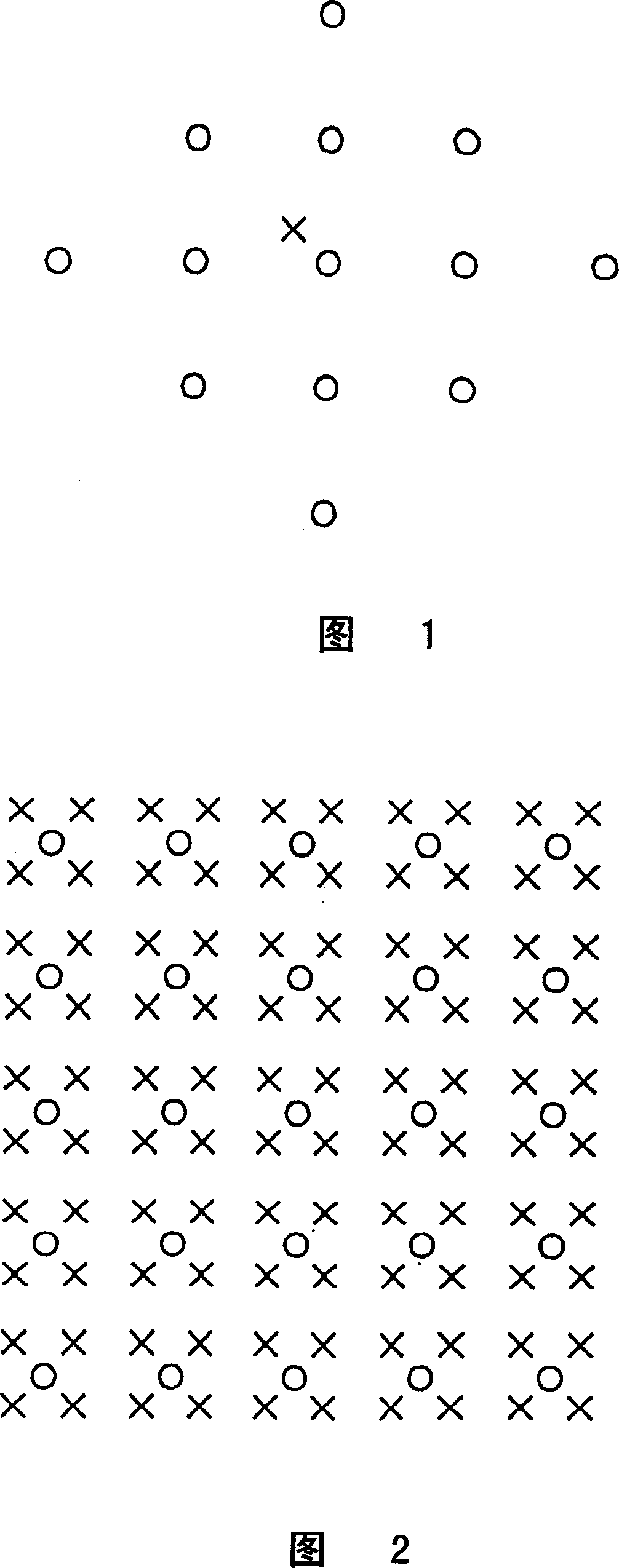
[0012] In signal processing, spatial filtering has many applications. For example, given the set of pixels represented by the circles in Figure 1, sample values can be est...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com