Controlled data network error recovery
A network and network node technology, which is applied in the field of error recovery of controlled data networks, can solve problems such as information loss, and achieve the effect of minimizing network load and avoiding load
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example A
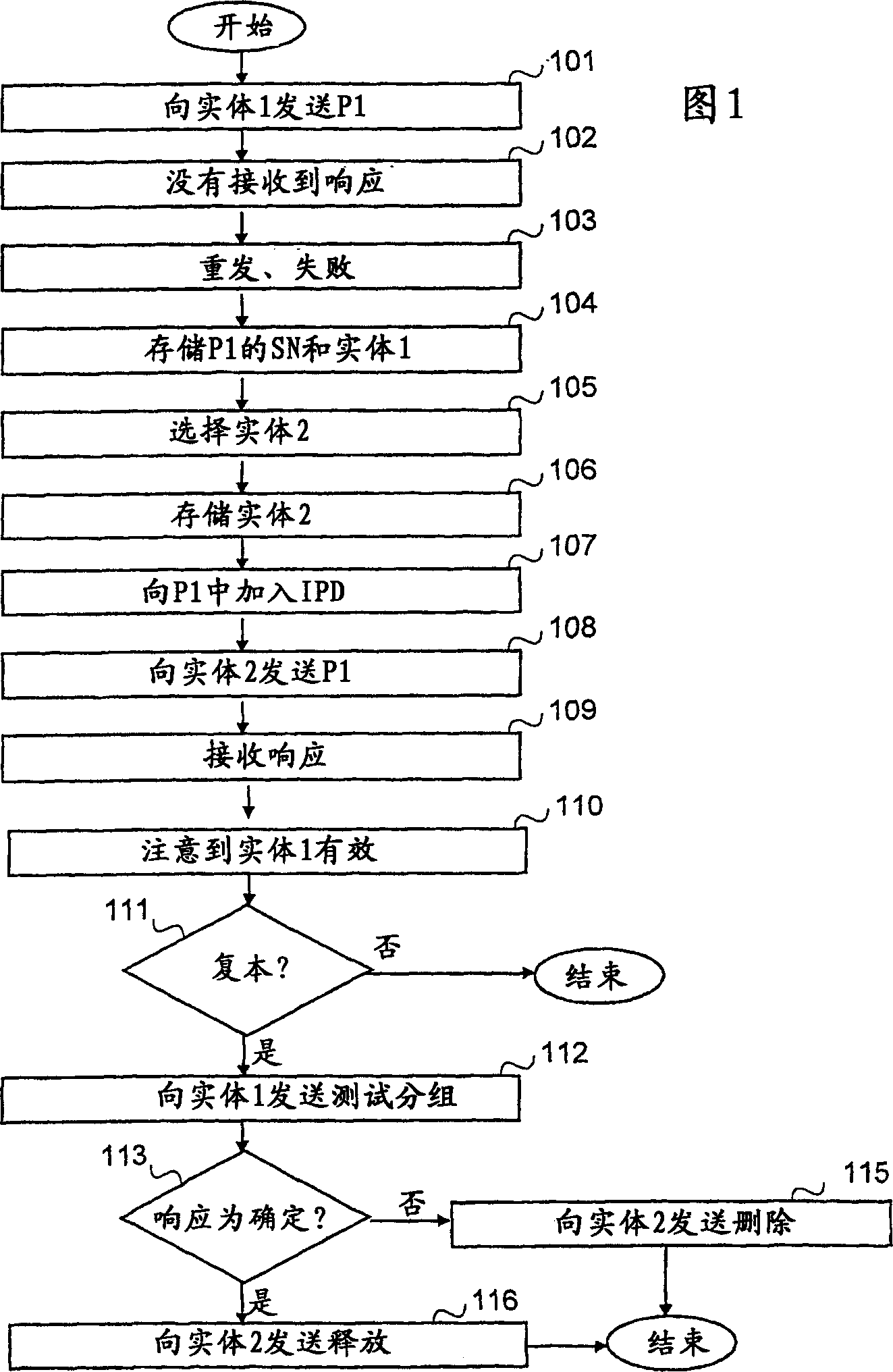
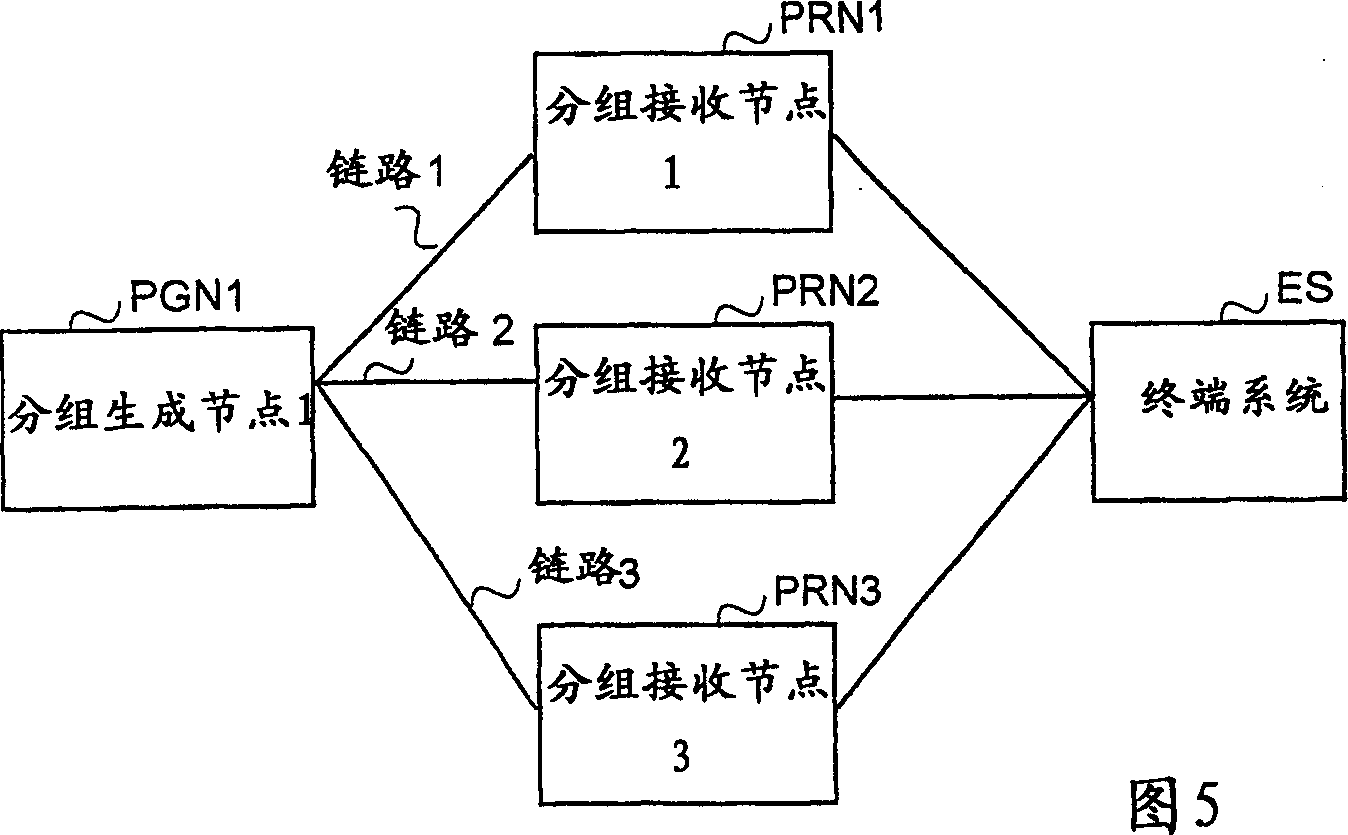
[0065] In this example, sequence numbers are used for packets (typically in the packet's frame) on each link from a packet generating node (PGN) to a packet receiving node (PRN). The sequence number is incremented one by one and flipped to 0 after reaching eg 65535, but it is very important that the maximum sequence number is greater than the maximum receive window size of the PRN.
[0066] If PRN1 fails, packets are redirected (marked with a potential replica flag) to a parallel node PRN2 (or PRN3 and others if PRN2 is unavailable for some reason). PGN1 also sends identification information of PGN1 to PRN2, so that PRN2 can identify these packets. This is necessary because PRN2 may have packets from other PGNs with the same sequence number and marked with the Duplicate Likely flag.
[0067] The PRN keeps packets marked as likely duplicates in a memory buffer or mass storage so that information of its data source (PGN1 or PGN2 or other PGN) can also be associated with the pac...
example B
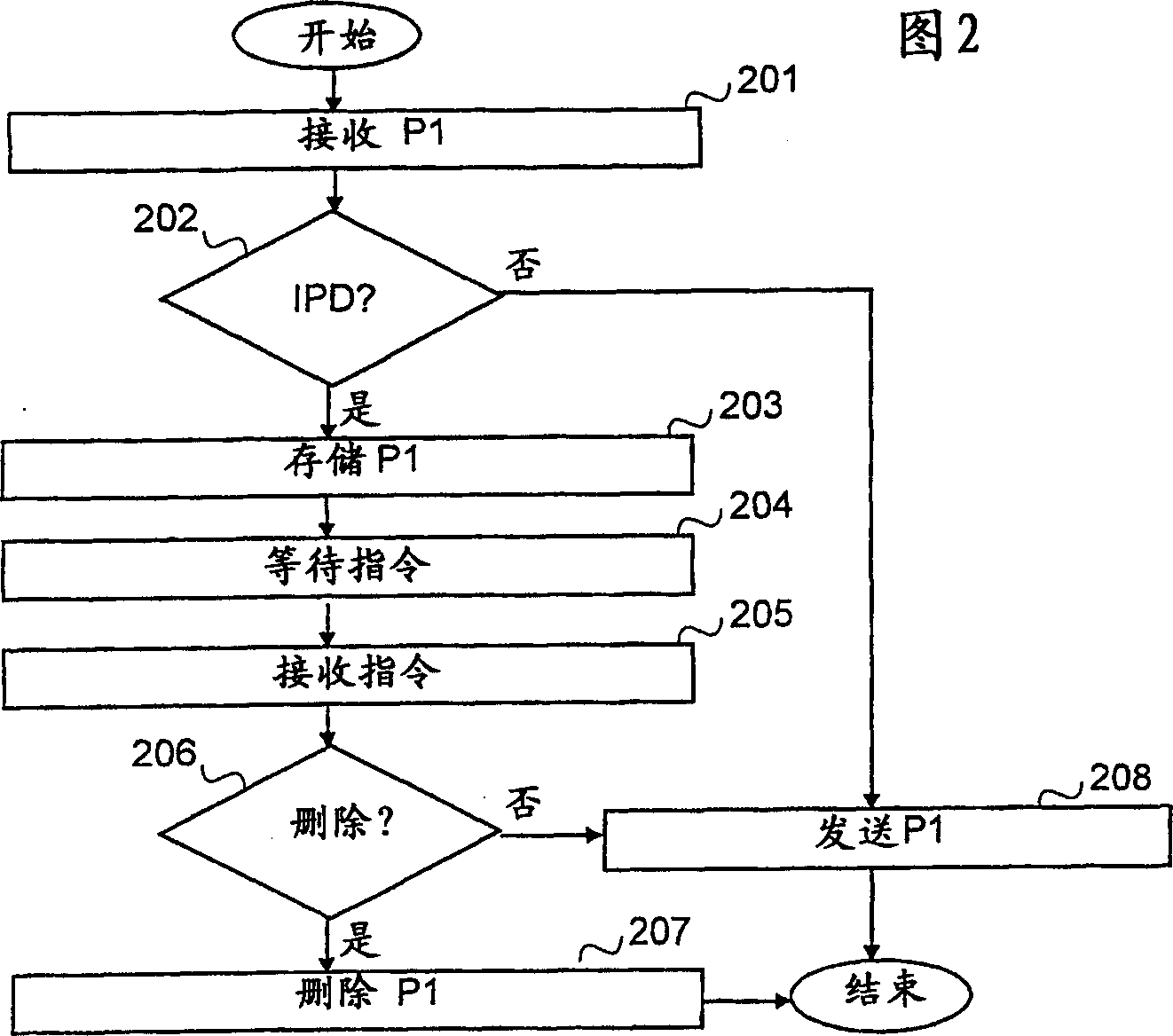
[0073] Similar to example A, but the detection method used to find out whether PRN1 (which has stopped working, but is valid again) has successfully processed a packet with a certain sequence number (sent by PGN1) is different. Here, PGN1 will again send a normal full packet to PRN1, the only difference being that the packet is now marked as a possible duplicate. This requires intermediate storage for the entire packet to either reside in PGN1, or the entire packet (possibly copied) should first be fetched from PRN2 (where it is in intermediate storage, waiting as to whether it can be sent to ES taken out of the final judgment). PGN1 can ask PRN2 to return a specific potentially duplicated packet by referring to the sequence number of the packet, and after getting the potentially duplicated packet from PRN2, it can be resent to PRN1. After this, PRN1 will give PGN1 a response (as to whether it has finished sending, ie processed the packet successfully, or whether it is gettin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com