Crank mechanism with pistons connected in series and double connecting rods
A crank mechanism and double connecting rod technology, applied in mechanical equipment, machines/engines, etc., can solve problems such as exhaust advance angle, vulnerable connecting parts, engine vibration, etc., to achieve high power use efficiency and stable operation of the mechanism , The effect of improving engine life
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
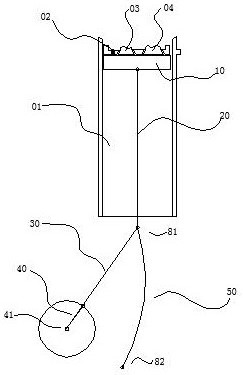
[0034] Embodiment one, combining figure 1 , 2 , 3, a kind of engine structure, comprises cylinder block 01, spark plug and fuel injection assembly 02, intake valve 03, exhaust valve 04, piston 10, and piston 10 is hinged upper connecting rod 20, and one end of upper connecting rod 20 is hinged simultaneously The lower connecting rod 30 and the sliding block on the arc guide rail 50 ; the lower connecting rod 30 is hinged to the crankshaft 40 , and the crankshaft 40 pushes the crankshaft 41 . The structural parameters of this engine are: if the stroke of the piston 10 is set to 100, the length of the upper connecting rod 20 is 110, the length of the lower connecting rod 30 is 67.8, the length of the crankshaft 40 is 20, and the arc guide rail is 50. The radius of curvature is 128.44.
[0035] Since the present invention uses the lower connecting rod 30 and the arc-shaped guide rail 50, the stressed position of the crankshaft 40 is changed, and the rotation angle of the piston...
Embodiment 2
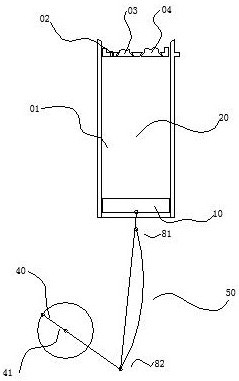
[0036] Embodiment two, combining Figure 4 , an engine structure, the difference from Embodiment 1 is that the curved guide rail 50 is hinged to the frame at the lower end point 82 of the upper link, and a motor-driven motor is provided below the upper end point 81 of the upper link. The cam 61 is provided with a hinged shift fork 62 in the groove of the cam 61 , and the shift fork 62 is slidably connected with the arc guide rail 50 .
[0037] The motor drives the cam 61 to rotate, and the cam 61 drives the shift fork 62 to shift, and the shift of the shift fork 62 causes the arc-shaped guide rail 50 to swing along the lower end point 82 of the upper connecting rod, thereby resulting in a change in the stroke of the piston 10, resulting in a change in the compression ratio. It is beneficial for the engine to be suitable for various power outputs. Other structures and principles are the same as those in Embodiment 1, and will not be repeated here.
Embodiment 3
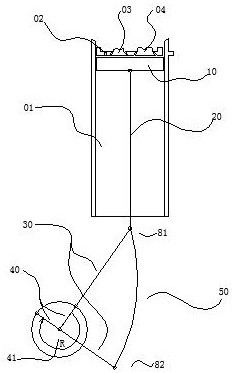
[0038] Embodiment three, combining Figure 5 , an engine structure, the difference from Embodiment 1 is that: the curved surface guide rail 50 is hinged to the frame at the lower end point 82 of the upper link, and a motor-driven wire is provided below the upper end point 81 of the upper link. The rod 63 and the lead screw 63 drive the nut 64, the nut 64 is hinged with a shift fork 62, and the shift fork 62 is slidably connected with the arc surface guide rail 50.
[0039] The motor drives the lead screw 63 to rotate, and the lead screw 63 drives the nut 64 hinged with the shift fork 62 to shift. The shift of the shift fork 62 causes the curved guide rail 50 to swing along the lower end point 82 of the upper link, thereby resulting in a change in the stroke of the piston 10. It leads to a change in the compression ratio, which is beneficial for the engine to be suitable for various power outputs. Other structures and principles are the same as those in Embodiment 1, and will ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com