Recombinant acid-resistant yeast with suppressed glycerol production and method of producing lactic acid using the same
A technology of acid-resistant yeast and glycerin, applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problems of unreasonable and difficult to predict the effect of reducing the production cost of the process, so as to improve the conversion rate , Inhibit the effect of cross-linking
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
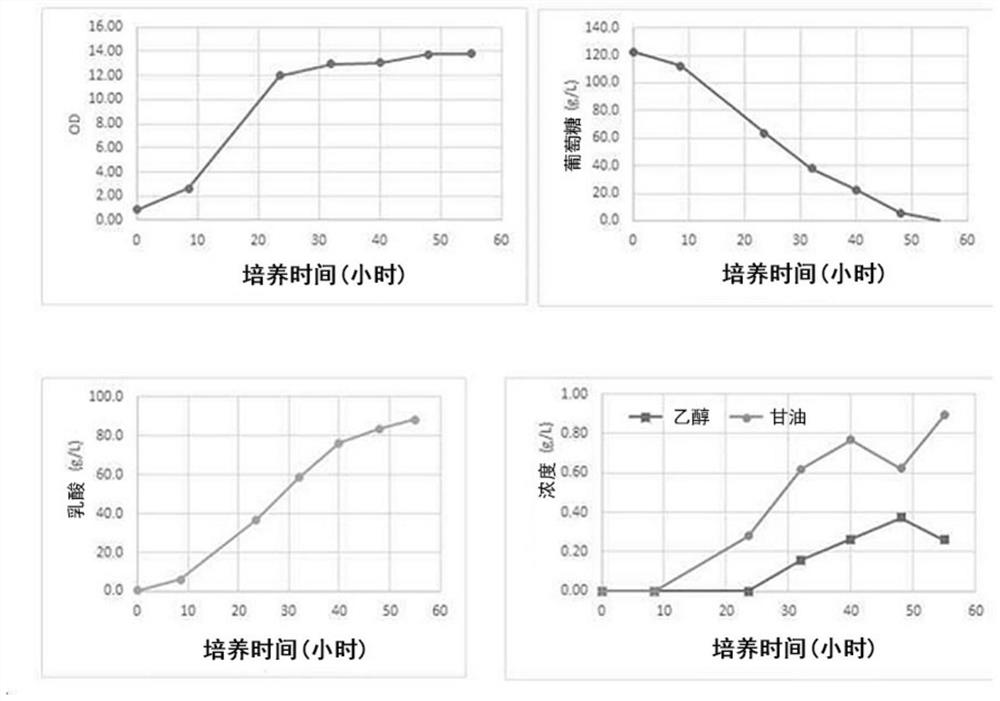
[0069] Example 1: Analysis of glycerol-producing genes in the genome of acid-tolerant strain YBC
[0070] The present inventors selected strains having acid resistance by testing various yeast strains, and determined that they had the best acid resistance by adding lactic acid to the medium at the beginning of the culture of the yeast strains and monitoring the growth and sugar consumption rate of the microorganisms. The strain, namely the YBC strain, was deposited in the Bioresource Center of the Korea Institute of Bioscience and Biotechnology with the accession number KCTC13508BP.
[0071] Phylogenetic analysis showed that the YBC strain (KCTC13508BP) is a strain similar to S. cerevisiae, is diploid, and is Crabtree positive.
[0072] Using bioinformatic information from Saccharomyces cerevisiae and whole genome sequence data from this YBC strain, g1544 and g5617 were identified as genes annotated with GPD1 (glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase 1) and GPD2, respectively, which...
Embodiment 2
[0080] Embodiment 2: the mensuration of GPD gene expression level
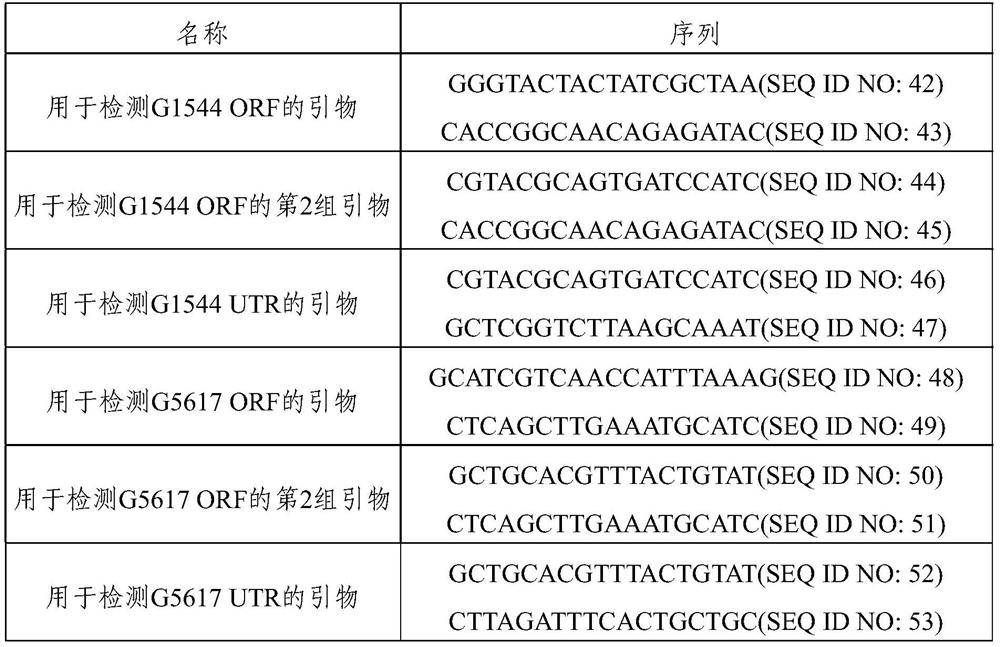
[0081] In order to confirm the expression levels of GPD1 (g1544) and GPD2 (g5617) of this YBC strain, RT-qPCR was performed using the following primers and the ALG9 gene as a housekeeping gene. The RT-qPCR method used in this example will be described as follows. RNA was extracted from the YBC strain during logarithmic growth, and cDNA was generated using the RNA as a template. Specific primers for each of the target genes (GPD1 and GPD2) and housekeeping genes (used as Ref genes) were synthesized and used for qPCR. The Ref gene used in the experiment was ALG9, and the size of the fragment amplified by the primers used was 147±3bp.
[0082] ALG9 forward primer: CTTTGAGTGCAAGTATCGCC (SEQ ID NO: 22)
[0083] ALG9 reverse primer: TGTGTAATTGTTCACCAAAGCC (SEQ ID NO: 23)
[0084] GPD1 (g1544) forward primer: GTCGATTCTCATGTTCGTGC (SEQ ID NO: 24)
[0085] GPD1 reverse primer: CTTAGCGACTTCAGTAGCGA (SEQ ID NO: 25) ...
Embodiment 3
[0090] Embodiment 3: the construction of the recombinant acid-resistant yeast strain that has deleted GPD gene
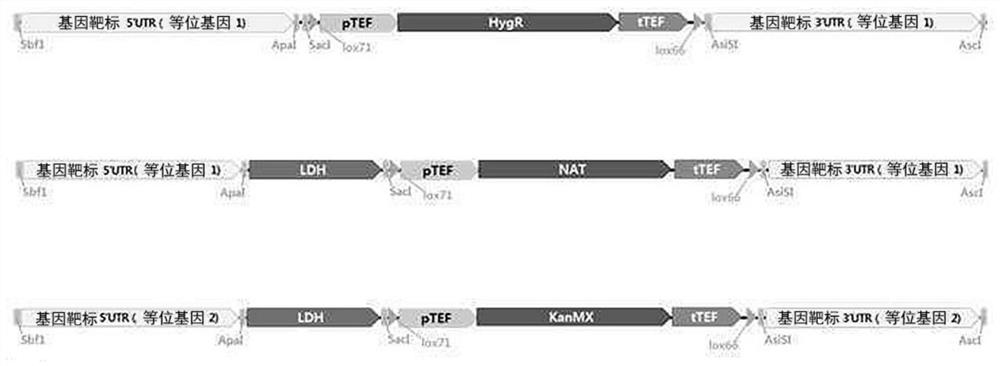
[0091]The g1544 gene, g5617 gene, g5443 gene and g4356 gene annotated with GPD1 gene, GPD2 gene, GPP1v1 gene and GPP1 v2 gene, respectively, were removed from the genome of this YBC strain to construct a strain.
[0092] The acid-resistant yeast strain used for the gene removal was the YBC1 strain constructed by introducing the LDH gene into this conventional YBC strain (instead of the YBC wild-type strain) and deleting ADH (alcohol dehydrogenase) therefrom, whereby, by introducing the LDH gene from the YBC1 The g3002-1 gene (PDC gene) was removed from the strain and LDH was introduced into it to construct a YBC2 strain capable of efficiently producing lactic acid and inhibiting ethanol production, and the YBC4 strain whose lactic acid consumption ability was removed was introduced into the strain by introducing the LDH gene and removing the lactic acid consumption ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com