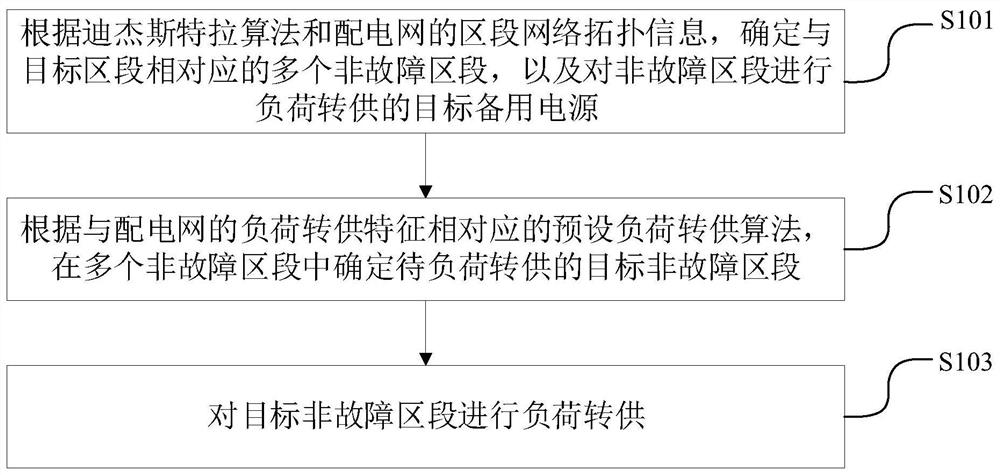
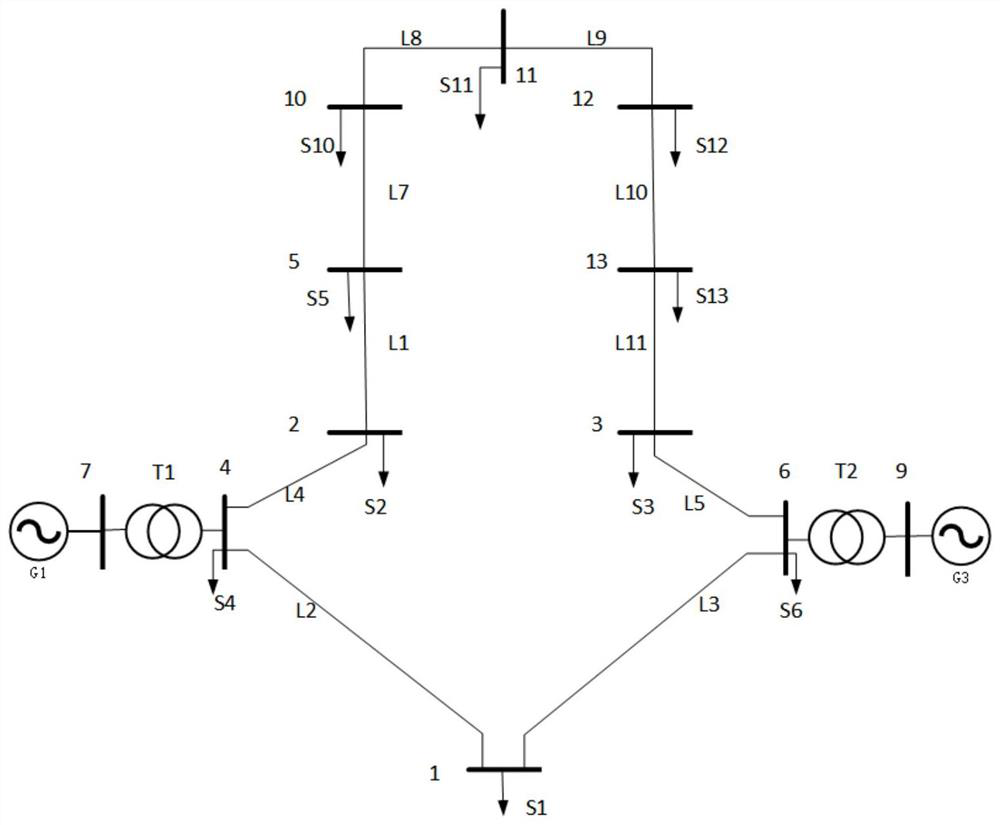
Power distribution network load transfer method and device, equipment and storage medium
A technology of load transfer and distribution network, applied in the field of distribution network, can solve problems such as poor load transfer effect, achieve the effect of improving reliability, improving load transfer effect, and improving load transfer capacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
[0093] When the load transfer characteristic is load transfer utilization rate, the rated load capacity of the non-fault section is taken as the value and weight of the knapsack algorithm, and the available load capacity is taken as the total weight of the knapsack algorithm, and the knapsack algorithm is used to determine the maximum The non-faulty section combination of load transfer utilization ratio, where the load transfer utilization rate is the ratio of all weights in the non-faulty section combination to the total weight;
[0094] All the non-faulty sections in the non-faulty section combination with the maximum load transfer utilization rate are determined as the target non-faulty sections.
[0095] First, a brief description of the 0-1 knapsack problem:
[0096] Suppose there are N kinds of items to be selected, each item is only 1 and indivisible, the value of item j is v(j), the weight is w(j), there is only 1 backpack and the total weight of the items that can be ...
no. 2 example
[0105] When the load transfer characteristic is the load level, sort multiple non-faulty sections according to the order of the load level from high to low and the distance between the non-faulty section and the target backup power supply from near to far;
[0106] Calculate the first difference between the total capacity of the rated load capacity of the first N non-faulty sections and the available load capacity, and the second difference between the total capacity of the rated load capacity of the first N+1 non-faulty sections and the available load capacity Value, N is a positive integer;
[0107] If the first difference is less than zero and the second difference is greater than zero, the top N non-faulty segments are determined as target non-faulty segments.
[0108] For all de-energized loads downstream of the fault point P i , sorting based on the importance of loads, that is, to restore first-level loads first, and then consider other ones. The purpose is to restore ...
no. 3 example
[0114] In the case that the load transfer characteristic is the load, sort the multiple non-faulty sections in the order of the load from large to small and the distance from the target backup power supply from near to far;
[0115] Calculate the third difference between the total capacity of the rated load capacity of the first M non-faulty sections and the available load capacity, and the fourth difference between the total capacity of the rated load capacity of the first M+1 non-faulty sections and the available load capacity Value, M is a positive integer;
[0116] If the third difference is less than zero and the fourth difference is greater than zero, the first M non-faulty segments are determined as target non-faulty segments.
[0117] For all de-energized loads downstream of the fault point P i , based on the perspective of load size, regardless of the load importance, the purpose of which is to reduce line loss and improve power supply efficiency.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com