Electrodialysis control method and device and water purifier
A control method and control device technology, applied in the field of water purifiers, electrodialysis control methods, and devices, can solve problems such as the temperature of the first cup of water cannot be reached, and the concentration of ions increases.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
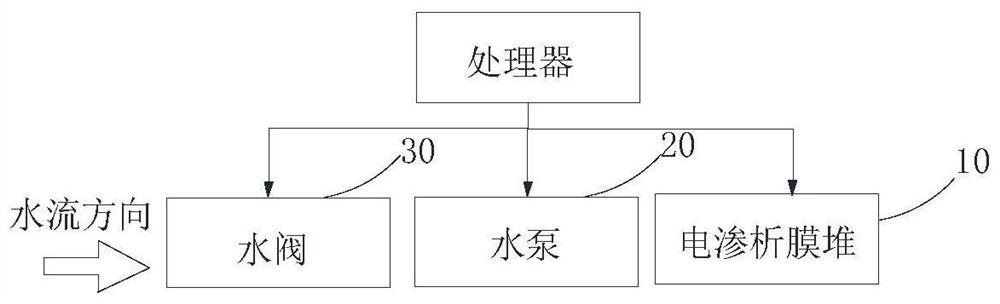
[0066] Embodiment 1 of the present invention provides an exemplary solution: provide a lower bias voltage to continuously supply pressure during shutdown to make the electrodialysis membrane stack work, so as to solve the problem of excessively high total dissolved solids value in the first cup of water.
[0067] see Figure 4 , Figure 4 It is a flow chart of the electrodialysis control method provided by Embodiment 1 of the present invention. In the embodiment of the present invention, the method to be executed in Embodiment 1 is:
[0068] Step S21: Determine that the electrodialysis membrane stack is in the running state, pass water to the electrodialysis membrane stack and apply a working voltage;
[0069] Step S22: Determine that the electrodialysis membrane stack is in a stopped state, and apply a bias voltage to the electrodialysis membrane stack.
[0070] It can be understood that when the electrodialysis membrane stack is in the running state, the electrodialysis m...
Embodiment 2
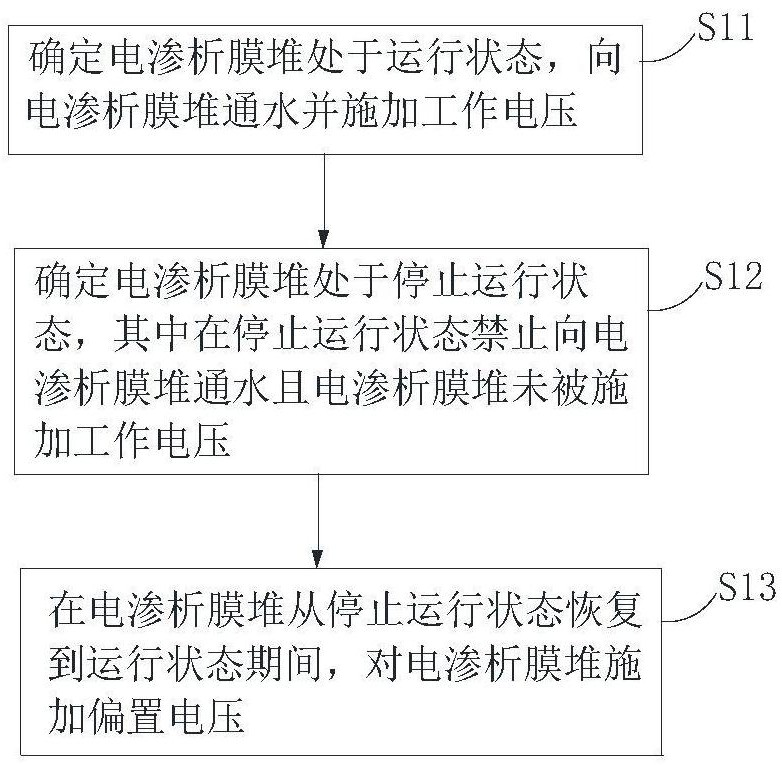
[0104] Embodiment 2 of the present invention provides an exemplary solution: do not pass water before each operation, apply a bias voltage to run for a period of time, and then apply water to apply a working voltage, so as to solve the problem that the total dissolved solids value of the first cup of water is too high .
[0105] see Figure 10 , Figure 10 It is a flow chart of the electrodialysis control method provided by the second embodiment of the present invention. In the embodiment of the present invention, the method to be executed in Embodiment 2 is:
[0106] Step S31, confirming that the electrodialysis membrane stack is in the running state, passing water to the electrodialysis membrane stack and applying a working voltage;
[0107] Step S32, determining that the electrodialysis membrane stack is in a shutdown state, wherein water flow to the electrodialysis membrane stack is prohibited in the shutdown state and no operating voltage is applied to the electrodialy...
Embodiment 3
[0140] Embodiment 3 of the present invention provides an exemplary solution: other methods are the same as Embodiment 1 and Embodiment 2, but only pass the water for a preset time after each stop, so as to solve the total dissolved solids value of the first glass of water Too high problem.
[0141] Specifically, the present invention is based on the method provided in Example 2. After the electrodialysis membrane stack is stopped, water is input to the electrodialysis membrane stack with frequent electrode reversal for cleaning, so as to avoid deposition of the membrane stack and can Dilute the high concentrated water to prevent the concentrated water from penetrating into the fresh water area.
[0142] In order to explain this scheme more clearly, it is also explained through a controlled experiment:
[0143] Control group: the total dissolved solids value of the municipal water entering the electrodialysis membrane stack is 500ppm, the working voltage of 20V is applied to t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com