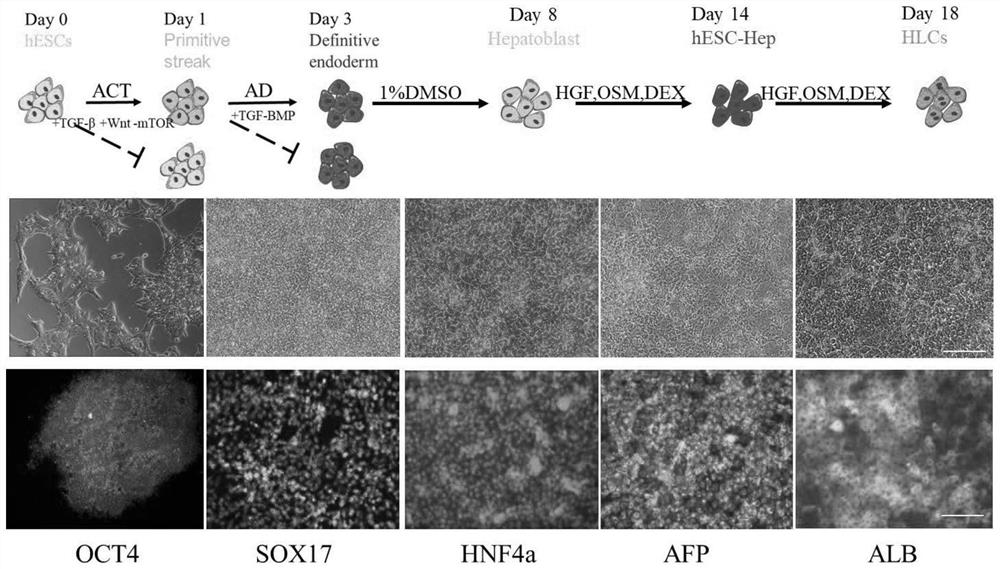
Induced differentiation method for efficiently shaping entoderm cells
A technique for finalizing endoderm and inducing differentiation, applied to embryonic cells, biochemical equipment and methods, germ cells, etc., can solve the problems of high differentiation cost, incomplete differentiation, and low differentiation efficiency, and achieve the effect of reducing costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0059] Taking induced differentiated liver sample cells as an example, a method of inducing differentiation of highly active constitutive endoderm cells, including the following steps:
[0060] A, DAY0, adding A (Activin A), C (CHIR999021), T (Torin 2) in stem cells for inducing differentiation, in the first stage medium, and the concentration of A is 20 ng / ml, C is 3 μm, T is 15 nm;
[0061] B, DAY1, the addition of A and D (LDN193189 / DM3189) induced by 20 ng / ml, D of 250 nm, and 2 days in the first stage medium completed 2 days. Stage.
[0062] C, DAY3, after completing the stages of the steering endoderm cells, into induce the hepatic procedure stage, add dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) induction differentiation, and completed the induced hepatic procedure stage in the second stage medium, DMSO concentration is 1 %;
[0063] D, DAY8, completing the induced hepatic progenitor cell stage, into induced hepatic cell stage, adding hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), antimotonin M, sugar...
Embodiment 2
[0071] Taking induced differentiated liver sample cells as an example, a method of inducing differentiation of highly active constitutive endoderm cells, including the following steps:
[0072] A, DAY0, adding A (Activin A), C (LY2090314), T (RAPAMYCIN) in stem cells to cultivate in the first stage medium, and a concentration of A is 100 ng / ml, C is 10 μm, T 1000 nm;
[0073] B, DAY1, the addition of A and D (K02288) induced by 10 ng / mL, D of 1000 nm, and 2 days in the first stage medium completed 2 days in the first phase of the cell.
[0074]C, DAY3, after completing the stages of the steering endoderm cells, into induce the hepatic procedure stage, add dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) induction differentiation, and completed the induced hepatic procedure stage in the second stage medium, DMSO concentration is 1 %;
[0075] D, DAY8, completing the induced hepatic progenitor cell stage, into induced hepatic cell stage, adding hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), antimotonin M, sugar cort...
Embodiment 3
[0081] Taking induced differentiated liver sample cells as an example, a method of inducing differentiation of highly active constitutive endoderm cells, including the following steps:
[0082] A, DAY0, adding A (Activin A), C (SAR502250), T (mtor inhibitor-3) in stem cells to induce differentiation, in the first stage medium, and the concentration of A is 5 ng / ml, C is 1μm, T is 10 nm;
[0083] B, DAY1, the addition of A and D (LDN193189) induced by 5 ng / mL, D of 10 nm, and completed 2 days in the first stage medium for 2 days to complete the stereotype endoderm cell stage.
[0084] C, DAY3, after completing the stages of the steering endoderm cells, into induce the hepatic procedure stage, add dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) induction differentiation, and completed the induced hepatic procedure stage in the second stage medium, DMSO concentration is 1 %;
[0085] D, DAY8, completing the induced hepatic progenitor cell stage, into induced hepatic cell stage, adding hepatocyte growt...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com