Rapid calibration method for directional antenna angle based on celestial body tracking scanning
A directional antenna and celestial body technology, which is applied in the field of aerospace measurement and control, can solve the problems of high cost, poor mobility, and high calibration cost, and achieve the effects of improving mobility, reducing costs, and improving deployment efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0030] In order to more clearly describe the embodiments of the present invention or the technical solutions in the prior art, the following will briefly introduce the drawings that are used in the embodiments. Apparently, the drawings in the following description are only some embodiments of the present invention, and those skilled in the art can also obtain other drawings according to these drawings without creative efforts.
[0031] The present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments, and the embodiments cannot be repeated here one by one, but the embodiments of the present invention are not therefore limited to the following embodiments.
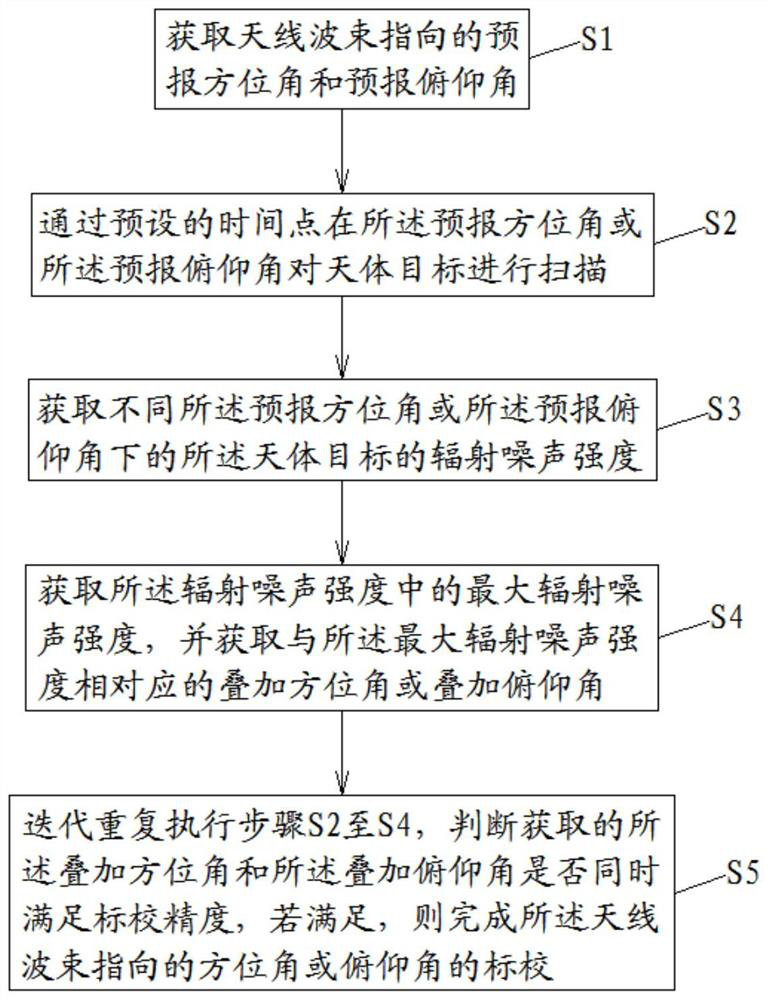
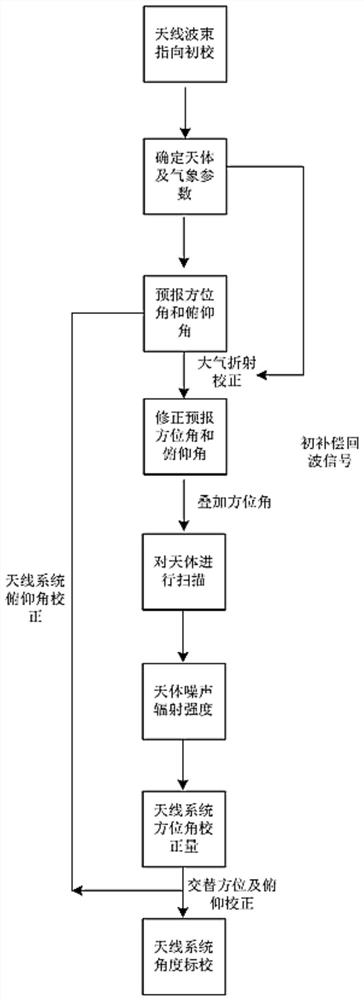
[0032] combine figure 1 and figure 2 As shown, according to an embodiment of the present invention, a method for quickly calibrating the directional antenna angle based on celestial body tracking and scanning of the present invention includes:
[0033] S0. Carr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com