A Series-Parallel Composite Pulse Multiplication Circuit Applied to the DC Side of the Rectifier
A technology of multiplication circuit and DC side, which is applied in the field of power electronics, can solve the problems of complex structure of pulse multiplication circuit and poor harmonic suppression ability, and achieve the effect of high reliability, small number of components and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
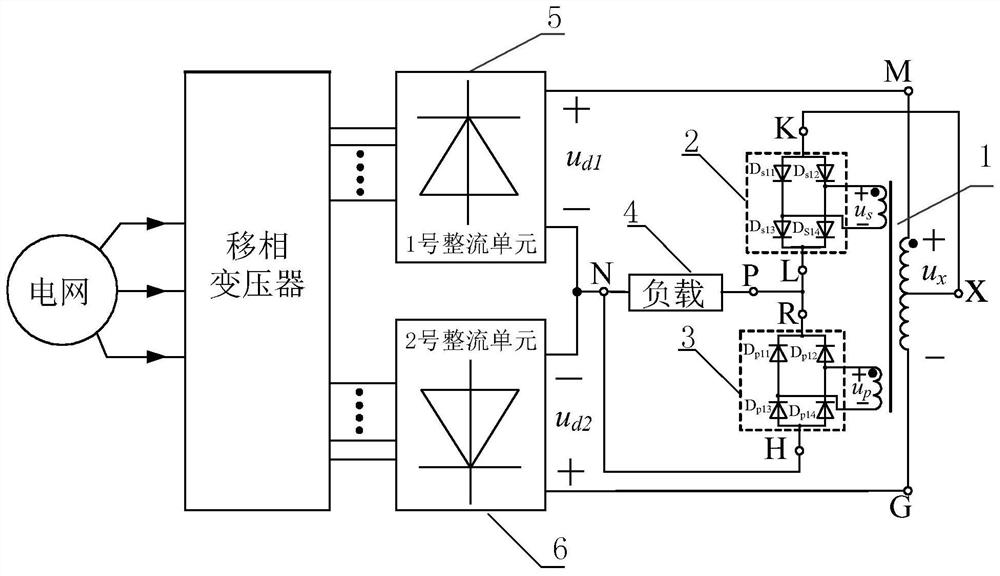
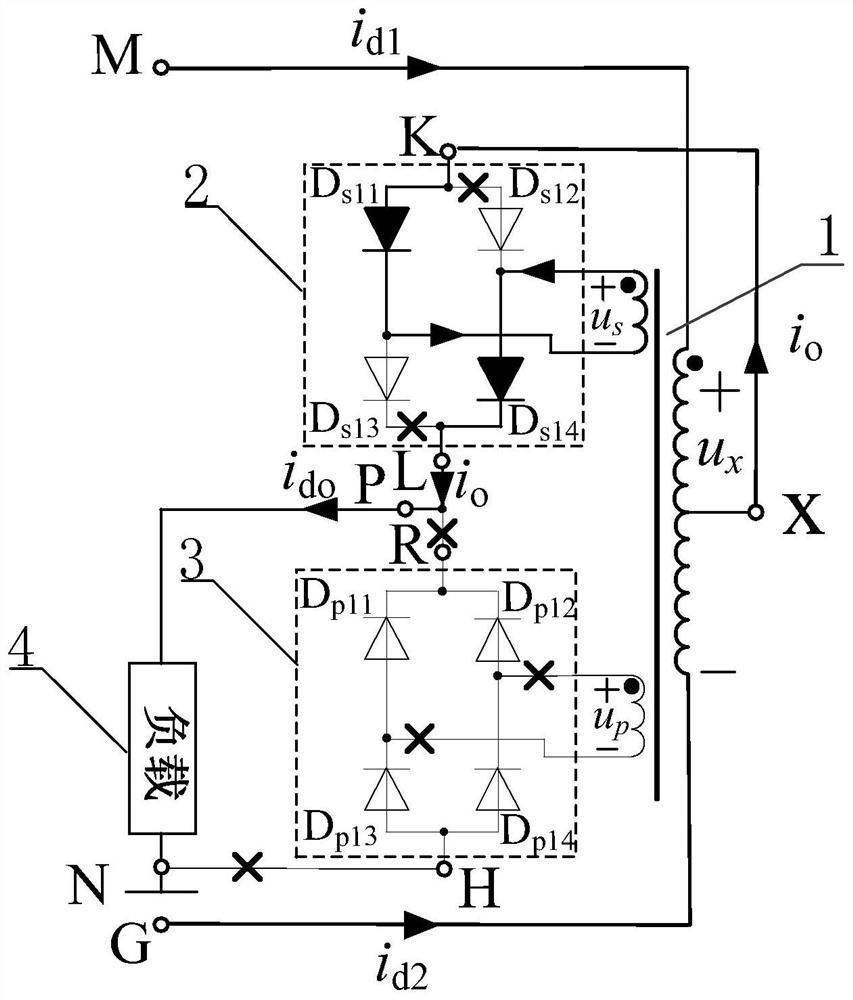
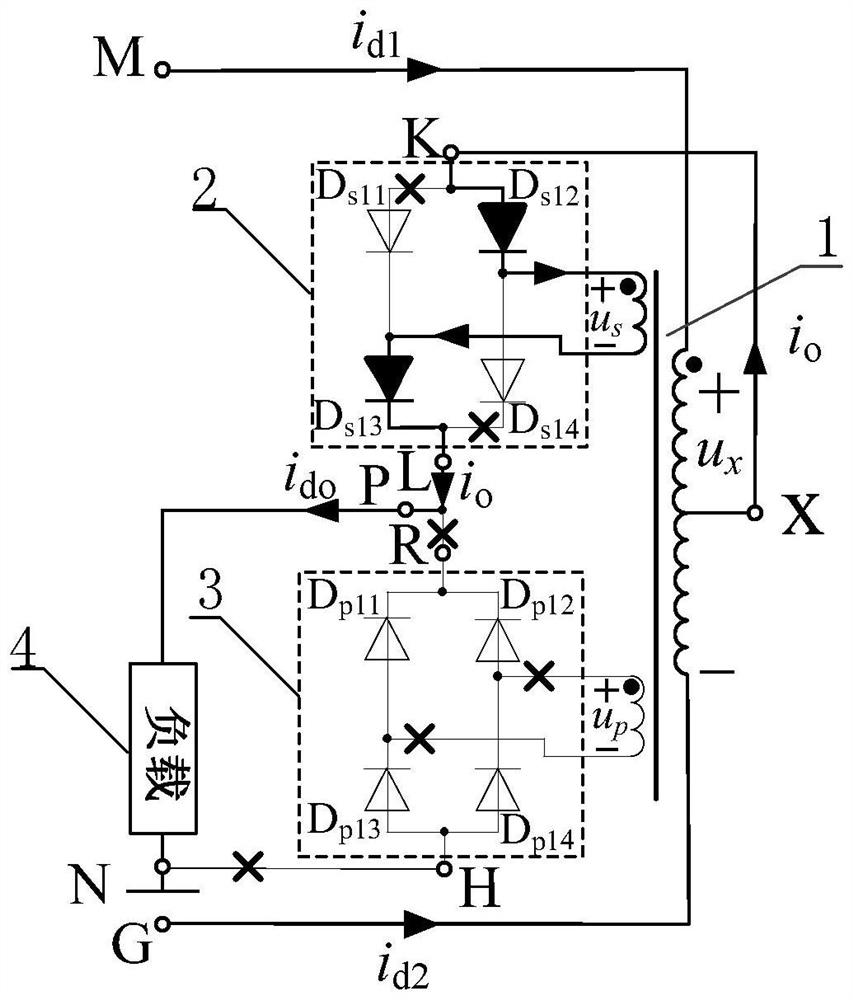
[0104] combine figure 1 , Figure 6 , Figure 11 and Figure 16 To illustrate this embodiment, the embodiment described
[0105] A series-parallel composite pulse multiplication circuit applied to the DC side of the rectifier,
[0106] Including a balanced reactor 1 with dual secondary windings;
[0107] The primary winding of the balanced reactor 1 with dual secondary windings is used to balance the instantaneous output voltage from the No. 1 rectifier unit 5 and the No. 2 rectifier unit 6, and the balanced electric energy supplies power to the load 4;
[0108] Also included are two single-phase rectifiers for increased pulse count;
[0109] The output end of each secondary winding of the balanced reactor 1 with double secondary windings is respectively connected to the input end of a single-phase rectifier, wherein the output end of one single-phase rectifier is connected in series in the circuit where the load 4 is located, and the other single-phase rectifier The out...
Embodiment 1-1
[0120] see figure 1 To illustrate this embodiment, the preferred embodiment 1-1 of the coordination mode between the balanced reactor 1 with double secondary windings and the single-phase rectifier in this embodiment 1 is:
[0121] When both secondary windings of the balanced reactor 1 with double secondary windings are secondary windings without a center tap, both single-phase rectifiers are single-phase full-bridge rectifiers.
[0122] The present invention only needs to connect a single-phase full-bridge rectifier to the outputs of the two secondary windings of the balanced reactor 1 with double secondary windings respectively, so that the effect of multiplying the pulse number of the rectifier by 3 times can be realized. The circuit has a circuit It has the advantages of simple structure, easy realization, few components and low cost.
[0123] see figure 1 Illustrate preferred embodiment 1-1, the preferred mode of two single-phase full-bridge rectifiers in preferred embo...
Embodiment 1-2
[0142] see Figure 11 To illustrate this embodiment, the preferred embodiment 1-2 of the coordination mode between the balanced reactor 1 with double secondary windings and the single-phase rectifier in this embodiment 1 is:
[0143] When both secondary windings of the balanced reactor 1 with double secondary windings are secondary windings with a center tap, both single-phase rectifiers are single-phase full-wave rectifiers.
[0144] The present invention only needs to connect a single-phase full-wave rectifier to the outputs of the two secondary windings of the balanced reactor 1 with double secondary windings respectively, so that the effect of multiplying the pulse number of the rectifier by 3 times can be realized. The circuit has a circuit It has the advantages of simple structure, easy realization, few components and low cost.
[0145] see Figure 11 Illustrate preferred embodiment 1-2, the preferred mode of two single-phase full-wave rectifiers in preferred embodimen...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com