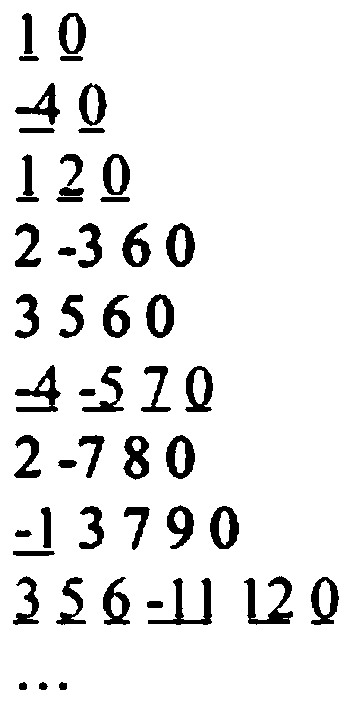Target algorithm prediction method for Boolean satisfiability problem based on graph
A technology of Boolean satisfiability and prediction methods, applied in the computer field, can solve problems such as impossible to understand, save considerable cost, time-consuming, etc., and achieve the effect of saving the cost of artificial design features
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0034] The present invention will be further explained below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
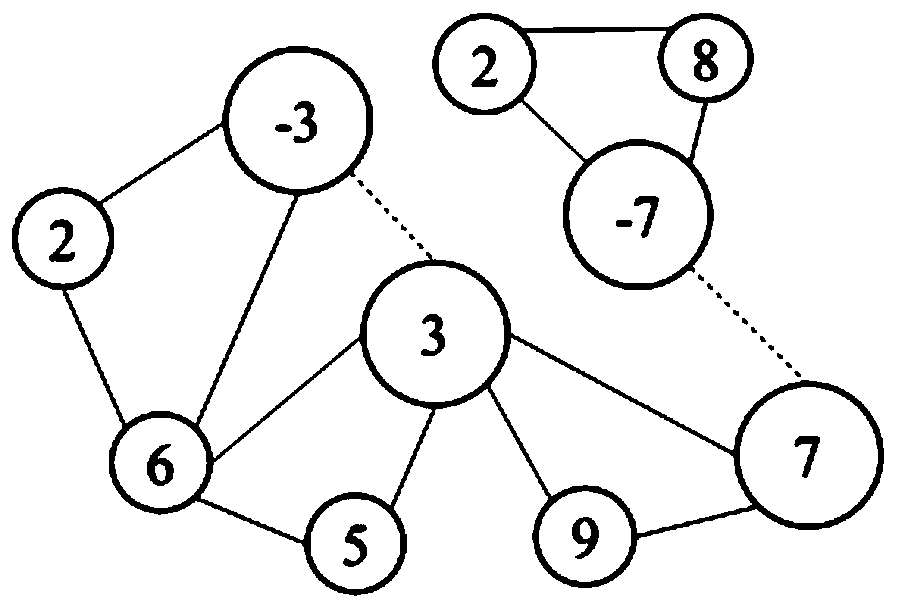
[0035]The Conjunctive Normal Form (CNF) representation of the Boolean satisfiability problem (SAT) is composed of strings line by line, such as figure 1 As shown in , each line represents a disjunctive item (clause), the number separated by spaces in the line is the number of the proposition variable (variable), and the number 0 at the end of the line is a newline placeholder. When constructing a graph structure, each propositional variable is regarded as a node of the graph. It should be noted that the normal form and its logical non-form of the same propositional variable represent different nodes respectively. If any two different variables appear in the same disjunction item at the same time, an edge is made between these two nodes. In addition, if a variable has two states, an edge is also required between these two nodes side to describe this relationship. Two ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com