Elevator Group Control Method for Predicting Passenger Riding Demand
A control method and elevator group technology, applied in the field of elevator control, can solve problems such as failure to analyze passengers in depth and failure of elevator ride requirements, and achieve the effects of improving ride experience, avoiding invalid waiting, and eliminating waiting time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] In this embodiment, the control method of an elevator group that predicts passenger demand for elevators, the elevator group includes multiple elevators and provides transportation services for passengers in a group manner, wherein:
[0025] Utilize a learning unit to learn the passenger's elevator habits and output to a policy determination unit, the learning unit learns according to the historical elevator operation data related to the passenger's trip by elevator;
[0026] Using the strategy determination unit to determine the control strategy of the elevator according to the elevator habit output by the learning unit;
[0027] using an allocation unit to allocate the elevators of the elevator group according to the control strategy determined by the strategy determination unit;
[0028] A control unit is used to control the elevators of the elevator group according to the dispatching result of the dispatching unit.
[0029] The elevator-riding habit is a general te...
Embodiment 2
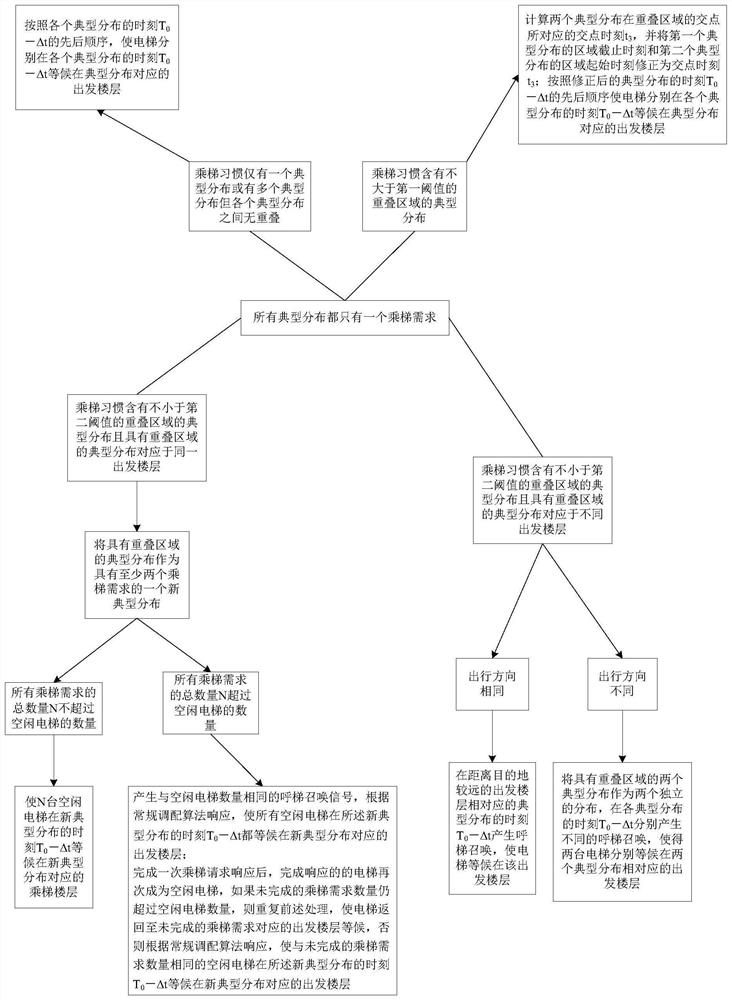
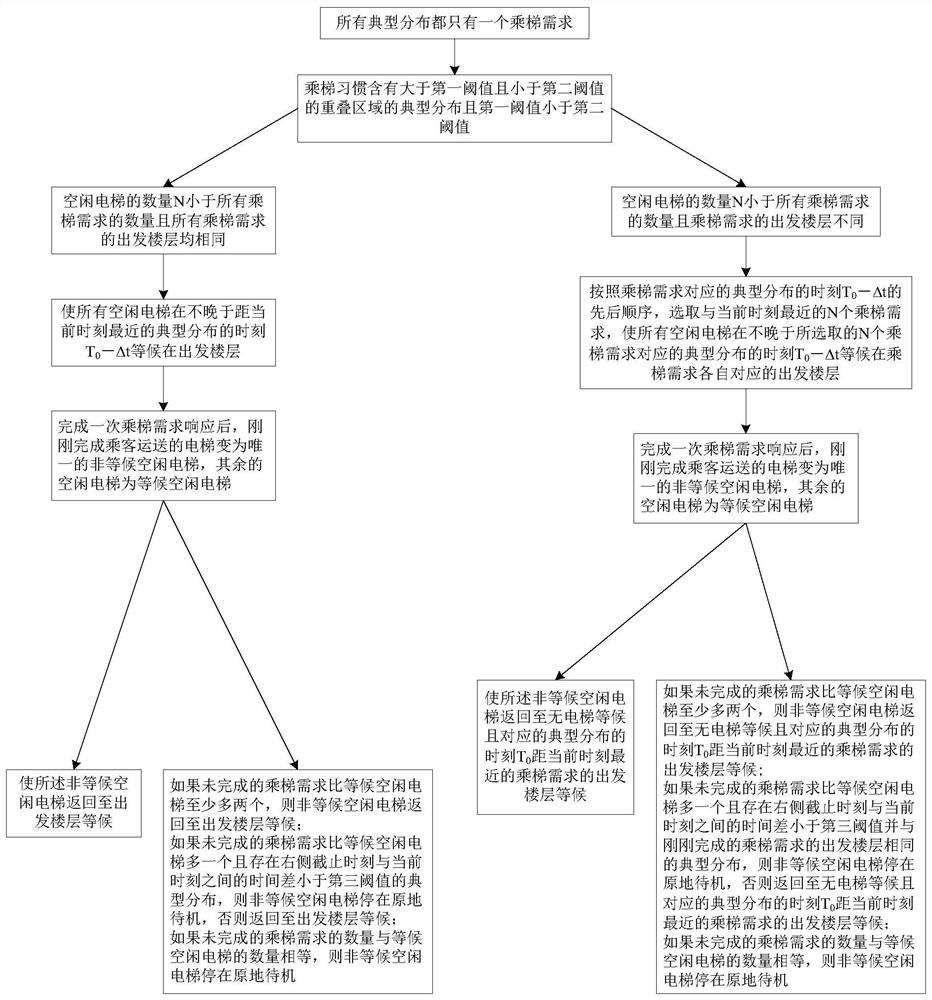
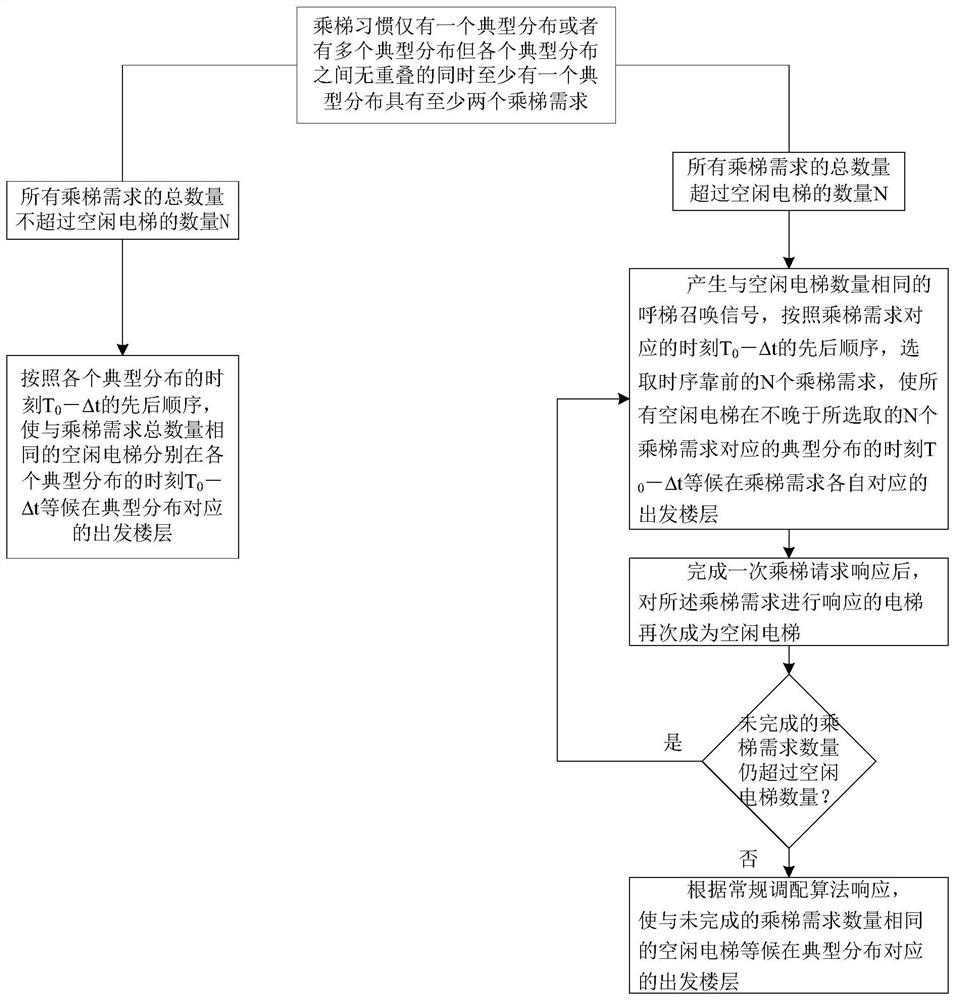
[0102] The principle of this embodiment is similar to that of Embodiment 1, except that this embodiment is mainly aimed at the situation that at least one typical distribution has at least two ride demands. The control strategy determined by the strategy determination unit in the control method of the elevator group is as follows: Figure 3 to Figure 7 shown. The specific rules for determining the control strategy are as follows:
[0103] 1) When the elevator habit has only one typical distribution or multiple typical distributions but there is no overlap between the typical distributions (non-overlap means that the time distance between two adjacent typical distributions is sufficient to ensure that the elevator completes a running cycle ) and the total number of all elevator demands does not exceed the number N of idle elevators, such as image 3 As shown, the control strategy determined by the strategy determination unit is: according to the time T of each typical distrib...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com