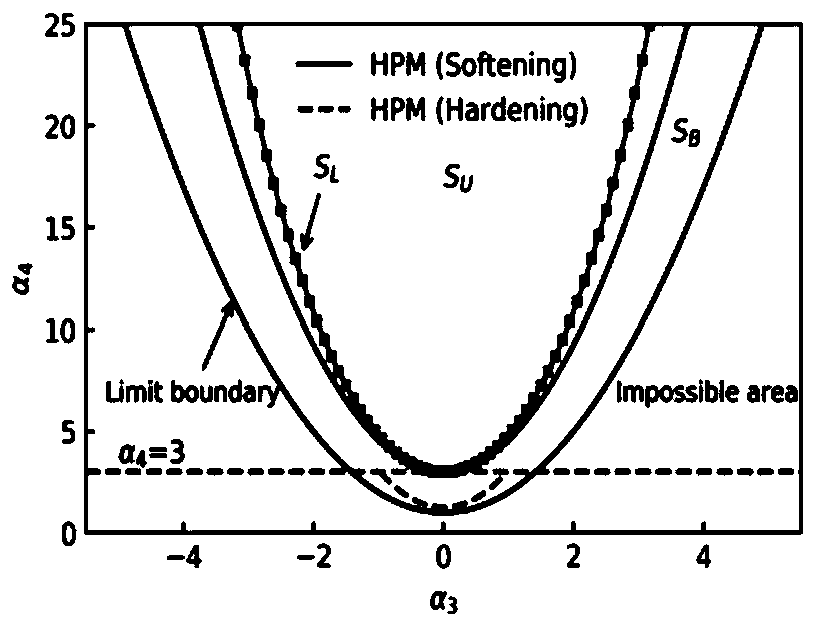
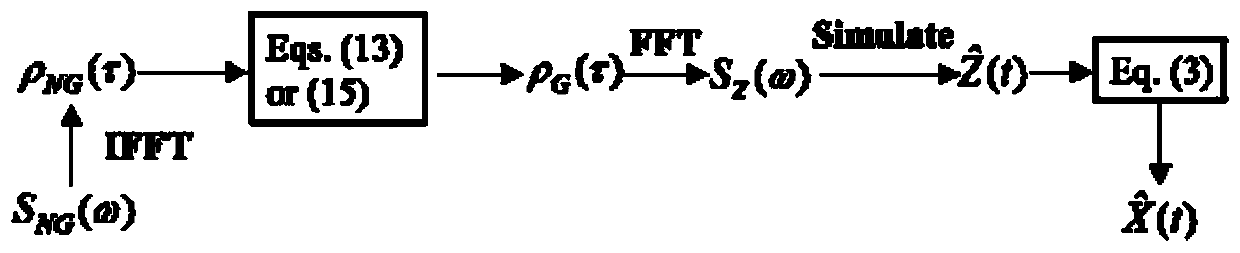
non-Gaussian wind pressure simulation method based on Johnson transformation
A simulation method, a technology for transforming models, applied in the field of non-Gaussian process simulation, and can solve problems such as the limited feasible area of Hermite
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
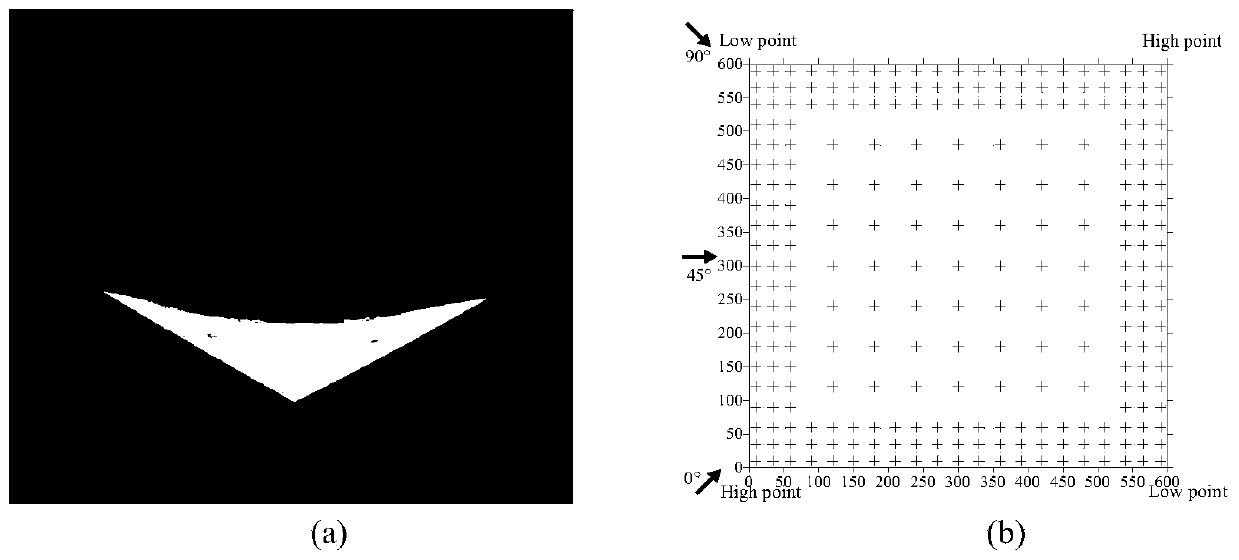
[0128] The present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments. The measured wind pressure data used in the numerical case comes from wind pressure experiments on saddle-shaped long-span roofs completed in the wind tunnel laboratory of Beijing Jiaotong University. Saddle roof models such as image 3 (a) shown. The scale ratio of the model is 1:100, and a total of 265 measuring points are arranged on the roof. The specific measuring point layout and wind direction angle definition are shown in Figure 3(b). The average wind speed at the reference height is 8.95m / s, and the sampling frequency and duration are 312.5Hz and 55min, respectively. The ratio of the model to the actual wind speed is 1:2, therefore, the corresponding actual sampling frequency and duration are 6.25Hz and 2750min, respectively. This paper only considers the case where the orientation angle is 90°. For details, please refer to...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com