A high-value customer identification method, system, device and storage medium
A customer identification, high-value technology, applied in character and pattern recognition, instruments, calculations, etc., to achieve high recognition accuracy and strong pertinence
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
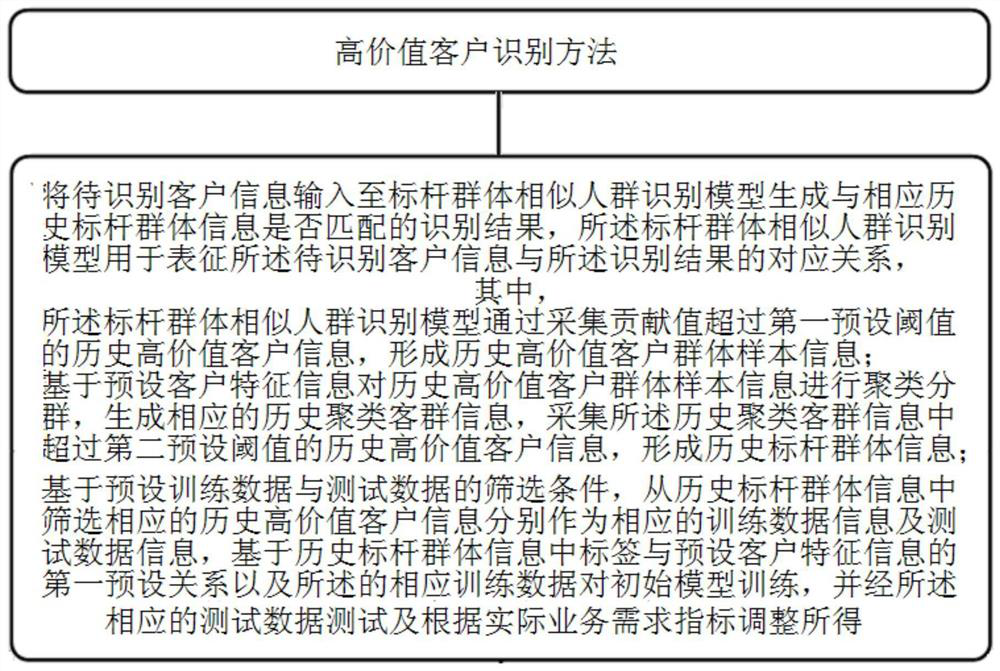
[0056]This embodiment provides a method for identifying high-value customers, such asfigure 1 As shown, including the following steps:
[0057]S1. Collect historical high-value customer information whose contribution value exceeds the first preset threshold to form historical high-value customer group sample information. Specifically, you can select the past year's contribution income (high value) to rank in the top n1Of customers, form historical high-value customer group sample information to identify high-value groups, among which the first preset threshold n is determined according to actual business conditions1Value (may be 5%-10%);
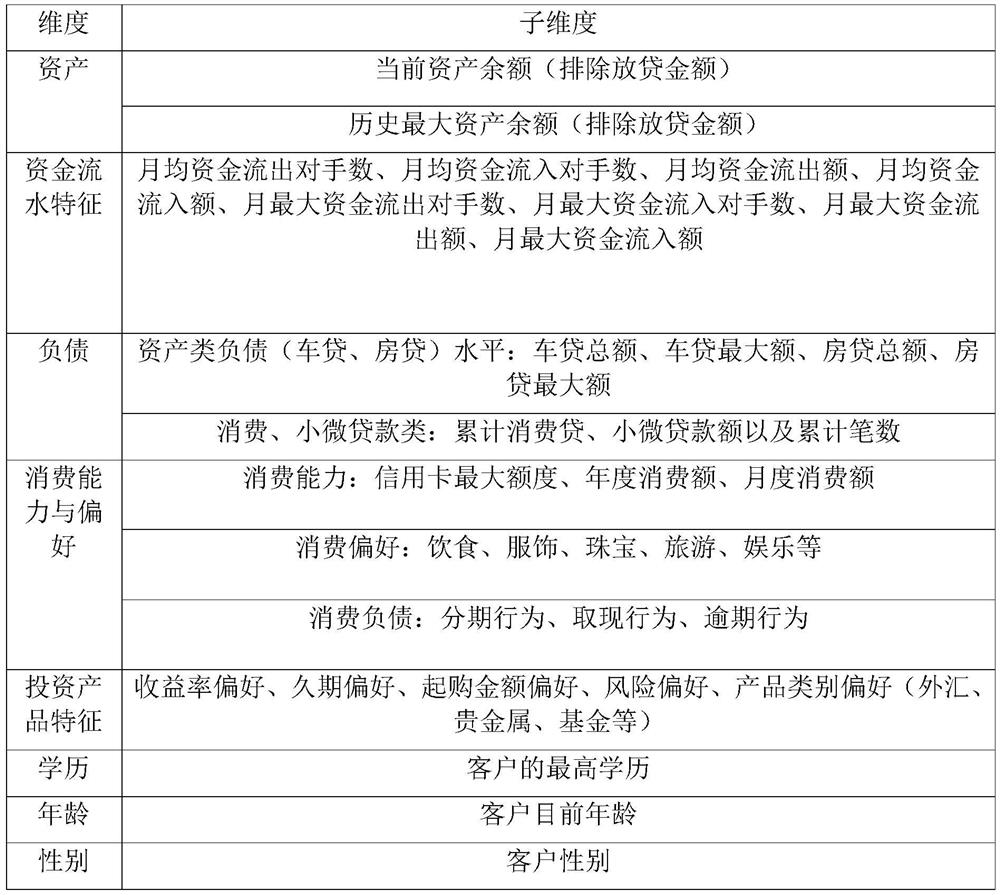
[0058]S2. Clustering and grouping sample information of historical high-value customer groups based on preset customer characteristic information. The preset customer characteristic information includes assets, turnover characteristics, liabilities, consumption power and preferences, investment product characteristics, and basic personal characteristics...
Embodiment 2
[0111]The features of this embodiment that are the same as those of the first embodiment will not be repeated here. The features of this embodiment are different from those of the first embodiment:
[0112]Specifically, you can select the top n of contribution income (high value) in the past six months1Of customers, form historical high-value customer group sample information to identify high-value groups, among which the first preset threshold n is determined according to actual business conditions1Value (can be 5%);
[0113]S221. Discard features with a high missing rate. The cleaning features may be incomplete due to different business conditions, and the removal rate is greater than n3Characteristics of n3It can be 10%.
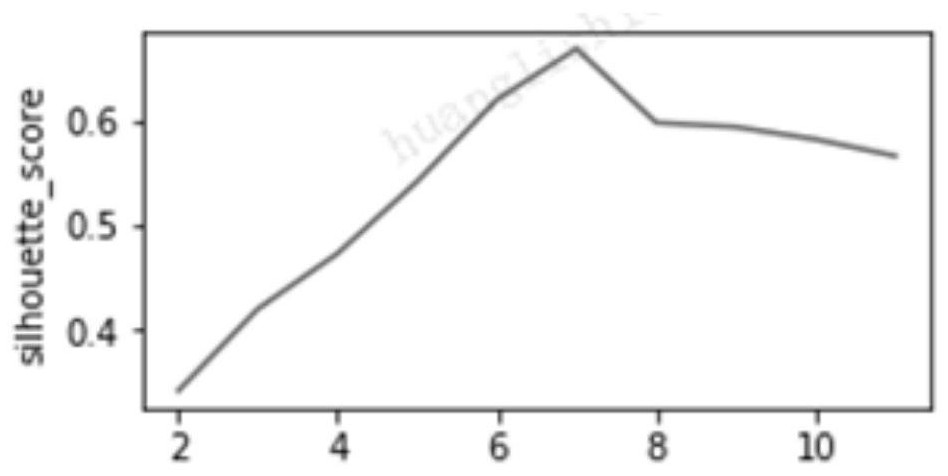
[0114]S23. To TOP n1Customers are clusters of samples of historical high-value customer groups to obtain k historical clustered customer groups. Take the K-means algorithm as an example, use the contour coefficient method to determine the number of clusters, that is, tr...
Embodiment 3
[0125]The features of this embodiment that are the same as those of the first embodiment will not be repeated here. The features of this embodiment are different from those of the first embodiment:
[0126]Specifically, you can select the top n of contribution income (high value) in the past year1Of customers, form historical high-value customer group sample information to identify high-value groups, among which the first preset threshold n is determined according to actual business conditions1Value (can be 10%);
[0127]S221. Discard features with a high missing rate. The cleaning features may be incomplete due to different business conditions, and the removal rate is greater than n3Characteristics of n3It can be 30%.
[0128]S23. To TOP n1Customers are clusters of samples of historical high-value customer groups to obtain k historical clustered customer groups. Take the K-means algorithm as an example, use the contour coefficient method to determine the number of clusters, that is, try to ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com