Fracturing lamination propping agent
A proppant and film coating technology, which is applied in the directions of production fluid, wellbore/well components, drilling composition, etc., can solve the problem of high friction resistance of sand-carrying water pumping, and achieve moderate viscosity, good drag reduction performance, Good fluidity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
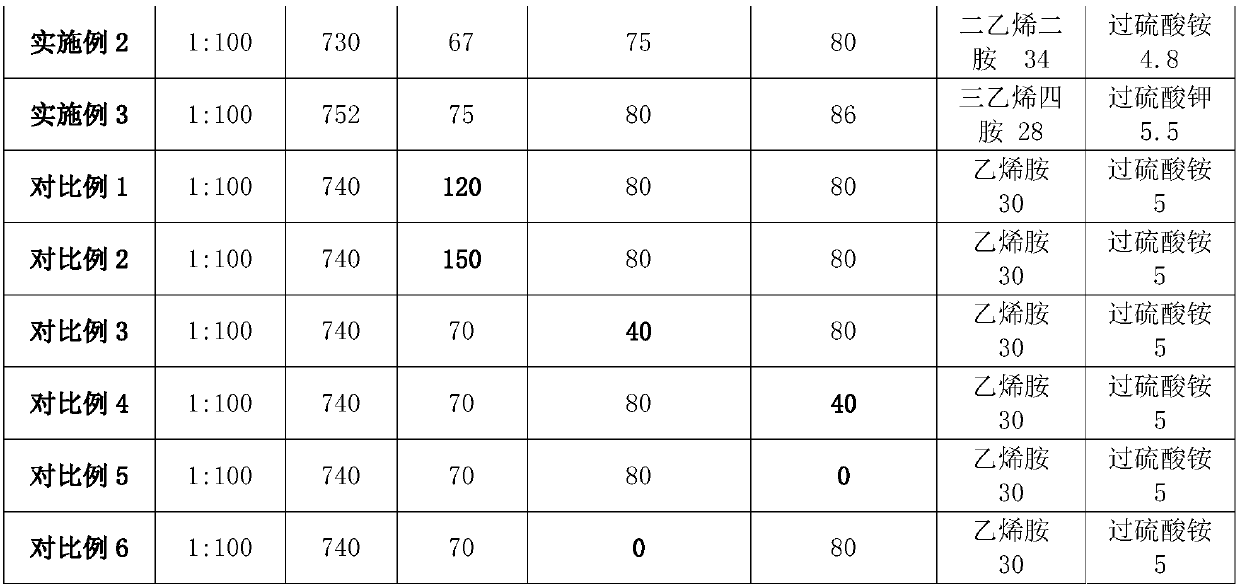
[0033] This embodiment discloses a film-coated proppant for fracturing, which includes a proppant body and a drag-reducing membrane base material covering the surface of the proppant body, and the mass-number ratio of the drag-reducing membrane base material to the proppant body is 1: 100. The drag-reducing film base material is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by mass: 740 parts of water, 70 parts of acrylamide, 80 parts of 2-acrylamido-2-methylpropanesulfonic acid, 30 parts of polyenylamine, dimethyl dimethicone 80 parts of allyl ammonium chloride and 5 parts of initiator; ammonium persulfate is selected as the initiator, and vinylamine is selected as the polyenamine; the drag reducing film base material can also include the following raw materials, the concentration is 1% sodium hydroxide solution .
[0034] In this embodiment, the proppant body is made of the following raw materials in parts by mass: 100 parts of aggregate, 5 parts of resin and 2 parts o...
Embodiment 4
[0046] The difference between Example 4 and Example 1 is that in this example, the proppant body includes aggregate and a film layer wrapped outside the aggregate, and the film layer is prepared from resin, curing agent, catalyst and amine compound . The aggregate is 30 / 50 quartz sand, the resin is propanol polymer, the curing agent is diphenylmethane diisocyanate, the catalyst is lead isooctanoate, and the amine compound is ethylenediamine. Among them, 100 parts of aggregate, 2.5 parts of resin, 2 parts of curing agent, 0.02 parts of catalyst, and 0.3 parts of amine compound;
[0047] The preparation process of the corresponding proppant body in step (5) is: heating the aggregate to 95°C, adding resin and catalyst, mixing and stirring; when the temperature drops to 85°C, adding amine compounds, stirring and mixing; when the temperature drops to 75°C, add the curing agent, mix and stir; the temperature drops to 50°C, take out the pot, and get the proppant body.
Embodiment 5
[0049] The difference between Example 5 and Example 1 is that in this example, the proppant body includes aggregate and a film layer wrapped outside the aggregate, and the film layer is prepared from resin, curing agent, catalyst and amine compound . The aggregate is 30 / 50 quartz sand, the resin is glycerol polymer, the curing agent is toluene diisocyanate, the catalyst is tributyltin, and the amine compound is diethylenetriamine. Among them, 100 parts of aggregate, 3 parts of resin, 2 parts of curing agent, 0.02 parts of catalyst, and 0.3 parts of amine compound;
[0050] The preparation process of the corresponding proppant body in step (5) is: heating the aggregate to 105°C, adding resin and catalyst, mixing and stirring; when the temperature drops to 95°C, adding amine compounds, stirring and mixing; when the temperature drops to 75°C, add the curing agent, mix and stir; the temperature drops to 50°C, take out the pot, and get the proppant body.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com