Dock-based dynamic displacement remote monitoring system and method
A remote monitoring and wharf technology, applied in the field of dock-based dynamic displacement remote monitoring system, can solve the problems of unable to monitor the status of the wharf, unable to deal with it in time, unattended, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0051] figure 1 and figure 2 It is a schematic diagram of a dock-based dynamic displacement remote monitoring system provided by an embodiment of the present invention.
[0052] The system is suitable for monitoring the dynamic displacement of the wharf infrastructure under harsh environments such as storm surges, and realizes the functions of collection, wireless transmission, storage, remote control and intelligent analysis of the dynamic displacement signal of the wharf structure, and meets the conditions of all working conditions of the wharf structure Under the multi-point monitoring of dynamic displacement.
[0053] refer to figure 1 and figure 2 , the system includes: an acquisition system 10, a local data storage system 50, a monitoring processing module 60 and an alarm 70, the acquisition system 10 includes a structural displacement sensor group 15, and the structural displacement sensor group 15 includes a lateral displacement sensor 16, a longitudinal displacem...
Embodiment 2
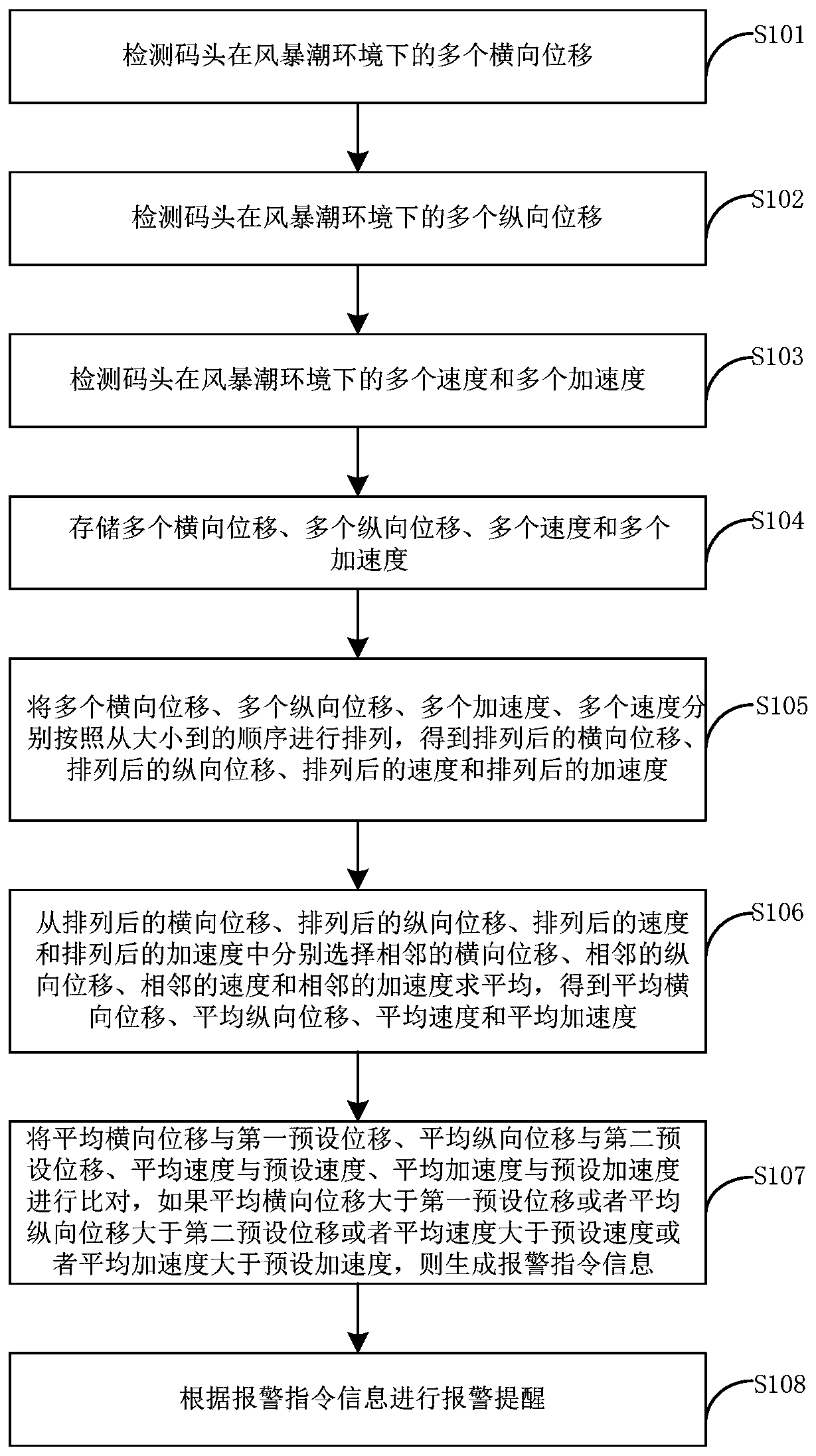
[0085] image 3 It is a flow chart of the dock-based dynamic variable remote monitoring method provided by Embodiment 2 of the present invention.
[0086] refer to image 3 , the method includes the following steps:
[0087] Step S101, monitoring the lateral displacement of the wharf in a storm surge environment;
[0088] Step S102, monitoring the longitudinal displacement of the wharf in a storm surge environment;
[0089] Step S103, monitoring the speed and acceleration of the wharf in a storm surge environment;
[0090] Step S104, storing lateral displacement, longitudinal displacement, velocity and acceleration;
[0091] Step S105, arranging multiple lateral displacements, multiple vertical displacements, multiple accelerations, and multiple velocities in order from size to to obtain the horizontal displacement after arrangement, the longitudinal displacement after arrangement, the velocity after arrangement and the arrangement after the acceleration;
[0092] Step S...
Embodiment 3
[0097] Figure 4 It is a schematic diagram of the electronic device provided by Embodiment 3 of the present invention.
[0098] refer to Figure 4 , the electronic device includes: a processor 30, a memory 31, a bus 32 and a communication interface 33, the processor 30, the communication interface 33 and the memory 31 are connected through the bus 32; the processor 30 is used to execute the executable module stored in the memory 31, For example a computer program. The processor implements the steps of the methods described in the method embodiments when the processor executes the program.
[0099] Wherein, the memory 31 may include a high-speed random access memory (RAM, Random Access Memory), and may also include a non-volatile memory (non-volatile memory), such as at least one disk memory. The communication connection between the system network element and at least one other network element is realized through at least one communication interface 33 (which may be wired or...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com