Adaptive alternating successive approximation analog-to-digital converter with low power consumption, and control method
A successive approximation, analog-to-digital converter technology, applied in the direction of analog/digital conversion, code conversion, instruments, etc., can solve the problem of increasing judgment and quantization steps, switching power consumption, comparing power consumption, digital control power consumption, increasing area and Power consumption and other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
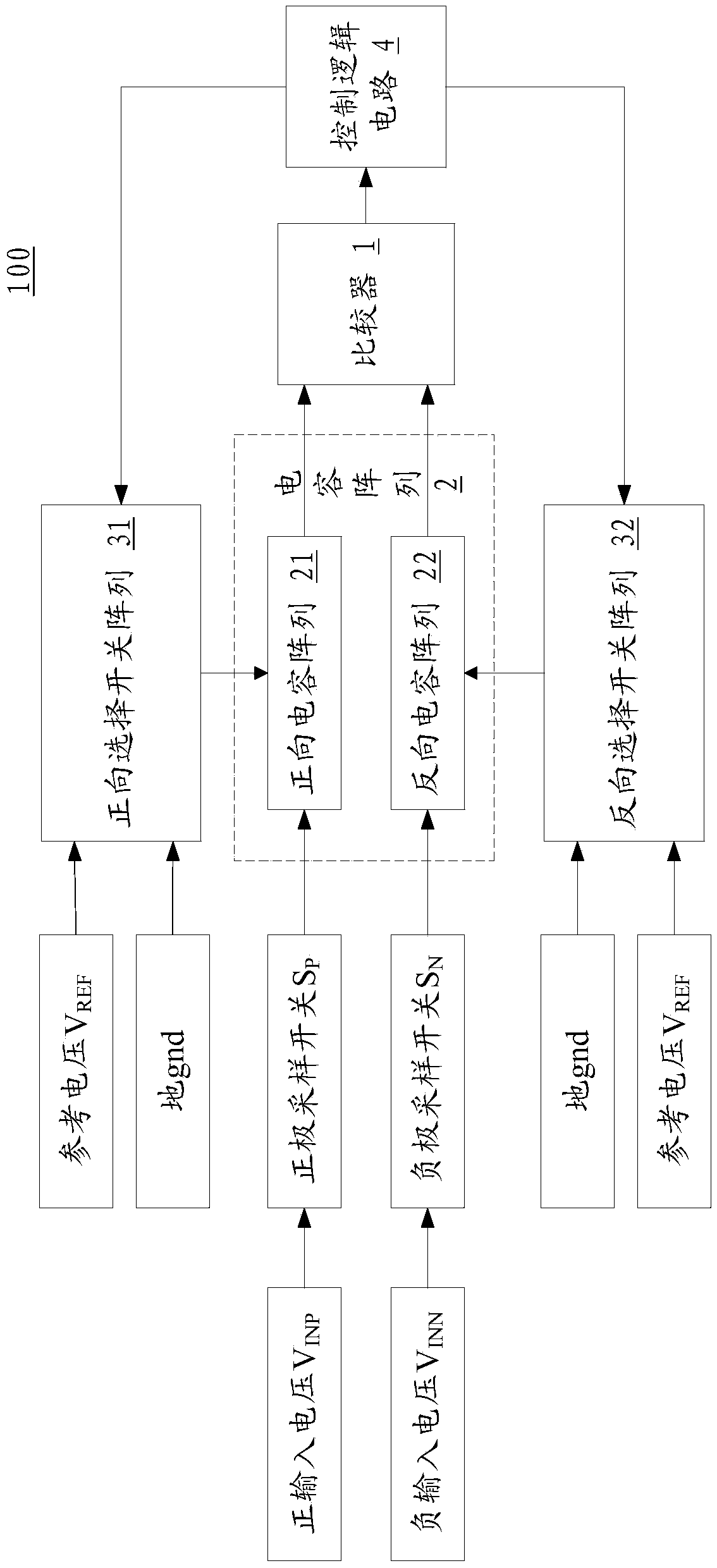
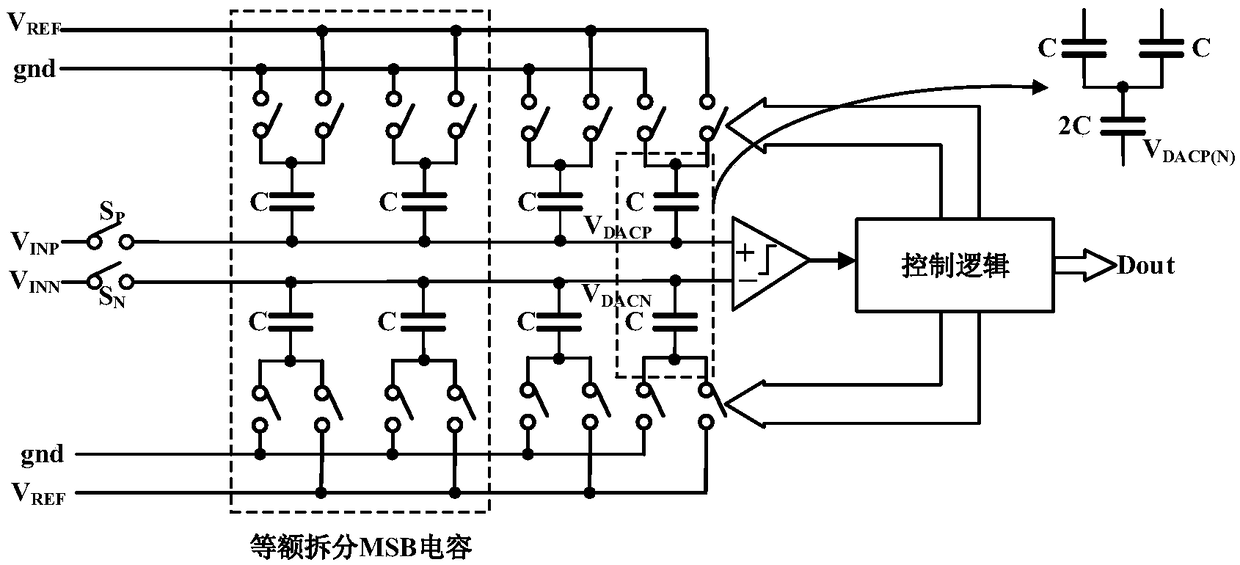
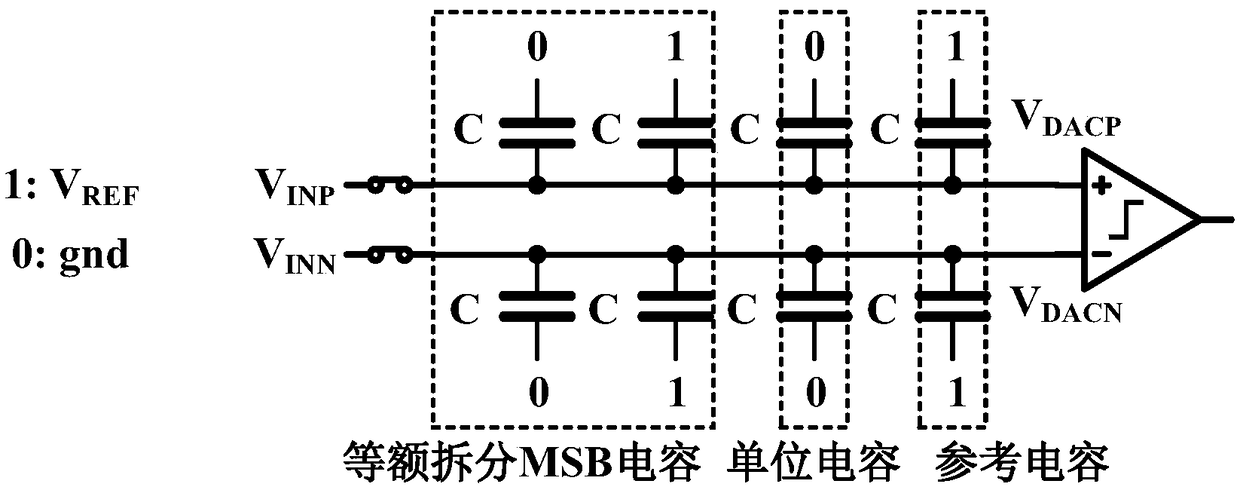
[0033] Please refer to figure 1 and figure 2 As shown, the low power consumption adaptive alternating successive approximation analog-to-digital converter 100 of the present invention, the analog-to-digital converter 100 includes a comparator 1, a capacitor array 2 and a control logic circuit 4; the capacitor array 2 Including a forward capacitor array 21 and a reverse capacitor array 22 identical to the forward capacitor array 21;
[0034] The positive input end of described comparator 1 is connected with described forward capacitance array 21, and the negative input end of described comparator 1 is connected with described reverse capacitance array 22; The output end of described comparator 1 is connected with described The control logic circuit 4 is connected;
[0035] The upper plate of the forward capacitor array 21 passes through a positive sampling switch S P with positive input voltage V INP The lower plate is respectively connected to the reference voltage V thro...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com