SAR image classification method based on sparse representation and Gaussian distribution
A Gaussian distribution and sparse representation technology, applied in the field of image processing, can solve problems such as large errors, inability to mine pixel relationships, and inability to fit image information, achieving the effects of enhancing reliability, improving accuracy, and improving classification accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
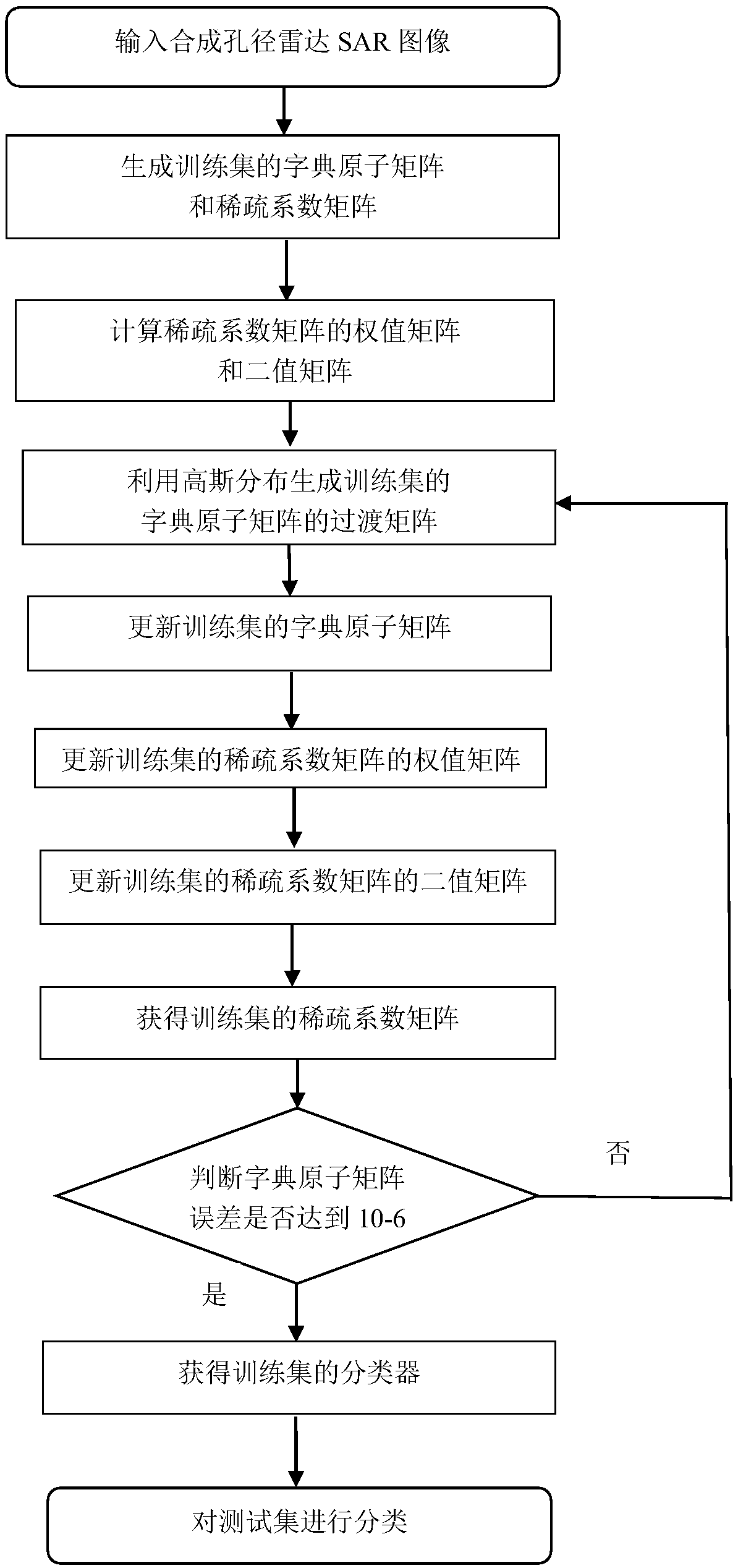
[0052] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
[0053] Refer to attached figure 1 , to further describe the specific steps of the present invention.
[0054] Step 1, input synthetic aperture radar SAR image.
[0055] At least 200 images of each class are randomly selected from at least two categories of SAR image sets to form a training set; from the SAR SAR image set, at least 1 image of each category in the same category as the training set is randomly selected to form a test set set.
[0056] The training set is generated into an m×N matrix, where m represents the number of pixels in each SAR image in the training set, and N represents the total number of all SAR images in the training set.
[0057] The test set is generated into an n×E matrix, where n represents the number of pixels in each SAR image in the test set, and E represents the total number of all SAR SAR images in the test set.
[0058] Step 2, ge...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com