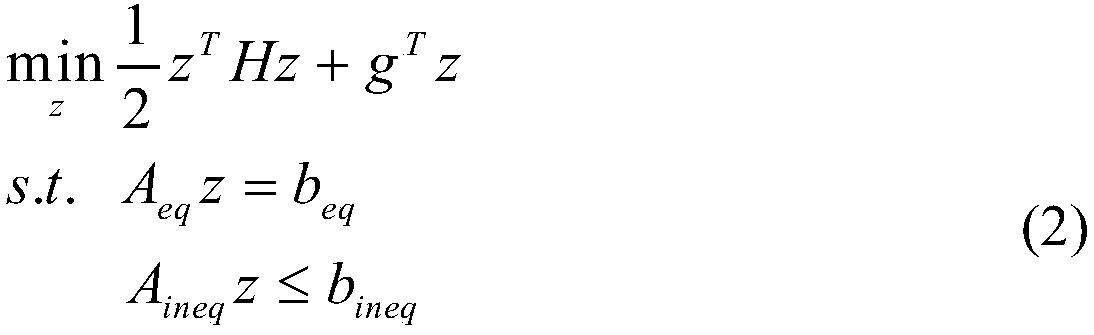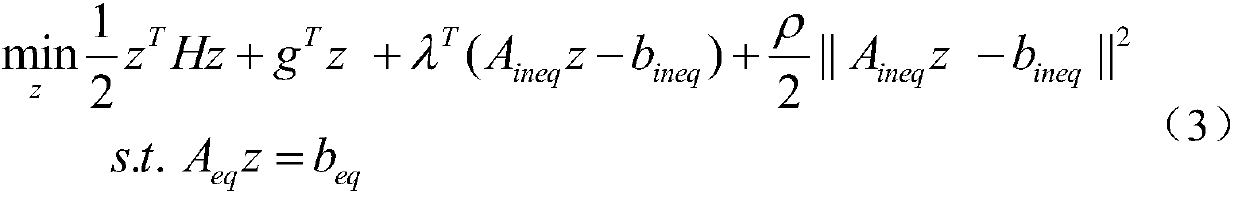Quick gradient algorithm for solving model prediction control law in real time
A technology of model predictive control and gradient algorithm, applied in the direction of complex mathematical operations, etc., can solve the problems that affect the convergence speed of the algorithm, the optimal solution is not unique, and the time-varying system is difficult to use, etc., to achieve the effect of improving the convergence speed.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0013] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with specific examples.
[0014] A fast gradient algorithm for solving the model predictive control law in real time, the specific implementation steps of the method are as follows:
[0015] In the first step, the MPC problem with general input state constraints is converted into a standard quadratic programming QP problem
[0016] 1.1) Formula (1) is used to describe the MPC problem with general input state constraints:
[0017]
[0018] Among them, N represents the prediction time domain, Indicates the initial state of the system; x k , u k represent the state variables and input variables of the MPC problem respectively; x N represents the final state of the system; represent the lower and upper bounds of the state variables, respectively; Represent the lower bound and upper bound of the input variable; Q, R represent the weight matrix of the state variable and the input variable respect...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com