Distributed optimization and spatial correlation-based wind power prediction method
A technology for wind power prediction and spatial correlation, applied in forecasting, wind power generation, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as being unable to adapt to large-scale wind power grid connection, consuming a lot of time and computer resources, and ignoring spatial correlation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0057] The above is only an overview of the technical solution of the present invention. In order to better understand the technical means of the present invention, the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
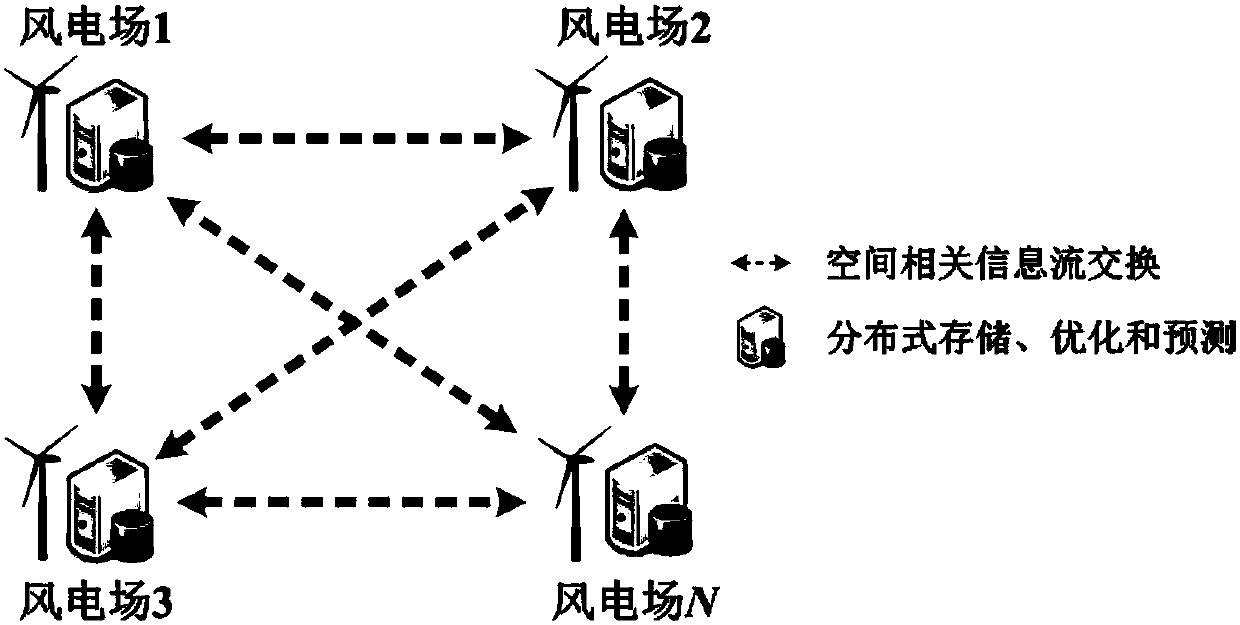
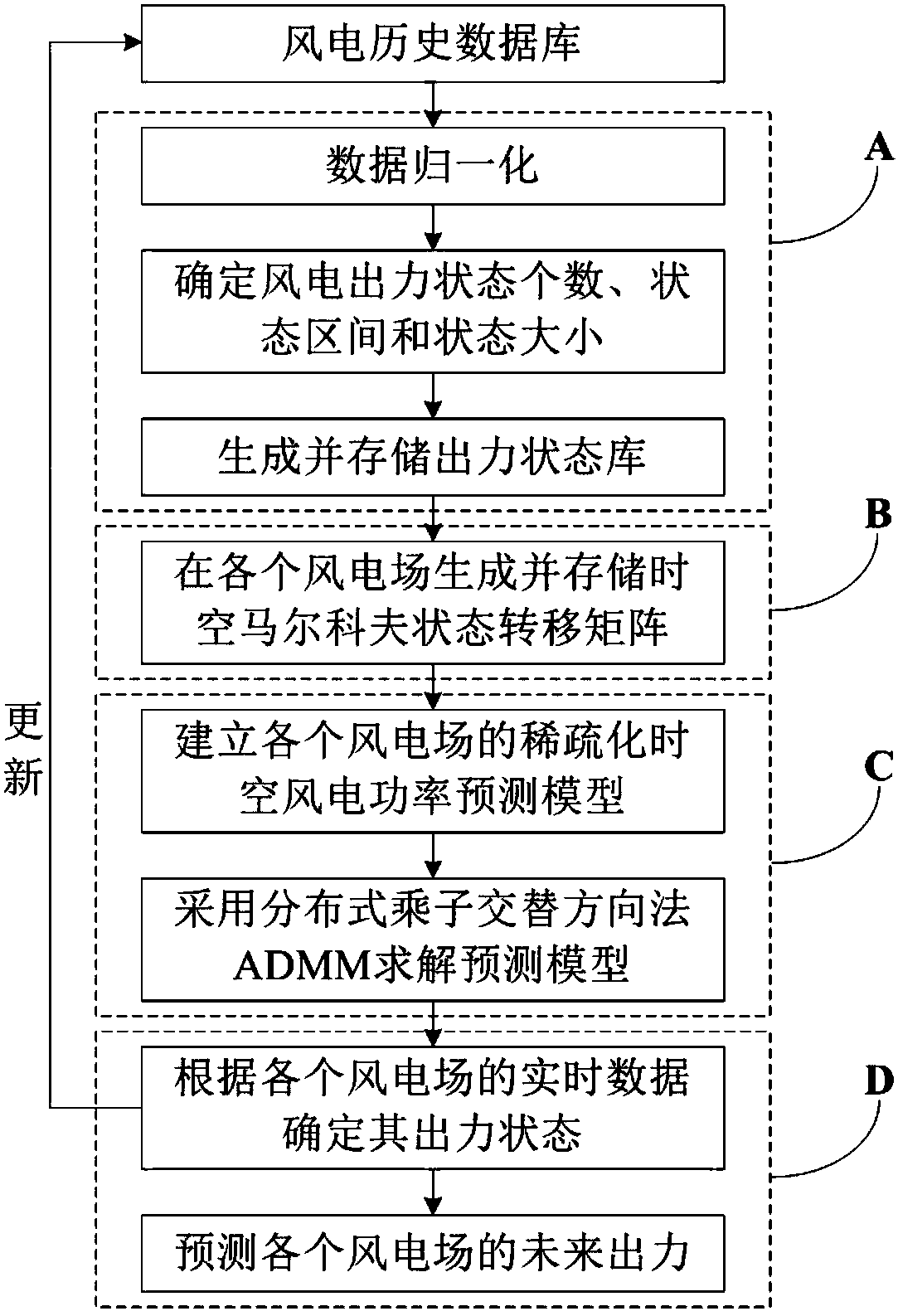
[0058] Such as figure 1 and figure 2 As shown, a wind power prediction method based on distributed optimization and spatial correlation includes the following steps:
[0059] A. Normalize the historical wind power data of each wind farm in an area during the same period, and divide the output state into equal intervals according to the fluctuation characteristics of each wind farm, generate a basic data set and a wind power output state library, and store the basic data The set and wind power output state database are stored in all wind farms.
[0060] Assuming that the set of wind farms in an area is Θ={1,2,…,N}, firstly, the original historical wind power time series of each...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com