Layered bionic building element used for 3D printing and preparation method thereof
A building component, 3D printing technology, applied in the field of building materials and 3D printing, can solve the problems of inability to know the tensile deformation ability, difficult to meet the special requirements of 3D printing, etc., to achieve good micro-crack distribution performance, good energy consumption performance, Simple preparation method
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
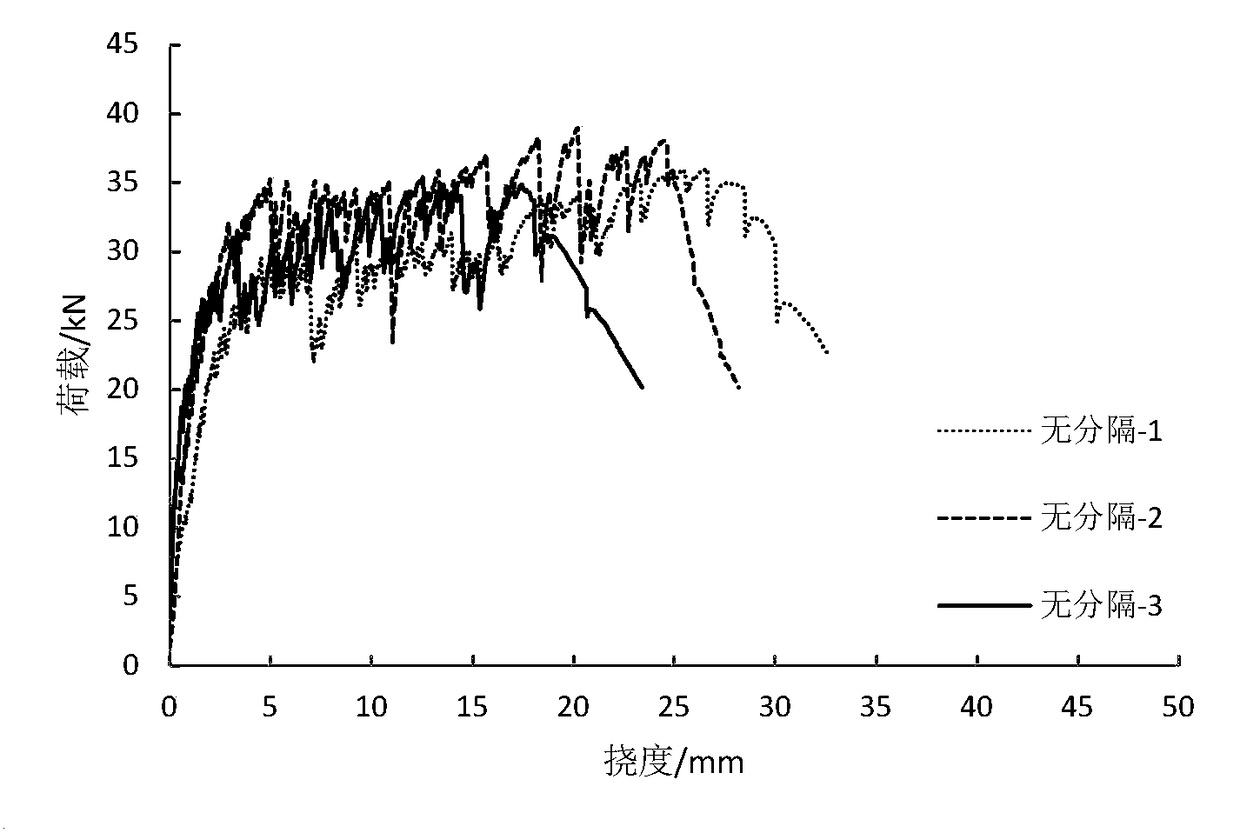
[0034] There are three products in this example, and their serial numbers are recorded as: no separation-1, no separation-2, and no separation-3.
[0035] The concrete used in this embodiment includes P.O.52.5 ordinary Portland cement, quartz sand, fly ash, water reducing agent, tap water and polyethylene fiber. Each component is shown in Table 1 below, and each part in the table is the content in parts by weight. The polyethylene fiber in Table 1 has a length of 12 mm and an aspect ratio of 400.
[0036] Table 1 product components and parts by weight content
[0037] label
Quartz sand
water
polyethylene fiber
No separation - 1
593
474
712
4
329
19
no separation-2
593
474
712
4
329
19
No separation - 3
593
474
712
4
329
19
[0038] The preparation process of the layered bionic building components suitable for 3D printing in this embo...
Embodiment 2
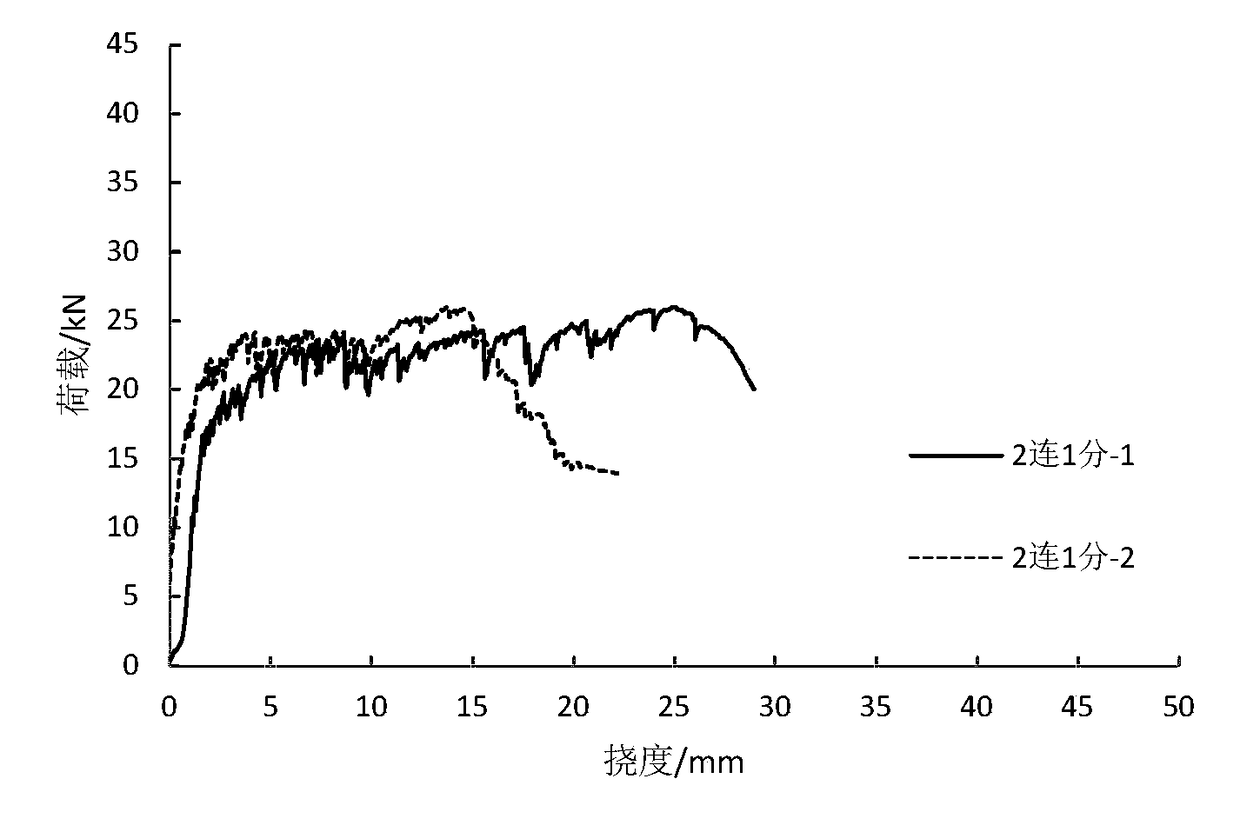
[0048] There are two products in this example, and their serial numbers are recorded as: 2 with 1 point-1, and 2 with 1 point-2.
[0049] The concrete used in this embodiment includes P.O.52.5 ordinary Portland cement, quartz sand, fly ash, water reducing agent, tap water and polyethylene fiber. Each component is shown in Table 3 below, and each part in the table is the content in parts by weight. In Table 3, the polyethylene fiber length is 12 mm, and the aspect ratio is 400.
[0050] Table 3 product components and parts by weight
[0051] label
Quartz sand
fly ash
water
polyethylene fiber
2 consecutive 1 point -1
593
474
712
4
329
19
2 consecutive 1 point -2
593
474
712
4
329
19
[0052] In this embodiment, when the bionic building components are poured in layers, a separation of 2 and 1 is used, that is, the separation film is a narrow PVC strip with a width of 1...
Embodiment 3
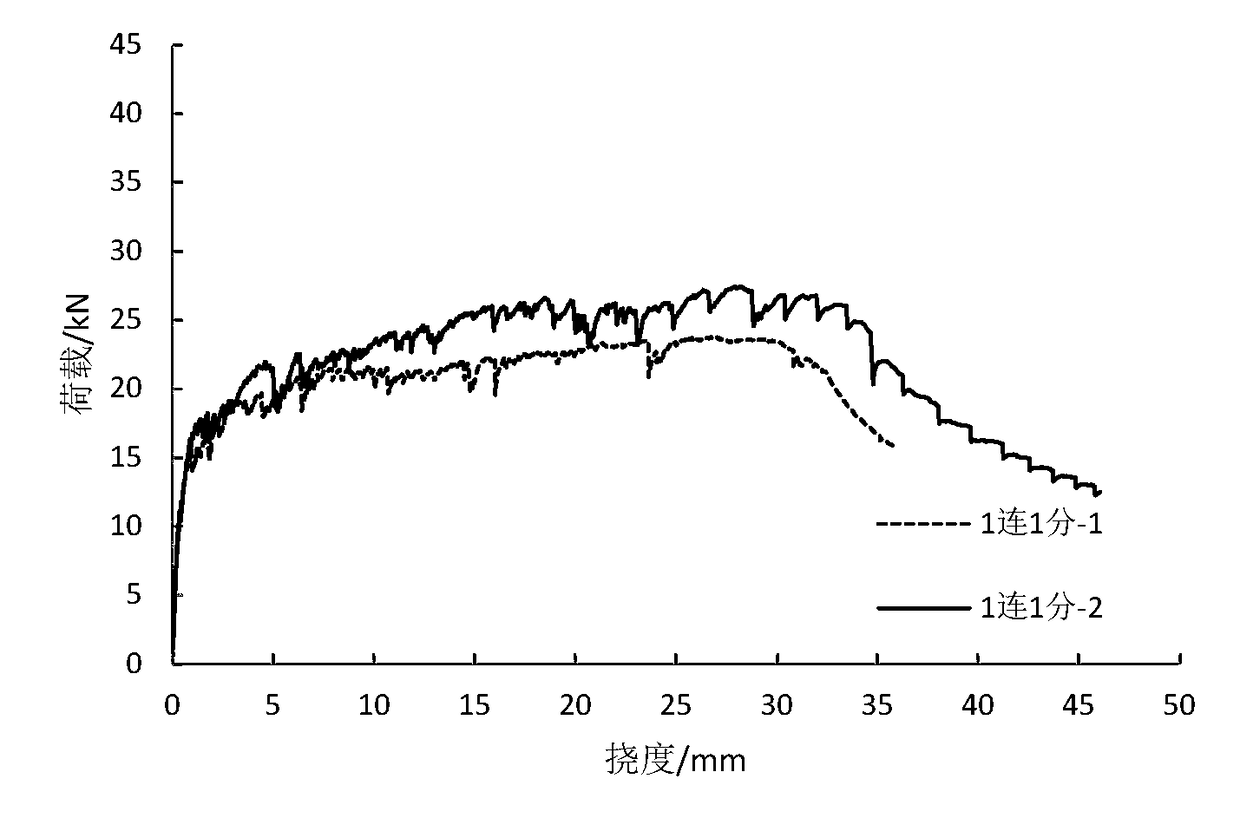
[0062] There are two products in this example, and their numbers are recorded as 1 with 1 point-1 and 1 with 1 point-2 respectively.
[0063] The concrete used in this example includes PO.52.5 ordinary Portland cement, quartz sand, fly ash, water reducing agent, tap water and polyethylene fiber, and each component is shown in Table 5 below, and each part in the table is the weight content , wherein, the polyethylene fiber length in Table 5 is 12mm, and the aspect ratio is 400.
[0064] Table 5 Product components and parts by weight
[0065] label
cement
Quartz sand
fly ash
water
polyethylene fiber
1 point in a row - 1
593
474
712
4
329
19
1 point in a row - 2
593
474
712
4
329
19
[0066] In this embodiment, when the bionic building components are poured in layers, a 1-to-1 separation is used, that is, the separation film is a PVC narrow strip with a width of 20 mm placed ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| compressive strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| flexural strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com