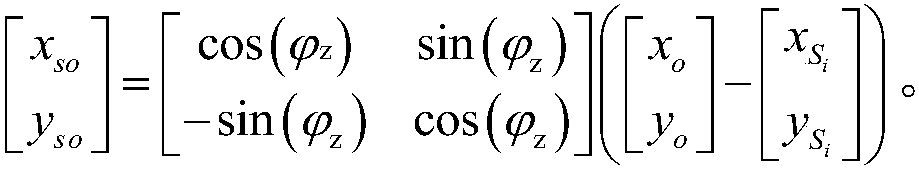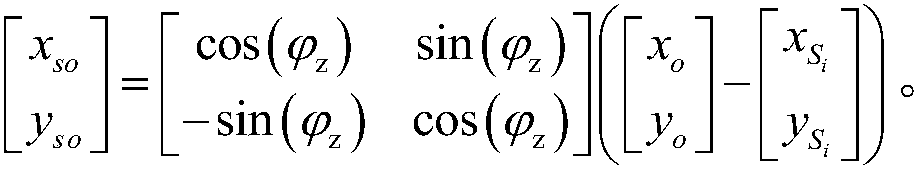Autonomous global relocation method for robots and robot
A robot and relocation technology, applied in the field of artificial intelligence navigation, can solve the problems of high production cost and R&D cost, achieve the effect of accelerating the convergence speed and solving the kidnapping problem
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] An autonomous global relocalization method for a robot, by rasterizing the existing map and assigning differential values to the grid with obstacles and the grid without obstacles, scanning the external obstacles with the lidar sensor at the same position as the robot The multiple distance data obtained and the angle data corresponding to the distance data are marked on the map in the form of laser points with the position of the simulated robot as the origin, and the assignment of the grid where the laser point corresponding to each simulated robot position is located Integrate, according to the principle that the higher the coincidence rate between the laser point and the grid with obstacles, the better, screen out at least one simulated robot position, and calculate the correct position of the robot from the initially screened simulated robot position through the particle filter algorithm. Location. In this embodiment, in the process of differentially assigning gri...
Embodiment 2
[0063] Different from Example 1, the transfer mode of the preferred particles is as follows:
[0064] Step 3.1, first in one of the preferred particle J i There are multiple transfer points randomly distributed around the robot for simulating the position of the robot, and one of the transfer points S i Establish a random coordinate system for the origin of random coordinates, take the direction of the transfer point as the origin as the X-axis or Y-axis direction of the random coordinate system, and the coordinate positions of the grids occupied by obstacles around the random coordinate origin are in the random coordinate system Re-described in ; in specific implementation, the orientation direction of the transfer point that can also be used as the origin is the Y-axis direction of the random coordinate system, and the corresponding calculation formula can be modified adaptively, and will not be described again.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com