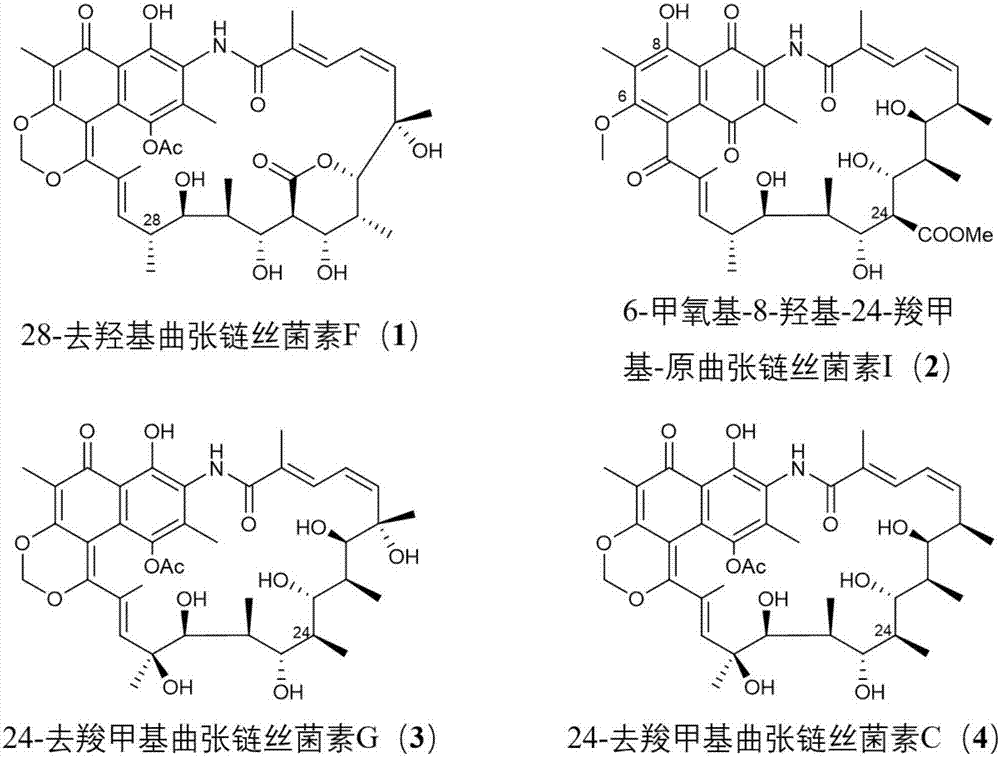
Streptovaricin derivative and preparation method and application thereof
A technology for streptothricin and derivatives, which is applied in the field of novel streptomycin derivatives and their preparation, can solve problems such as unclear steps, and achieve the effects of rich diversity and good antibacterial effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0089] [Example 1] Production of novel streptothricin derivatives (1 and 2) construction of engineering strains
[0090] The engineering strain for producing novel streptothricin derivatives is a streptothricin-producing strain that inactivates or deletes the stvP4 gene.
[0091] (1) stvP4 in-frame knockout recombinant plasmid pWHU2801( figure 2 a)
[0092] 1) Using the chromosomal DNA of Streptomyces XW-1 (preservation number: CCTCC NO: M2017417) as a template, using stvP4-L-F and stvP4-L-R as primers, amplified at the upstream of the stvP4 gene The 1990bp fragment is used as the stvP4 in-frame knockout homologous left arm stvP4-L. Using stvP4-R-F and stvP4-R-R as primers, a 1989bp fragment was amplified downstream of the stvP4 gene as the stvP4 in-frame knockout homologous right arm stvP4-R.
[0093] 2) Ligate the homologous left arm stvP4-L directly to the pEASY vector to obtain the recombinant plasmid pEASY-stvP4-L, after restriction enzyme digestion and sequencing ver...
Embodiment 2
[0098] [Example 2] Production of novel streptothricin derivatives (3 and 4) construction of engineering strains
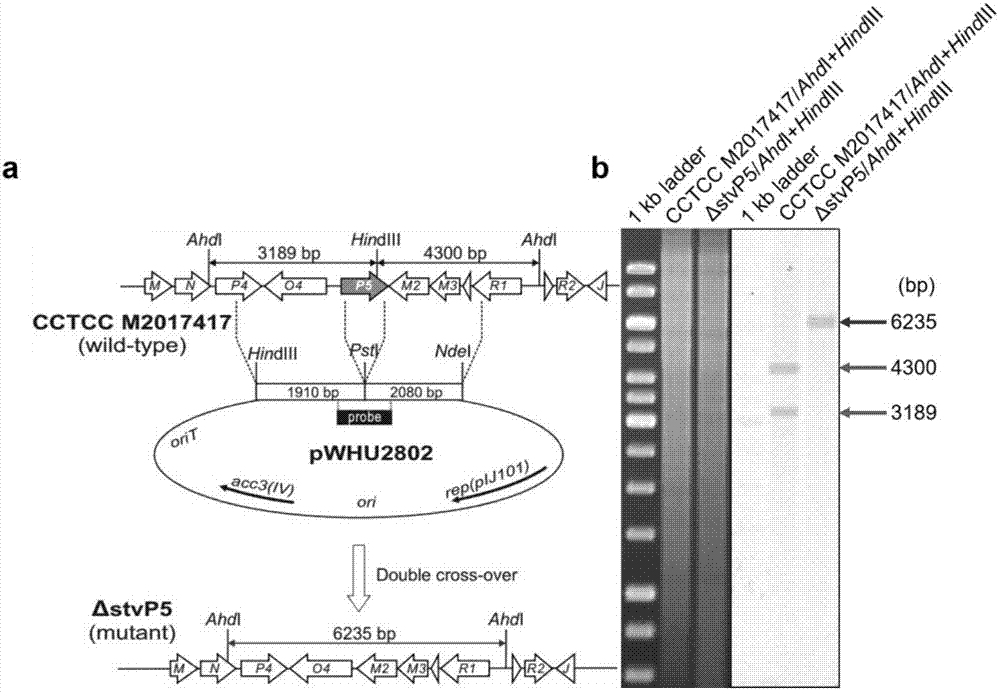
[0099] The engineering strain for producing novel streptothricin derivatives is a streptothricin-producing strain with inactivation or deletion of stvP5 gene.
[0100] (1) stvP5 in-frame knockout recombinant plasmid pWHU2802( image 3 a)
[0101] 1) Using the chromosomal DNA of Streptomyces XW-1 (preservation number CCTCC M2017417) as a template and using stvP5-L-F and stvP5-L-R as primers, a 2098bp fragment was amplified upstream of the stvP5 gene The homologous left arm stvP5-L was knocked out in frame as stvP5. Using stvP5-R-F and stvP5-R-R as primers, a 1928bp fragment was amplified downstream of the stvP5 gene as the stvP5 in-frame knockout homologous right arm stvP5-R.
[0102] 2) The homologous left arm stvP5-L was directly connected to the pEASY vector to obtain the recombinant plasmid pEASY-stvP5-L. After verification by enzyme digestion and sequencing,...
Embodiment 3
[0107] [Example 3] HPLC-UV analysis of bacterial strain fermentation product
[0108] The high-yield strains constructed above and the control group wild-type XW-1 were subjected to 50mL small-scale parallel fermentation and product extraction, and the fermentation products were detected by HPLC-UV. The ion peaks were extracted and the results were as follows Figure 4 shown.
[0109] The mutant strain ΔstvP4 accumulated streptothricin D as expected, and its production was about 100-fold higher than that of the wild-type XW-1. Alternative metabolites (1 and 2); mutant ΔstvP5 was still able to produce protostreptothricin I, and simultaneously accumulated two distinct intermediates or alternative metabolites of streptothricin biosynthesis (3 and 4 )( Figure 4 ).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com