Power distribution method for non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) system
A non-orthogonal multiple access and access system technology, applied in the field of power allocation of non-orthogonal multiple access systems, can solve problems such as waste of resources and reduce system performance, achieve optimal and reasonable allocation, solve reachability and rate maximized effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
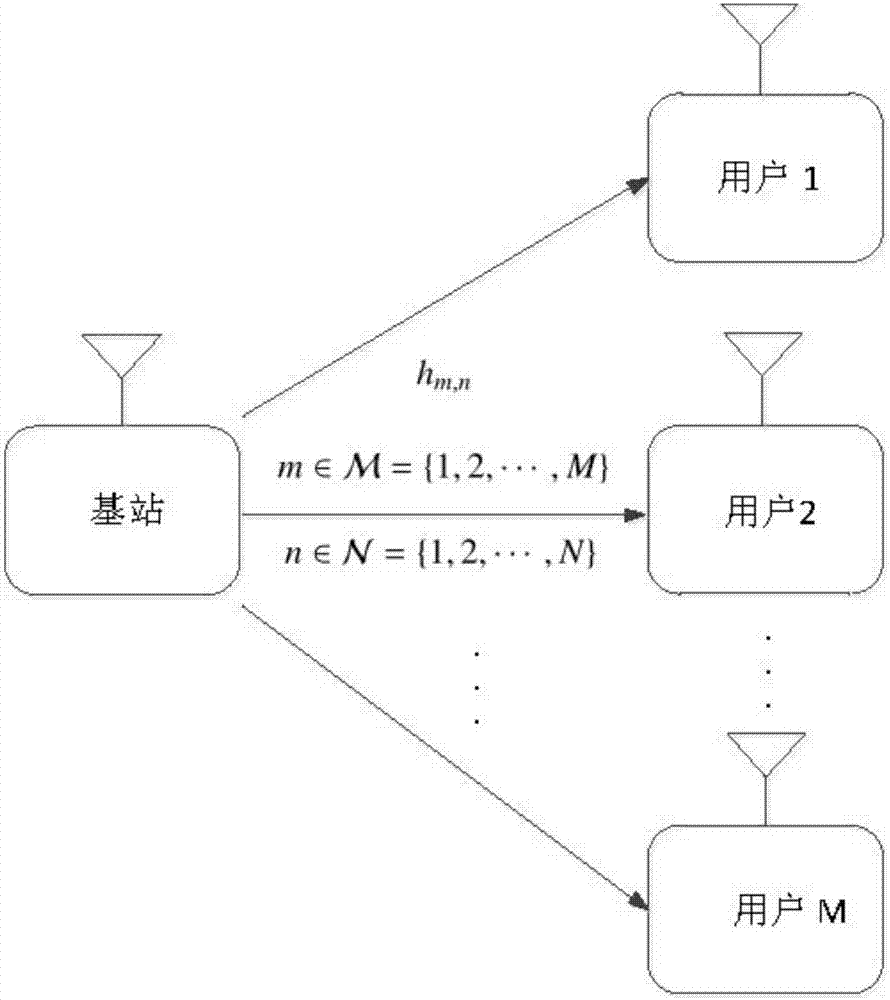
[0034] refer to figure 1 , the system model of the non-orthogonal multiple access system applicable to the present invention consists of a base station and M receiving users, and each node has only a single antenna. The entire bandwidth of the system is divided into N subcarriers, and each subcarrier is allowed to be shared by M users. On each subcarrier, the transmitted signal from the base station experiences flat channel fading. On the nth subcarrier, the channel response from the base station to the mth user is denoted by h m,n ,in, It is assumed that the base station can fully know the channel state information (Channel State Information, CSI) of the entire network system. Therefore, the base station can properly allocate its transmission power to increase the reachability and rate of the entire network.
[0035] According to the non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) protocol, the sending end adopts superposition coding technology, so the base station is located at t...
Embodiment 2
[0105] The effect of the present invention can be further illustrated by the following simulation experiment results, and the basic process of the simulation experiment is referred to Figure 4 .
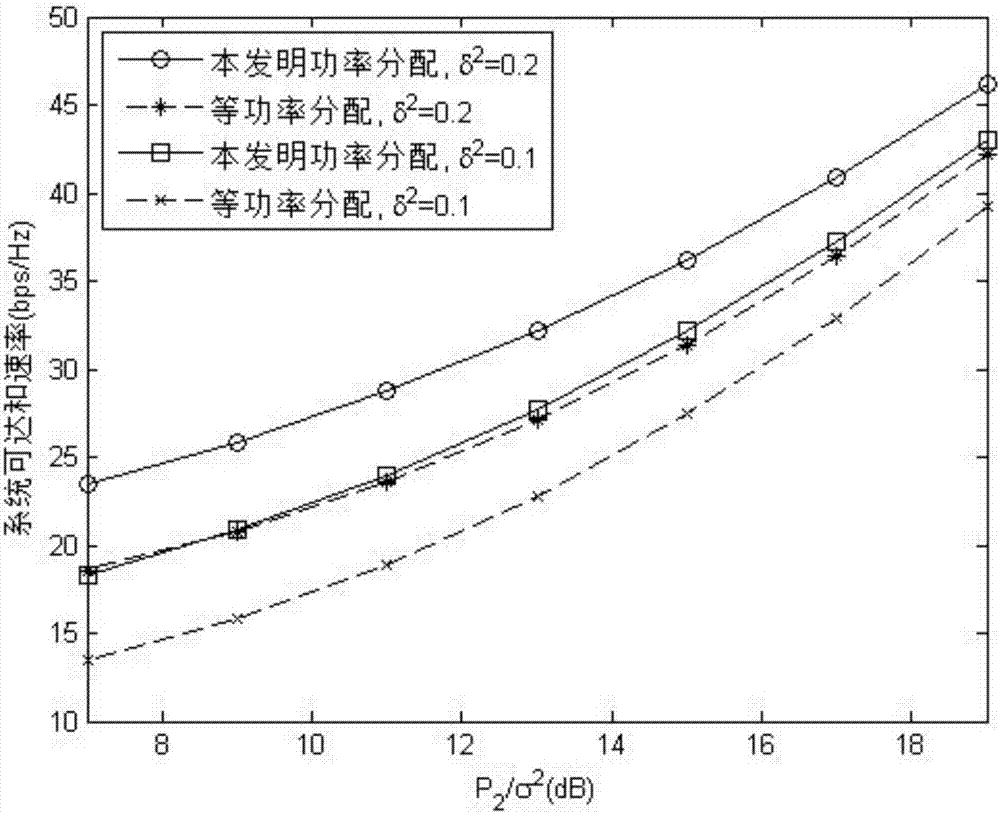
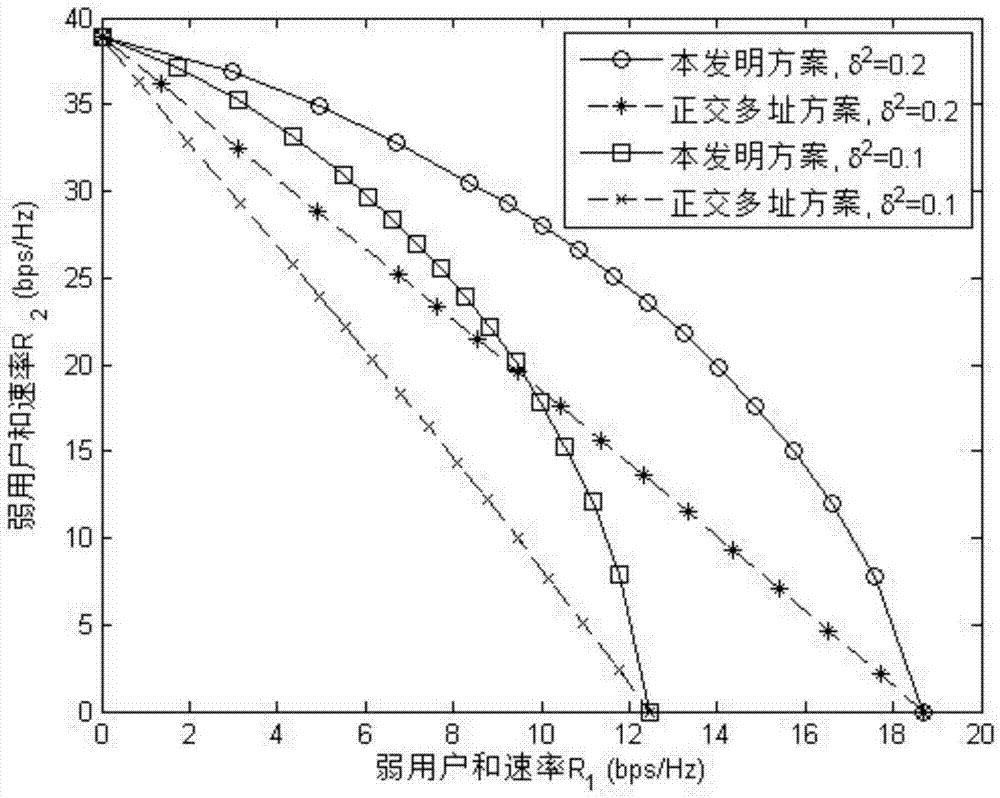
[0106] for figure 2 and image 3 , the number of subcarriers corresponding to the system is N=16, and the number of receiving users M=2. On all subcarriers, the channel response from base station to user 1 is zero mean and variance δ 2 The independent and identically distributed complex Gaussian random variable of ; the channel response from the base station to user 2 is an independent and identically distributed complex Gaussian random variable with mean 0 and variance 1. By limiting δ 2 ≤1, indicating that user 1 and user 2 are weak users and strong users, respectively. Therefore, the reachability and rate of weak users on all subcarriers is expressed as Strong users are
[0107] figure 2 is the variance of responses to different channels, given P 1 =19dB, the power ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com