A quintic polynomial planning method for industrial robot trajectory
A quintic polynomial, industrial robot technology, used in instruments, simulators, computer control, etc., can solve problems beyond the limits of robot motion parameters, and achieve the effect of continuous speed and acceleration, smooth planning curve, and continuous acceleration and jerk
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
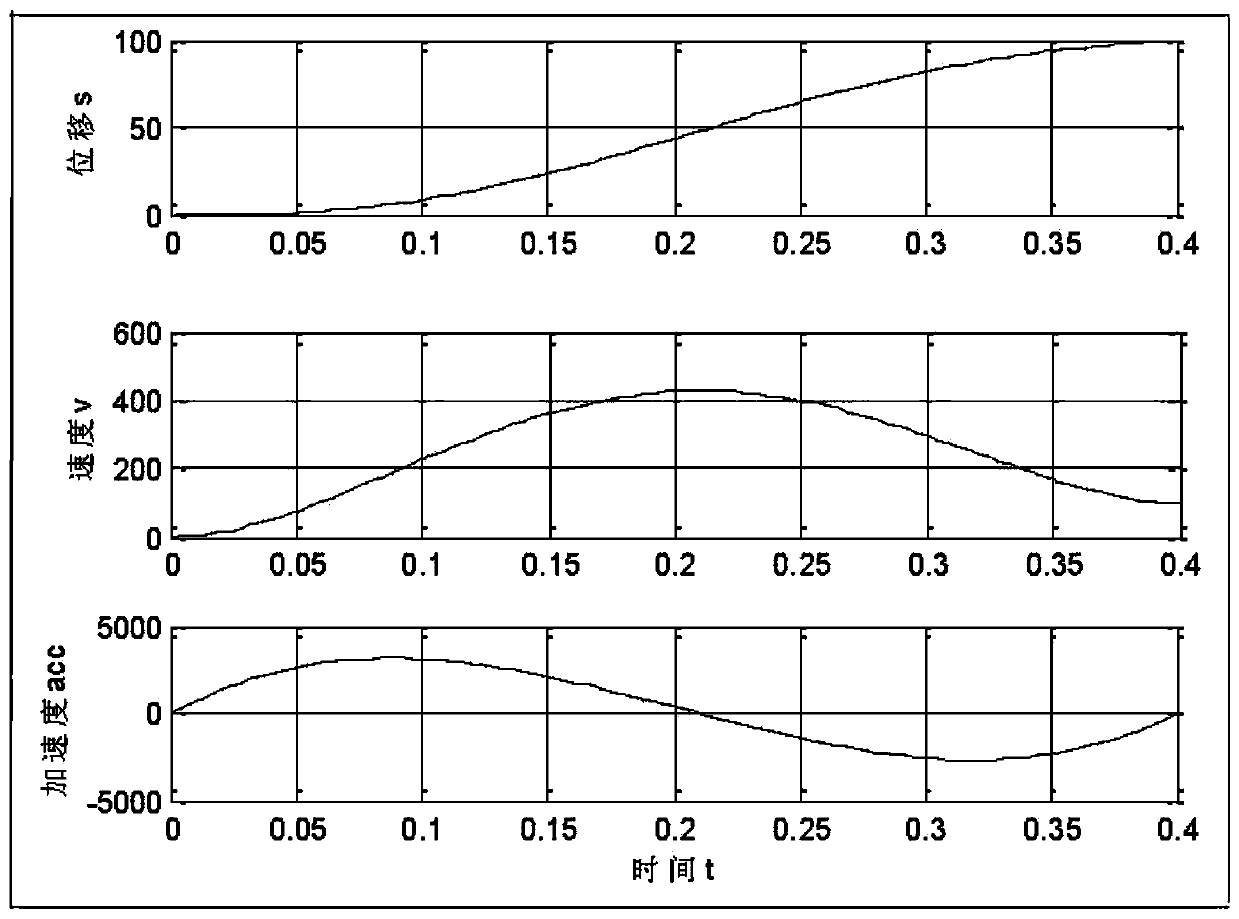
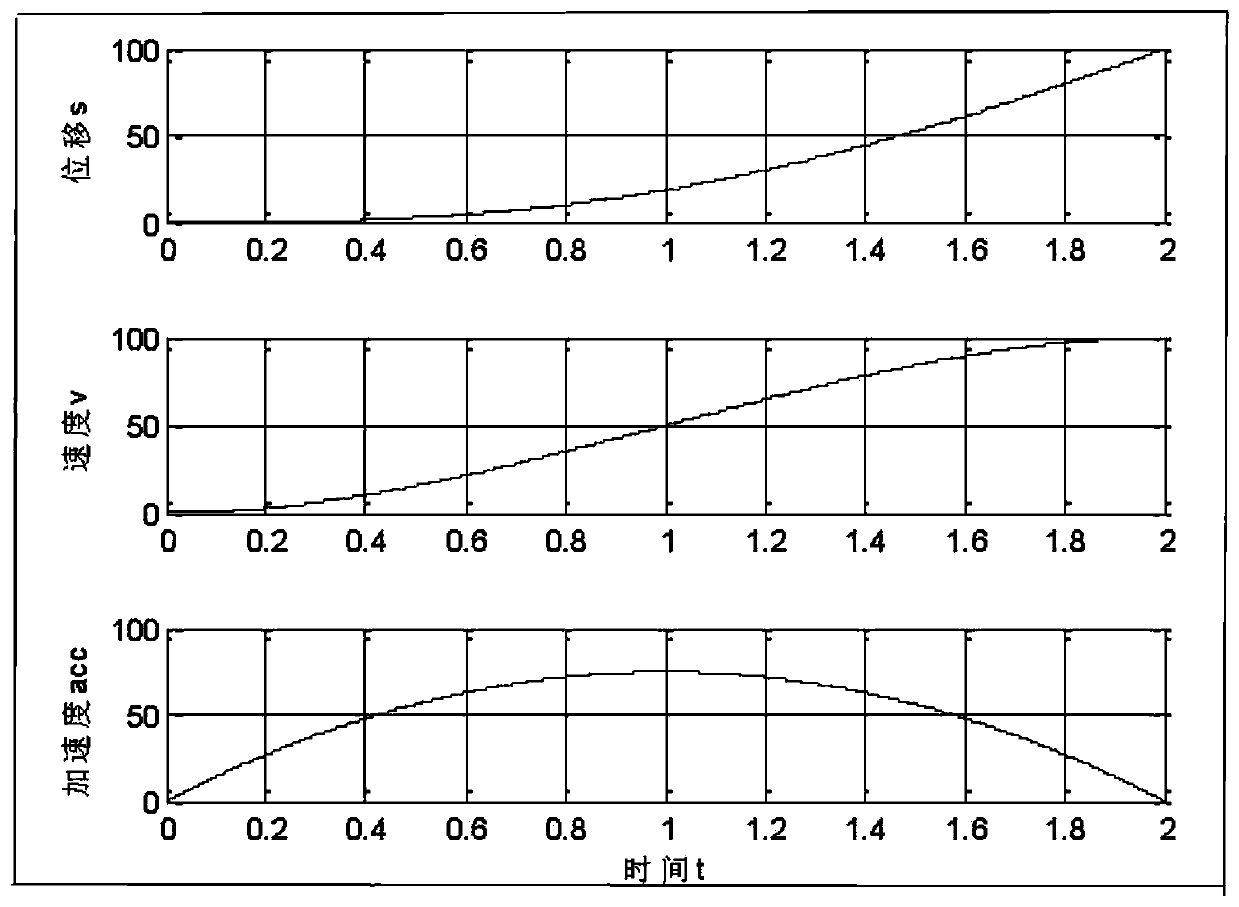
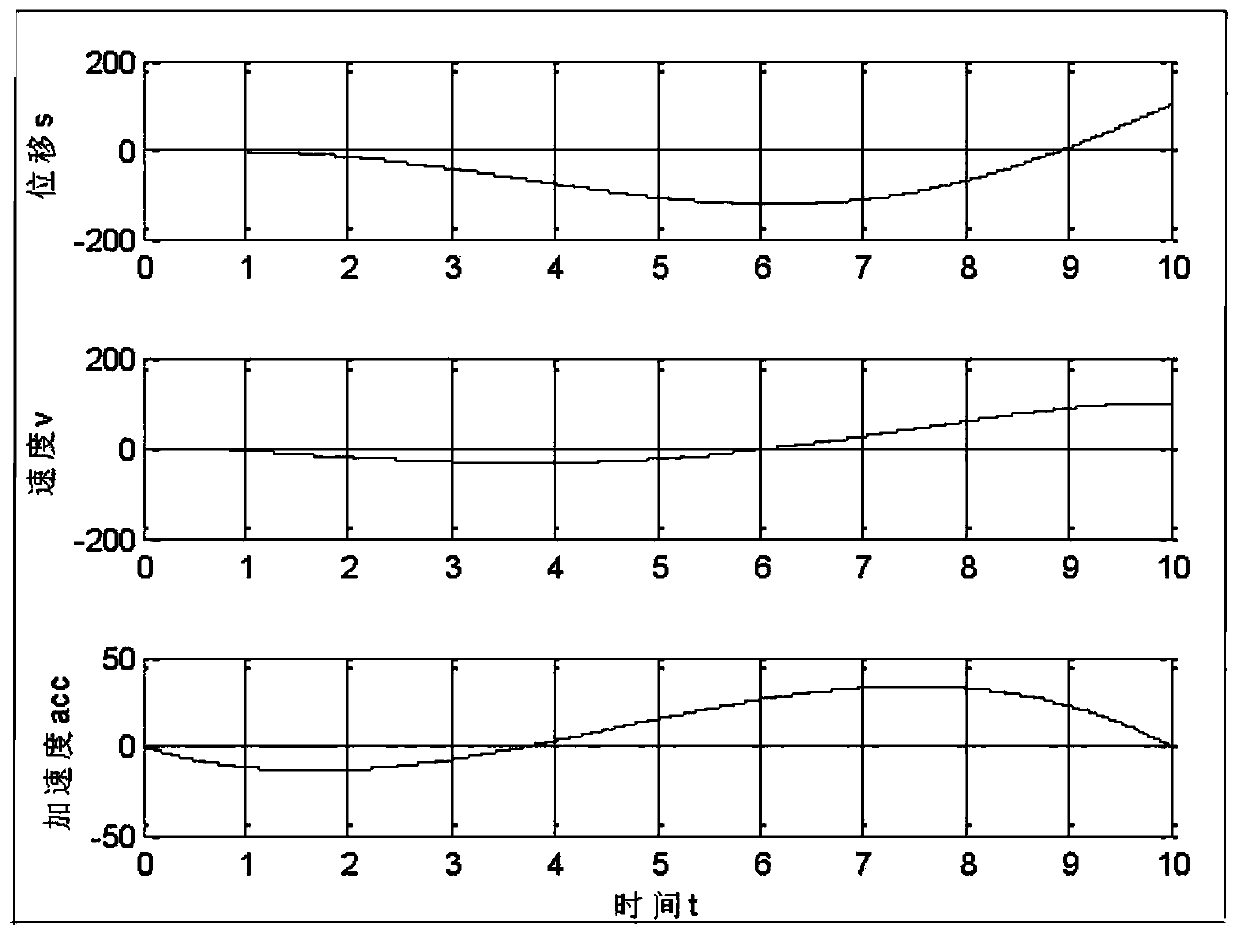
[0042] Taking the transition between straight lines of an industrial robot as an example, quintic polynomial trajectory planning is used.
[0043] 1. Determine the starting and ending displacement, velocity and acceleration information of the trajectory
[0044] The trajectory preprocessing module determines the effective starting and ending displacement, velocity and acceleration information of the trajectory according to the taught start and stop position points, combined with the inherent motion parameter limitations.
[0045] the s 0 = 0, v 0 =20, acc 0 = 0;
[0046] the s e = 100, v e =82, acc e =0.
[0047] 2. Determine the interpolation time of the fifth planning
[0048] The interpolation time determined by formula (3) is 1.961s. Since the fine interpolation period of the system is 0.004s, the interpolation time is taken as an integer multiple of the fine interpolation period and rounded up to determine the fifth planning interpolation time t e = 1.964s.
[0...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com