A Lattice Reduction Aided Linear Detection Method in Generalized Spatial Modulation
A technique of generalized spatial modulation and linear detection, which is applied in the field of linear detection assisted by lattice reduction in generalized spatial modulation, and can solve problems such as not meeting LR requirements.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
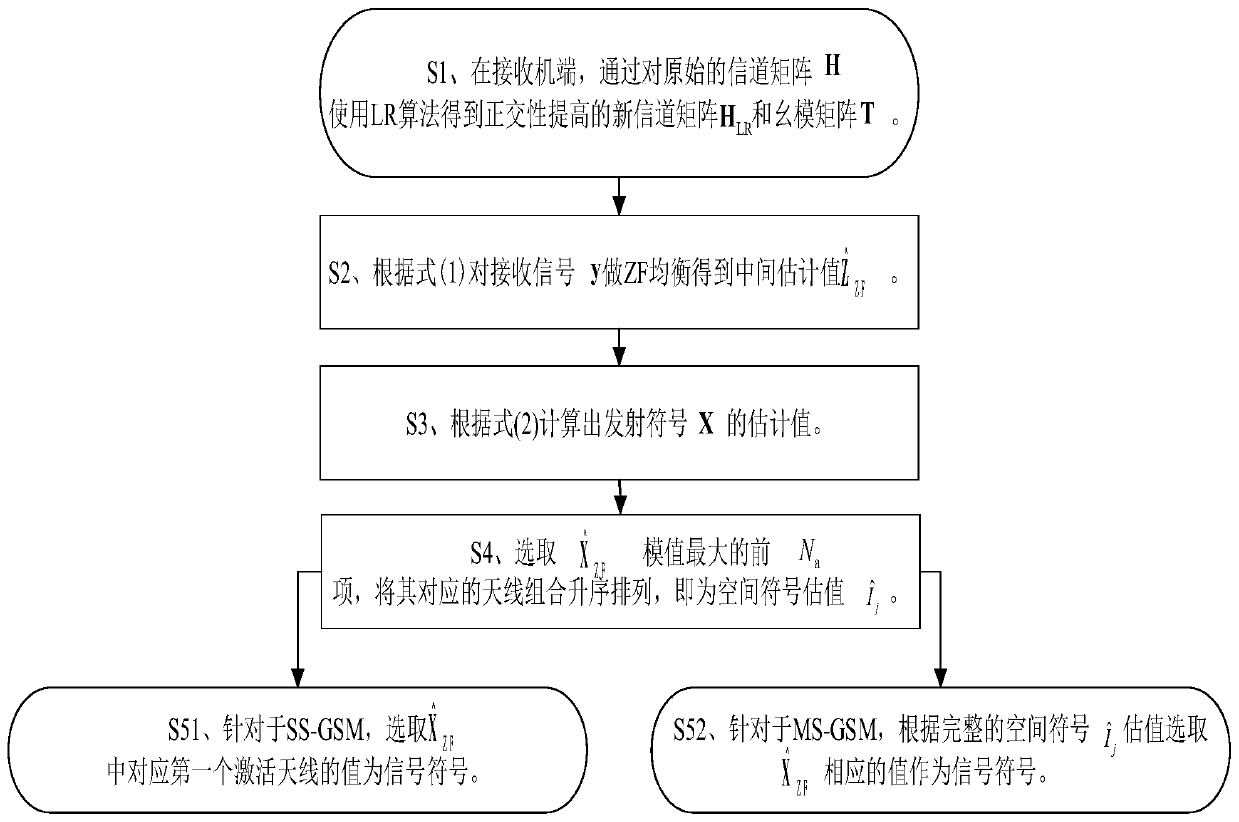
[0033] Specific implementation mode one: combine figure 1 To illustrate this embodiment, the specific process of a lattice-based reduction-assisted linear detection method in generalized spatial modulation in this embodiment is as follows:
[0034] Since MMSE equalization can be written in the form of ZF equalization under a certain matrix transformation, ZF equalization represents linear equalization in the following.
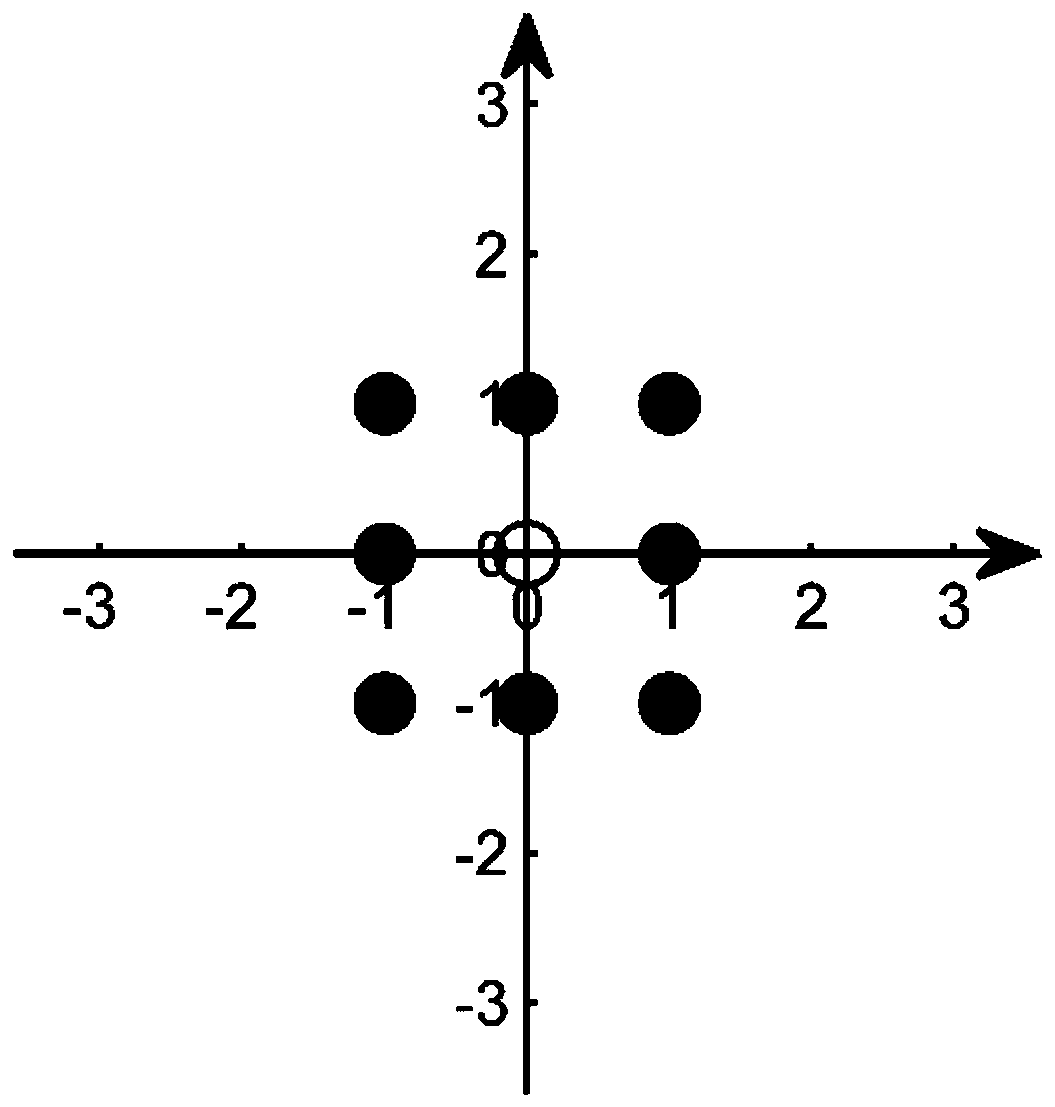
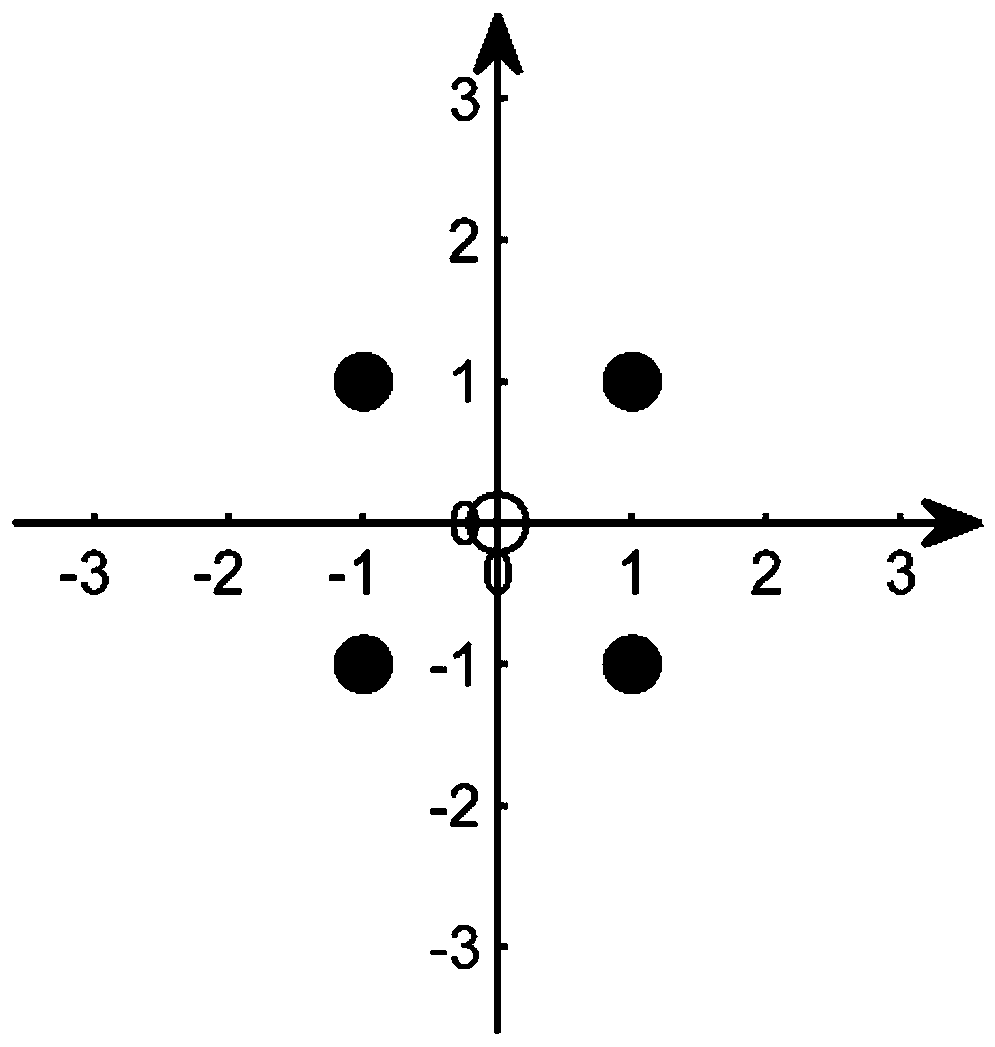
[0035] Step 1. Set an LR-assisted linear detection 8-QAM constellation diagram in GSM. The 8-QAM constellation diagram includes quadrature branch and in-phase branch. There are 9 grid points on the coordinate axes of quadrature branch and in-phase branch. : (-1,1), (0,1), (1,1), (-1,0), (0,0), (1,0), (-1,-1), (-1 ,0), (-1,1), where (0,0) is the constellation point adopted by the inactive antenna, and other constellation points are selected by the active antenna according to the bit content of the modulation symbol information; for example:
[0036] ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0045] Embodiment 2: This embodiment differs from Embodiment 1 in that: the LR algorithm in the step 2 uses a complex LLL algorithm; the LLLs are A.K. Lenstra, H.W. Lenstra, and L. Lovász.
[0046] Other steps and parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0047] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one or two is: the new channel matrix H obtained according to step two in step three LR Perform ZF equalization on the received signal y to obtain an intermediate estimate The specific process is:
[0048]
[0049] in Indicates rounding each dimension component of the vector; for H LR The conjugate transpose of ; * is the conjugate transpose.
[0050] Other steps and parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1 or Embodiment 2.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com