Clustering algorithm based on minimal spanning tree
A clustering algorithm and tree-spanning technology, applied in computing, computer components, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of reducing data volume, expensive algorithm time, sensitive parameter input, etc., and achieve good stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
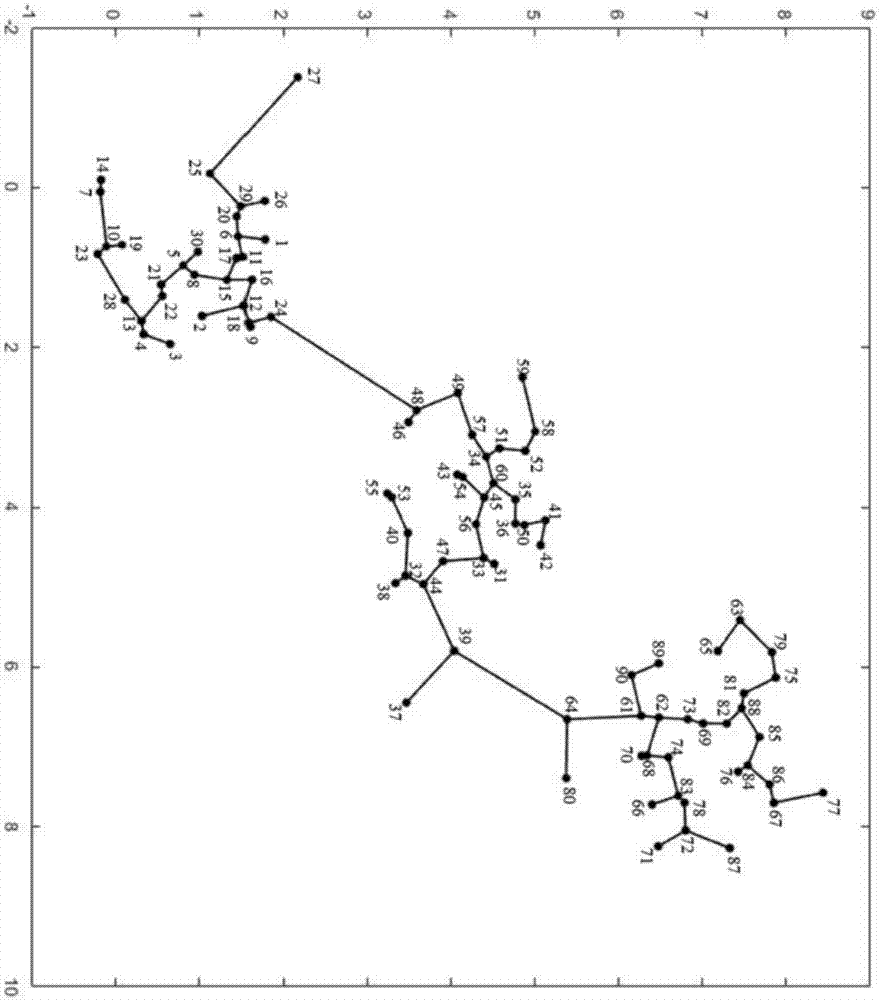
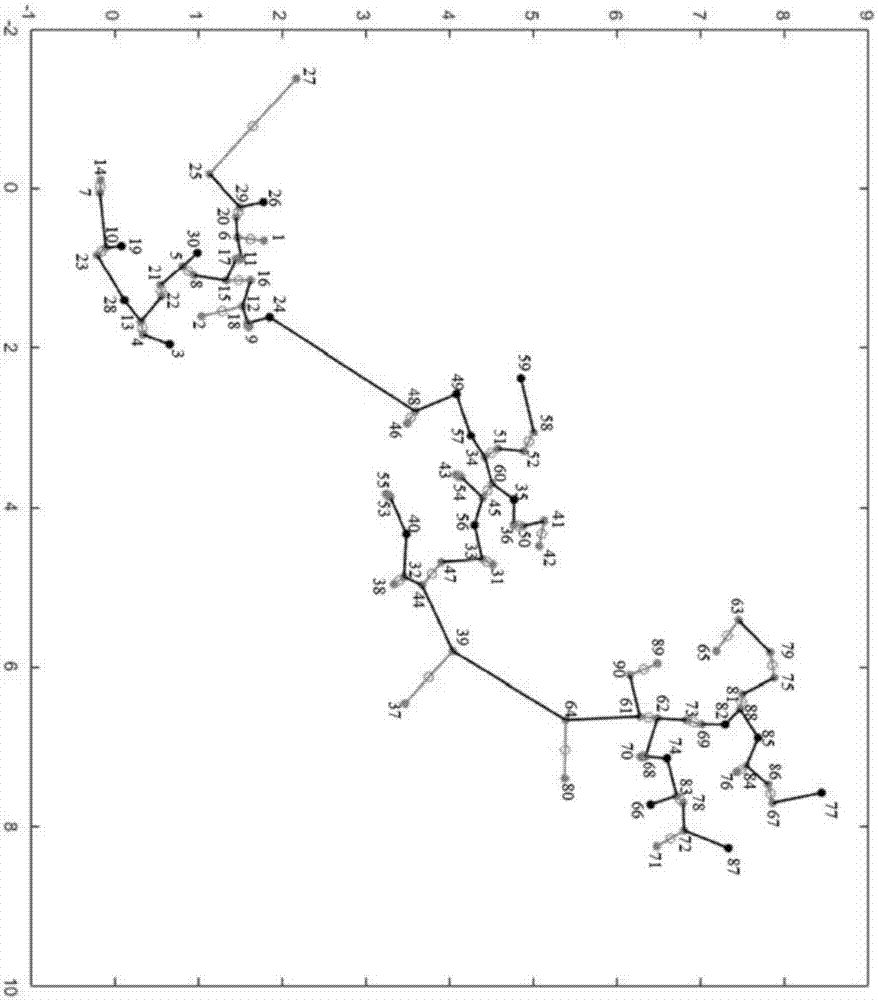
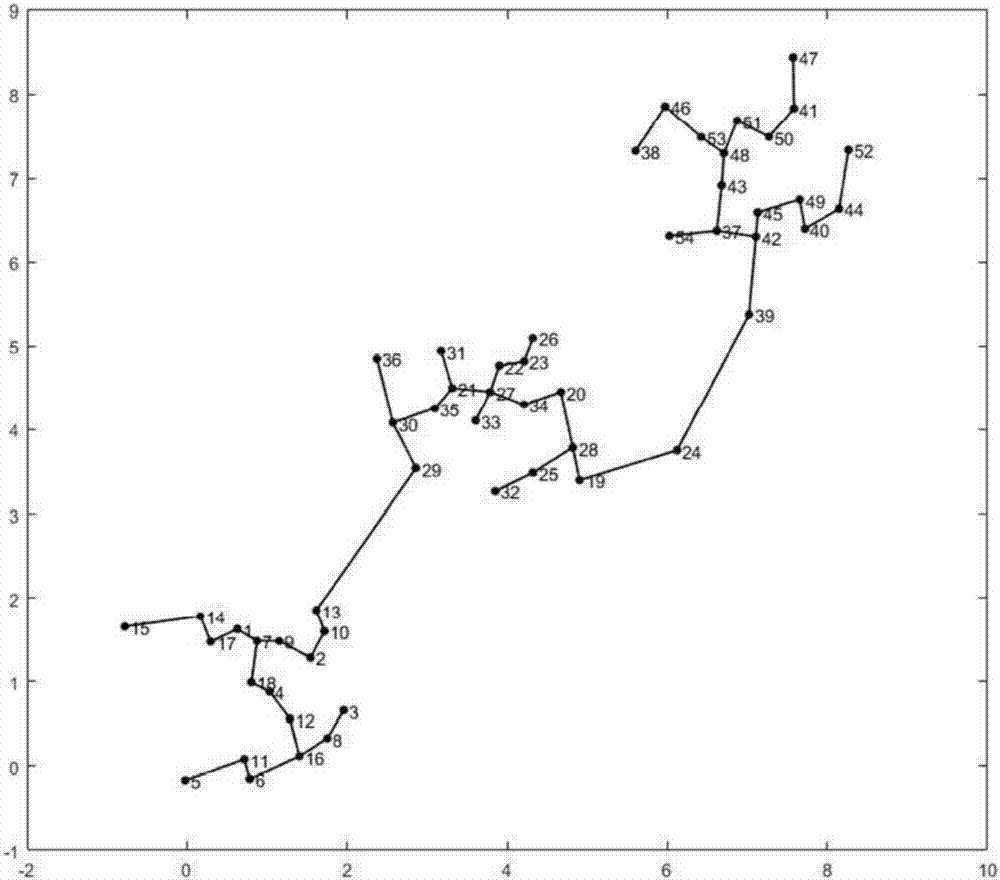
[0074] (1), artificially generate a data set D={d containing 90 data points 1 , d 2 ,...,d 90}, the number of categories in this data set is K=3, and the attribute dimension of each data point is 2-dimensional. Below, the specific attributes of all data points are listed:
[0075] d 1 (0.6497, 1.7818), d 2 (1.6068, 1.0395), d 3 (1.9584, 0.6588), d 4 (1.8344, 0.3428), d 5 (0.9730, 0.8138), d 6 (0.6096, 1.4670), d 7 (0.0519, -0.1745), d 8 (1.0918, 0.9471), d 9 (1.7432, 1.6060), d 10 (0.7359, -0.1005), d 11 (0.8657, 1.5185), d 12 (1.4774, 1.5292), d 13 (1.6692, 0.3167), d 14 (-0.0975, -0.1654), d 15 (1.1549, 1.3355), d 16 (1.1517, 1.6261), d 17 (0.8829, 1.4484), d 18 (1.6915, 1.5909), d 19 (0.7179, 0.0843), d 20 (0.3600, 1.4522), d 21 (1.2138, 0.5507), d 22 (1.3562, 0.5652), d 23 (0.8315, -0.2052), d 24 (1.6167, 1.8522), d 25 (-0.1759, 1.1356), d26 (0.1674, 1.7774), d 27 (-1.3797, 2.1704), d 28 (1.4039, 0.1191), d 29 (0.2324, 1.4981), d 30 (0.8039, 0....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com